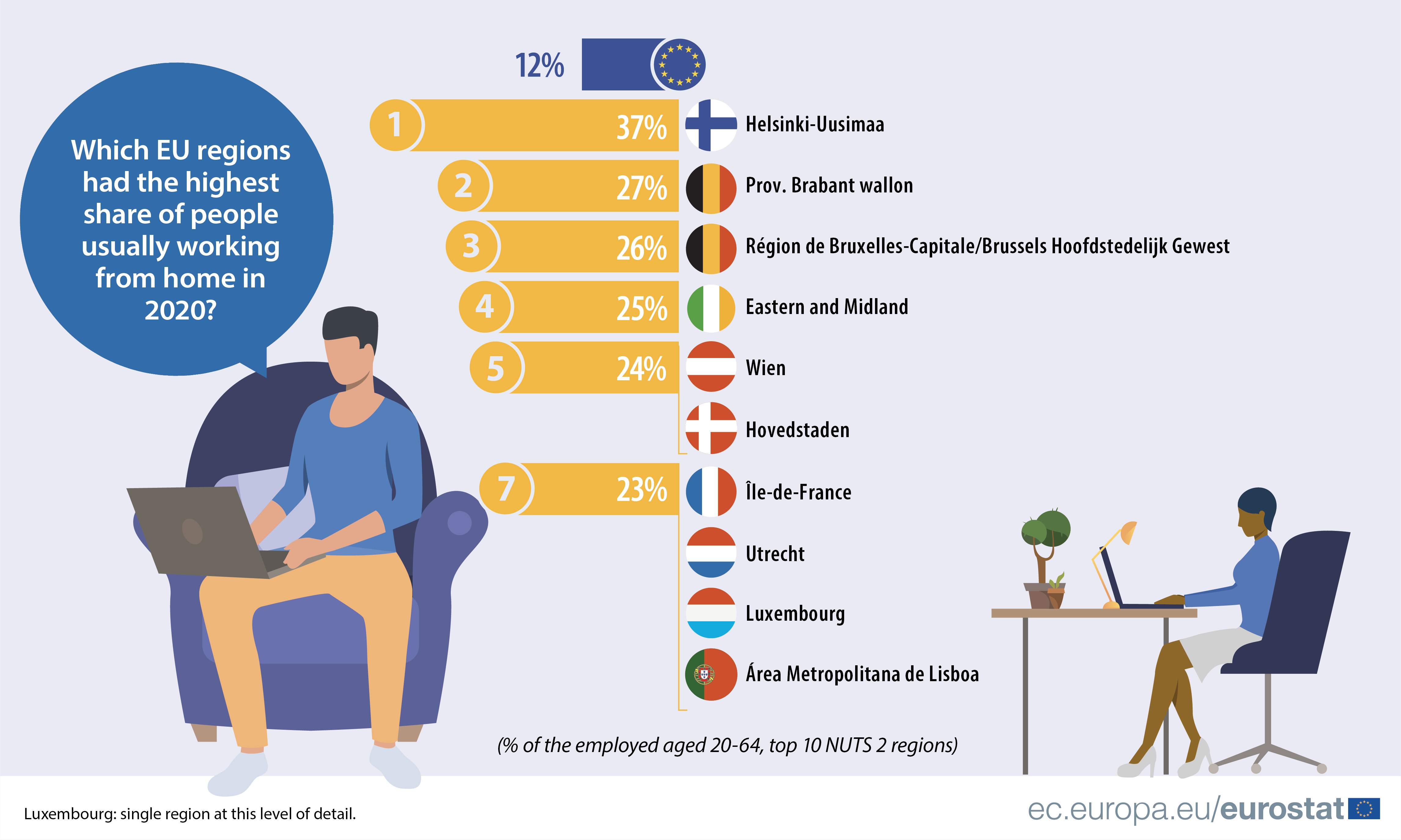
More people started to work from home following the introduction of the social distancing measures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. In 2020, 12% of employed people aged 20-64 in the EU usually worked from home, while this share had remained constant at around 5 or 6% over the past decade.
Among the EU regions, Helsinki-Uusimaa, the capital region of Finland, recorded the highest share in 2020 (37%), followed at a distance by two Belgian regions: Province du Brabant wallon (27%) and the capital region, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale/Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest (26%).
Around one in four employed usually worked from home in these capital regions: Eastern and Midland in Ireland (25%), Wien in Austria and Hovedstaden in Denmark (both 24%) as well as Île-de-France in France, Utrecht in the Netherlands, Luxembourg (single region) and Área Metropolitana de Lisboa in Portugal (all 23%).
Source: EU Labour Force Survey special data extraction
In contrast, working from home was less common in many eastern and southern regions of the EU. In 2020, less than 5% of the workforce was usually working from home in both regions of Croatia, as well as in Cyprus, Latvia and Bulgaria (only national data available), in the vast majority of regions across Hungary and Romania (except for the capital regions) and Greece.
Highest uptake of work from home in capital regions
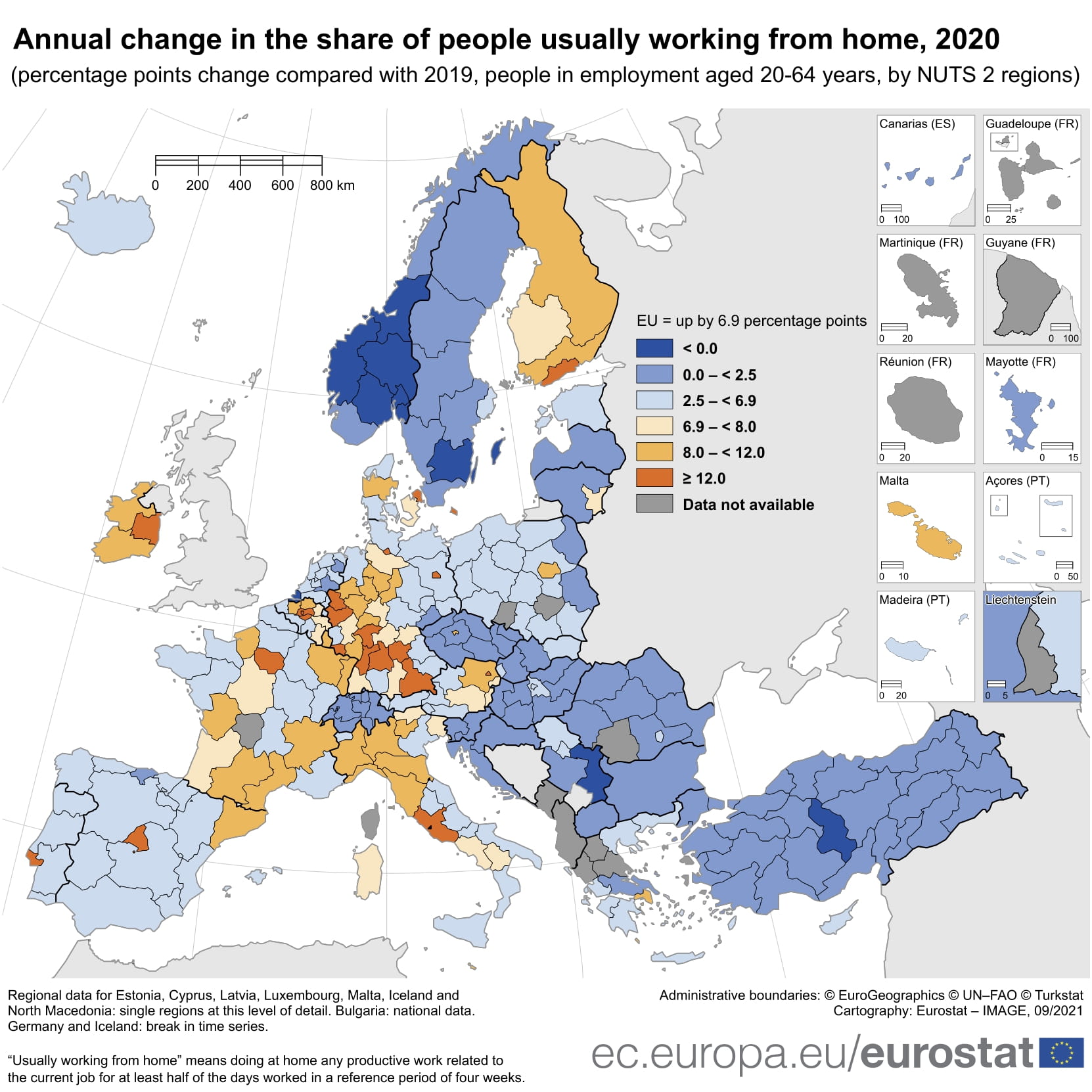
Among EU regions, the largest annual increases in the share of the employed usually working from home in 2020 (of around 19 percentage points compared with 2019) were recorded in:
- Région de Bruxelles-Capitale/Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest - the capital region of Belgium,
- Province du Brabant wallon also in Belgium,
- Helsinki-Uusimaa - the capital region of Finland, as well as in
- Eastern and Midland - the capital region of Ireland.
These regions were followed by the capital regions of Denmark, Germany, Spain, France, Italy, Austria and Portugal.
Source: Regional yearbook 2021, chapter 4: Labour market at regional level (map 3)
Would you like to know more about the labour market in the different EU regions?
You can read more in the dedicated chapter of the Eurostat regional yearbook 2021 as well as in the corresponding maps in the Statistical Atlas.
For more information:
- In this article, the regional data are presented at NUTS 2 level. Regional data for Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Luxembourg, Malta, Iceland and North Macedonia: single regions at this level of detail. Bulgaria: national data.
- Germany and Iceland: break in time series. In Germany, since the first quarter of 2020, the Labour Force Survey (LFS) has been integrated into the newly designed German microcensus as a subsample. Unfortunately, for the LFS, technical issues and the COVID-19 crisis have had a large impact on the data collection processes, resulting in low response rates and a biased sample. The published German data are preliminary and may be revised in the future. For more information, see here.
- “Usually working from home” means doing at home any productive work related to the current job for at least half of the days worked in a reference period of four weeks. Employment and remote work in 2020 is analysed in the Eurostat Statistics Explained article on employment - annual statistics.
- Eurostat regional yearbook - 2021 edition, also available as a set of Statistics Explained articles
- Regions and cities, overview page on the Eurostat website
- Eurostat Statistical Atlas
- Eurostat Regions and cities illustrated
- Eurostat application “My Region” (web and mobile app)
- European Pillar of Social Rights indicators presented by region (NUTS level 2)
To contact us, please visit our User Support page.
For press queries, please contact our Media Support.