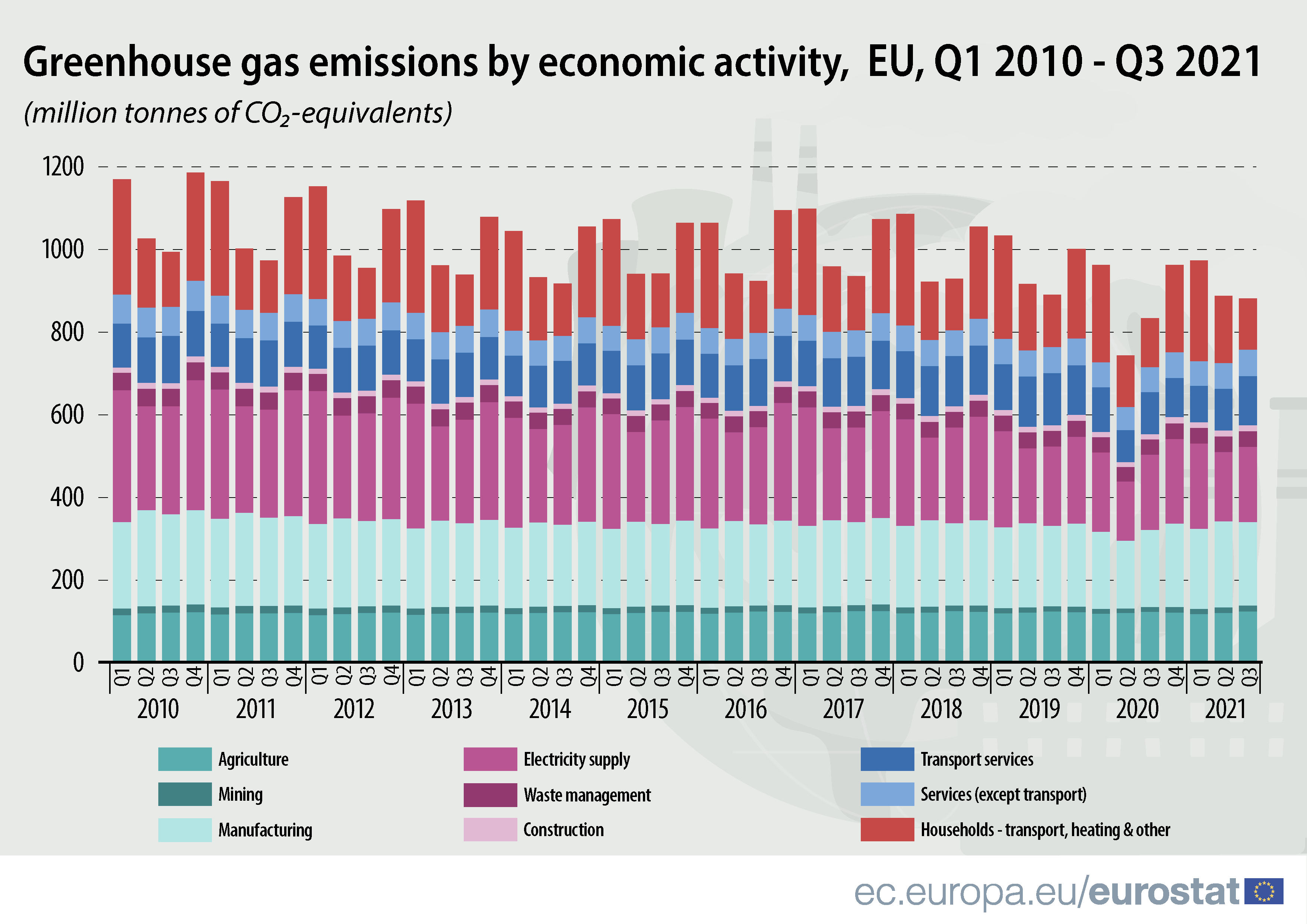
In the third quarter of 2021, EU economy greenhouse gas emissions totalled 881 million tonnes of CO2-equivalents (CO2-eq) which is slightly below pre-pandemic levels.
This information comes from data on quarterly estimates for greenhouse gas emissions by economic activity published by Eurostat today.
As graph 1 shows, EU economy greenhouse gas emissions in the third quarter of 2021 increased by 6% compared with the same quarter in the previous year. This increase is largely due to the effect of the economic rebound after the sharp decrease of activity in the same quarter of 2020 due to the COVID-19 crisis. In the pre-pandemic third quarter of 2019, emissions amounted to 891 million tonnes.
Graph 1
Source dataset: env_ac_aigg_q
In the third quarter of 2021, the economic sectors responsible for most emissions of greenhouse gases were manufacturing (23% of the total), electricity supply (21%), and households and agriculture (both 14%).
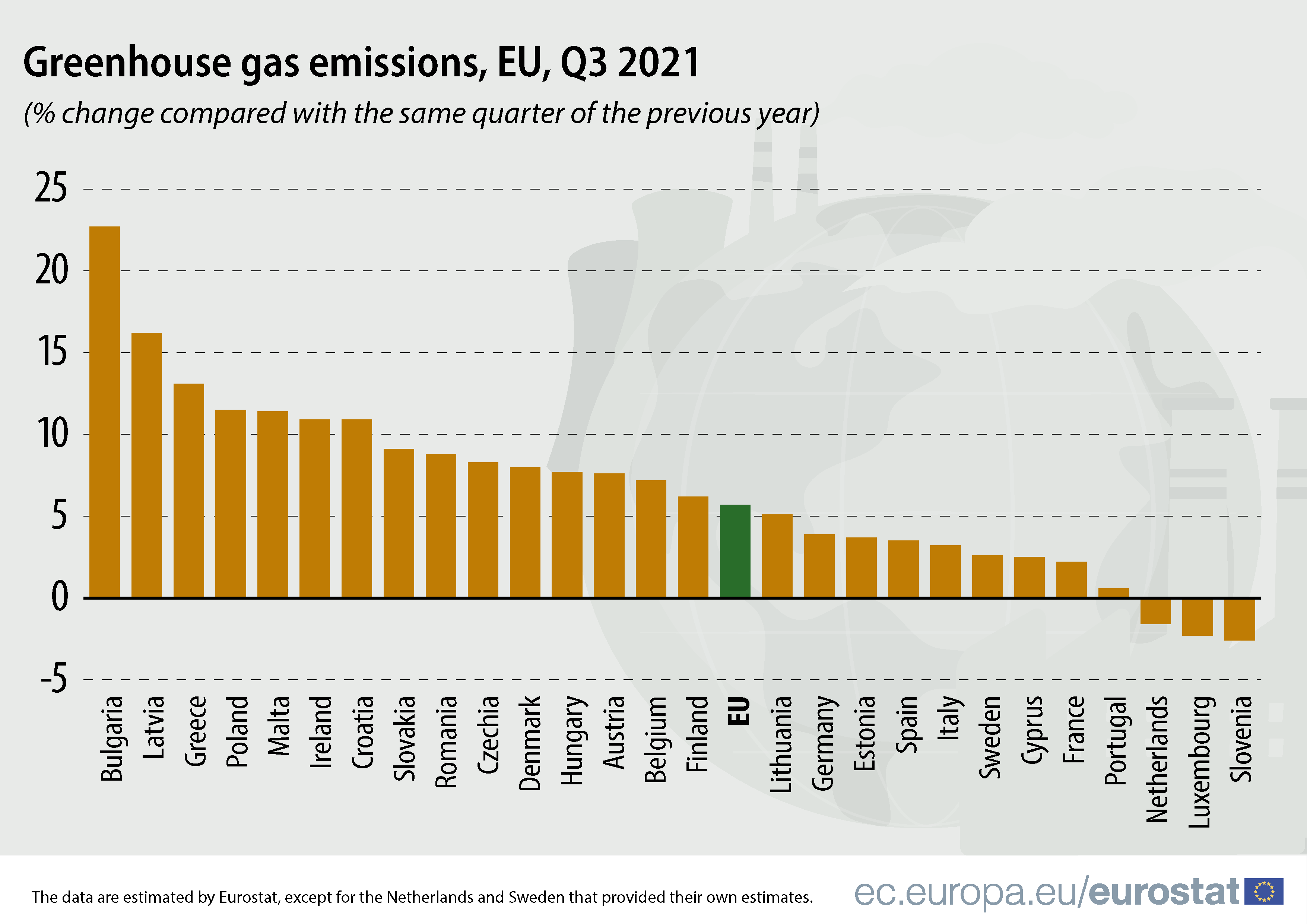
Based on economic activity data, in most EU Member States, the third quarter of 2021 showed an increase of greenhouse gas emissions compared with the same quarter of 2020, reflecting recovery from the pandemic.
Graph 2
Source dataset: env_ac_aigg_q
Emissions in the third quarter of 2021 decreased in Slovenia (-2.6% compared with the same quarter in 2020), Luxembourg (-2.3%) and the Netherlands (-1.6%). On the other hand, the largest increases in emissions were recorded in Bulgaria (+22.7%), Latvia (+16.2%) and Greece (+13.1%).
Despite the effect of the economic rebound between the third quarters of 2020 and 2021, the long-term trend of EU greenhouse gas emissions displays a steady reduction towards the EU targets.
For more information:
- Eurostat Statistics Explained article on quarterly greenhouse gas emissions
- Eurostat metadata on quarterly greenhouse gas emissions
- Eurostat database on climate change
- Eurostat dedicated section on climate change-related statistics
- Overview of the key types of greenhouse (GHG) emission estimates that are regularly published by bodies of the European Union (EU), including the EU inventory and the EU annual climate progress report
Methodological notes:
- Greenhouse gases cause climate change. The so-called ‘Kyoto basket’ of greenhouse gases includes carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases. They are expressed in a common unit, CO2-equivalents.
- The data presented here are estimates by Eurostat, except for the Netherlands and Sweden that provided their own estimates.
- Eurostat’s methodology differs from the monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions along the UN rules, which provides annual data on EU progress towards its targets. A main methodological difference is the attribution to individual countries of international transport, and the corresponding air emissions. The Eurostat estimates include the international transport emissions in the total for each country, according to the international System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA).
- The EU inventory is based on annual inventory reports by Member States and is prepared and quality checked by the European Environment Agency on behalf of the Commission and submitted to the UNFCCC each spring. The period covered by the inventory starts in 1990 and runs up until 2 years before the current year (e.g. in 2021 the inventories cover greenhouse gas emissions up to 2019). According to the European Climate Law, the EU’s climate target is to achieve –55 % net reduction by 2030 and climate neutrality by 2050.
To contact us, please visit our User Support page.
For press queries, please contact our Media Support.