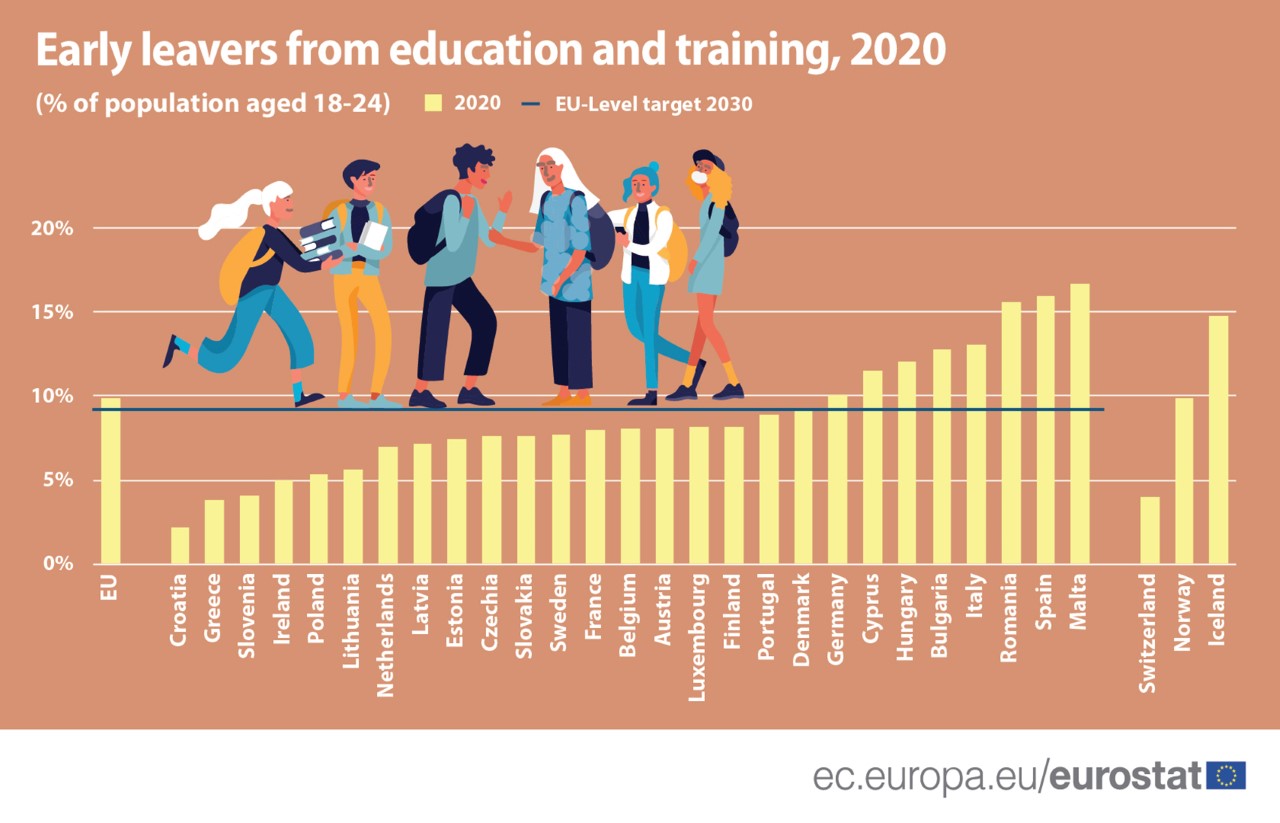
The share of 'early school leavers,’ a term that refers to early leavers from education and training (aged 18-24), has steadily decreased in the European Union (EU) over the last 10 years (from 13.8% in 2010 to 9.9% in 2020).
More young men left education and training early than women in 2020 - 11.8% of men compared to 8.0% of women. Compared to 2019, the share of male early school leavers remained the same, while the share of female dropped slightly (by 0.4 percentage points).
The EU Member States have set themselves a target to reduce the rates of early school leavers to below 9% at the EU level by 2030.
Compared with 2010, nearly all EU Member States reported a smaller proportion of early leavers in 2020, except for Slovakia, Czechia, Hungary, Sweden, Luxembourg and Bulgaria which all reported a small increase (below 3 percentage points).
Source dataset: edat_lfse_14
Lowest share of 'early school leavers' in Croatia, highest in Malta and Spain
In 2020, Member States that reported the lowest shares of early leavers from education and training were Croatia (2.2%), Greece (3.8%), Slovenia (4.1%), Ireland (5.0%) and Poland (5.4%).
In contrast, the highest shares were recorded in Malta (16.7%), Spain (16.0%), Romania (15.6%), Italy (13.1%) and Bulgaria (12.8%).
Eighteen Member States have already met the EU-level target for 2030 for this indicator: Belgium, Czechia, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, France, Croatia, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland and Sweden.
In 2020, the share of early leavers from education and training was lower for young women than for young men across all EU Member States apart from Romania and Czechia.
Source dataset: edat_lfse_14
For more information:
- Statistics Explained article Early leavers from education and training
- The indicator early leavers from education and training is defined as the percentage of the population aged 18-24 with at most a lower secondary education and who were not in further (formal or non-formal) education or training during the four weeks preceding the survey. 'At most lower secondary education' refers to ISCED (International Standard Classification of Education) 2011 level 0-2 for data from 2014 onwards and to ISCED 1997 level 0-3C short for data up to 2013. The change of ISCED has no impact on the comparability over time of this indicator for all Member States, except Estonia.
To contact us, please visit our User Support page.
For press queries, please contact our Media Support.