EU economy emissions in 2022: down 22% since 2008

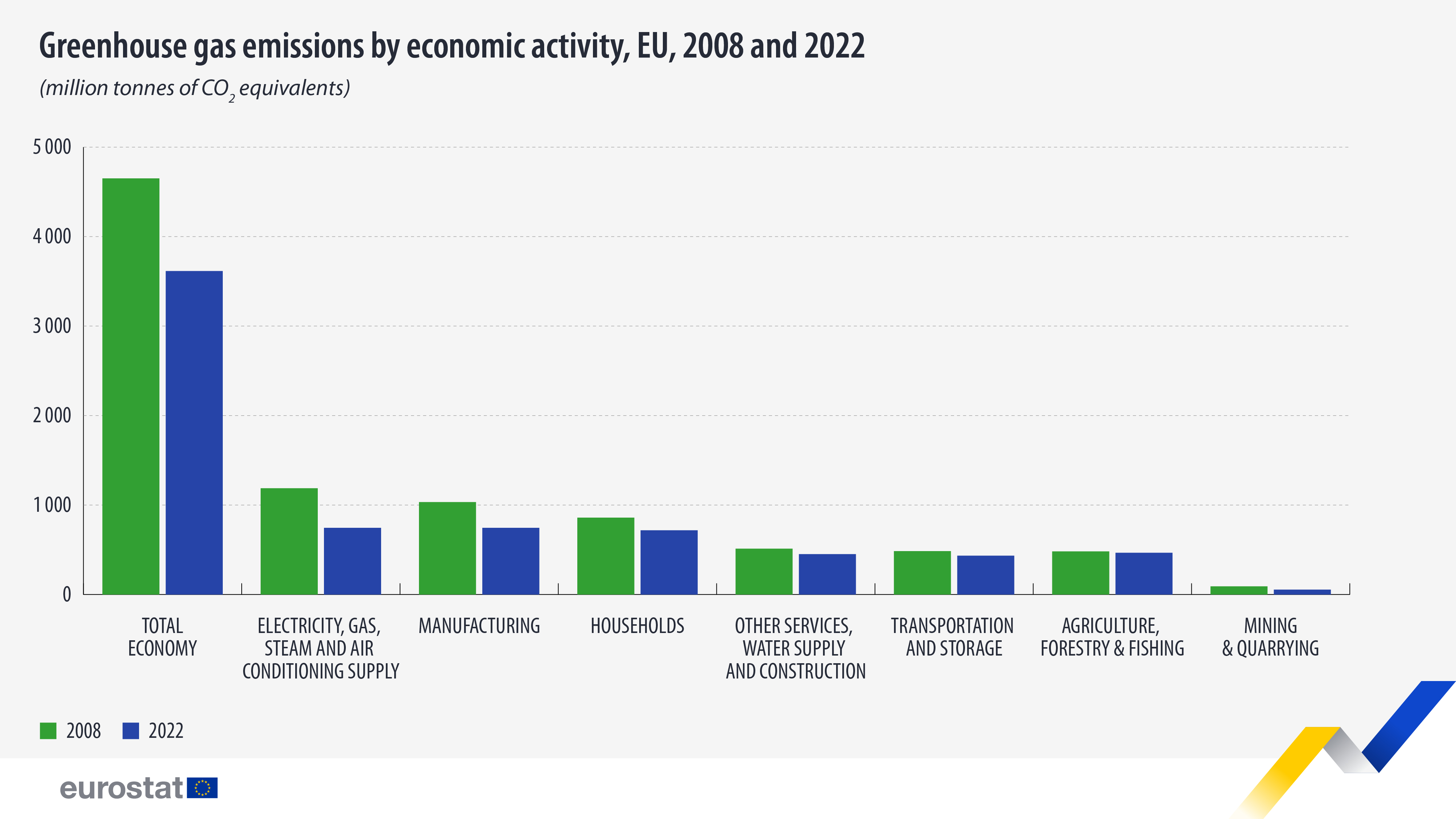
In 2022, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions generated by economic activities of EU resident units stood at 3.6 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalents (CO2-eq), indicating a 22% decrease compared with 2008.
The activities with the highest GHG emissions in 2022 were the manufacturing industry and the supply of electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning, both with 745 million tonnes of CO2-eq, representing 21% of total greenhouse gases emitted. These were followed by households (718 million tonnes of CO2-eq; 20%), which are emitters of greenhouse gases related to transportation, heating and other purposes.
Source dataset: env_ac_ainah_r2
Looking back, between 2008 (the first available year of data) and 2022, the largest relative decrease in GHG emissions was recorded in mining and quarrying (-40%), followed by the supply of electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning (-37%) and manufacturing (-28%).
These are estimates for the EU economy according to the air emissions accounts, which show the environmental impact of the whole economy, including international transport. Emitters are broken down by economic activity according to the classification NACE Rev. 2, as well as households, the same as in national accounts.
For more information
- Statistics Explained article on greenhouse gas emission statistics - air emissions accounts
- Thematic section on environment
- Database on environment
Methodological notes
- Greenhouse gases cause climate change. The so-called ‘Kyoto basket’ of greenhouse gases includes carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases. They are expressed in a common unit, CO2-equivalents.
- Since these emissions include international transport in order to cover all the actors of the EU economy, they have a larger scope than the Greenhouse gas emissions from the EU territory (inventories), reported under the United Nations Framework Convention for Climate Change (UNFCCC). Therefore the size and the trends are not identical.
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.