9% EU graduates engaged in mobility abroad

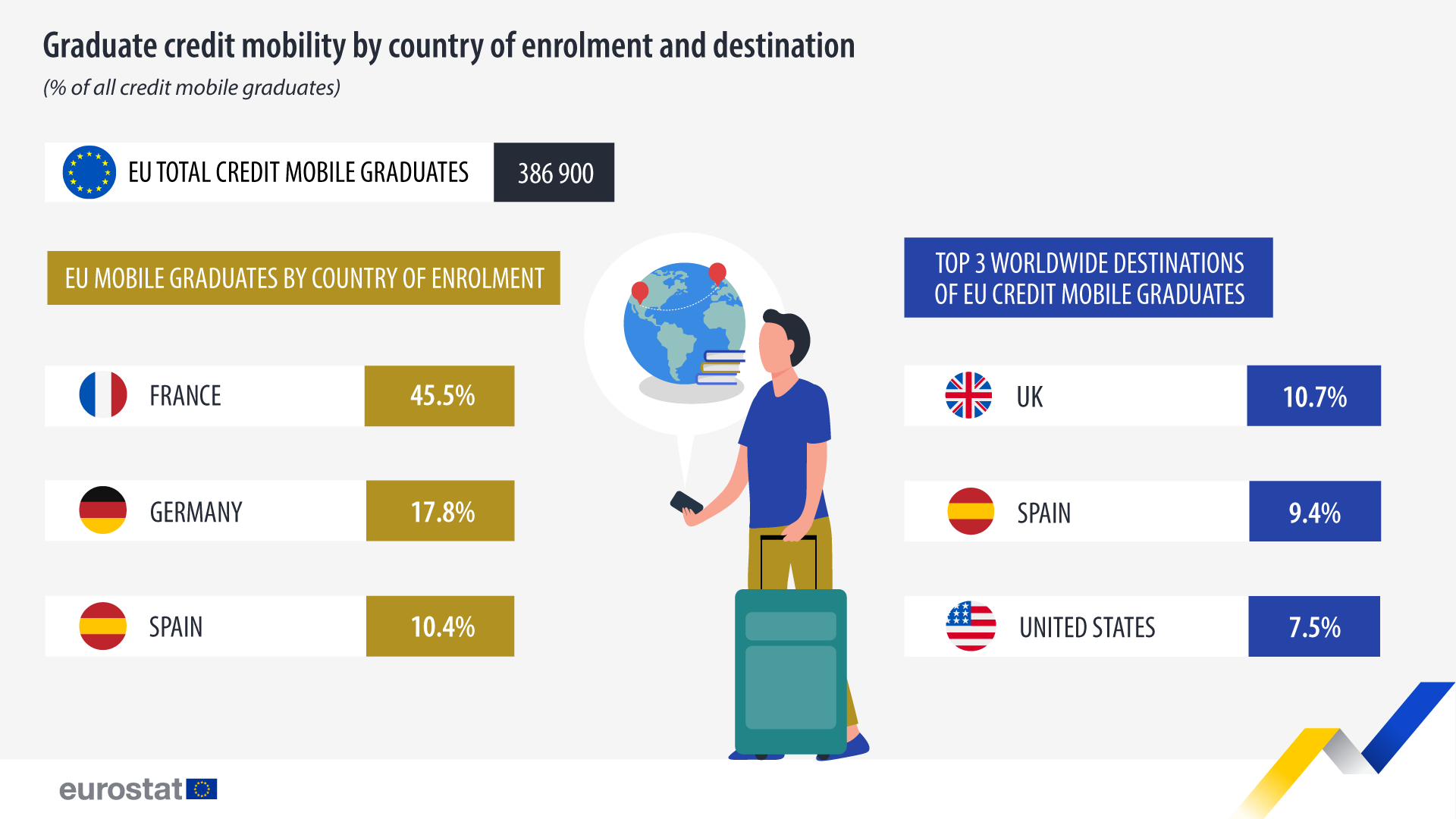
Approximately 386 900 students who graduated in 2021 in EU countries had studied abroad during their degree for at least 3 months (so-called credit mobile graduates, enrolled in tertiary education ISCED levels 5-8). As there were approximately 4.3 million graduates in the EU, this means that 9% of EU graduates participated in a mobility programme abroad.
In 2021, among the EU members, the largest number of graduates, who had credit mobility stays, was in France, numbering approximately 176 100, or a 45.5% share of the total. With 68 700 (excluding doctoral or equivalent studies), or a 17.8% share of the EU total, Germany had the second highest number of credit mobile graduates. Spain ranked third with approximately 40 100 credit mobile graduates, with a share of 10.4%.
The main destination for EU graduates who had studied abroad was the United Kingdom, accounting for 10.7% of all credit mobile graduates, followed by Spain (9.4%) and the United States (7.5%).
Source dataset: educ_uoe_mobc01, educ_uoe_mobc02
In some cases, other factors such as similar language, cultural and historical ties, as well as geographical proximity played an important role. Some EU members attracted large shares of students from specific EU countries. Greece had by far the highest share of students from Cyprus, 68%. Germany received 29.9% of credit mobile graduates from Luxembourg, while Czechia hosted 27% of students from Slovakia.
Examining the top three destinations for each EU country, Spain and Germany were the most common destinations. Among non-EU countries, the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia were the only countries to appear among the top three destinations for credit mobile graduates from any of the EU members.
This article marks the International Student’s Day celebrated annually on 17 November.
For more information
- Statistics Explained article on learning mobility statistics
- Thematic section on education and training
- Database on education and training
- Eurostat educational corner
Methodological notes
- Tertiary education ISCED levels 5-8:
- ISCED 5: Short-cycle tertiary education
- ISCED 6: Bachelor’s or equivalent level
- ISCED 7: Master’s or equivalent level
- ISCED 8: Doctoral or equivalent level
- Credit mobility is defined as temporary tertiary education and/or study-related traineeship abroad within the framework of enrolment in a tertiary education programme at a home institution (usually) for the purpose of gaining academic credit.
- In contrast to credit mobile, tertiary graduates may also be degree mobile if they completed secondary education somewhere other than the EU member country where they were studying, regardless of whether it was in another EU member country or in a non-member country. This news item refers to credit mobile graduates only. Tertiary graduates may be degree mobile and credit mobile at the same time.
- Data for credit mobile graduates for doctoral or equivalent studies (ISCED 8) are not available for some EU members: Germany, Estonia, Greece and the Netherlands.
- 'Top 3 worldwide destinations of EU credit mobile graduates’ refers to ISCED levels 5-7 only (ISCED 8 excluded).
- Ireland and Slovenia: data not available.
- Belgium: undercoverage, as the data refer only to the Flemish Community.
- Czechia: undercoverage for the short-cycle tertiary.
- Germany: data available for a limited number of partner countries. Based on data rounded to the nearest 100.
- Estonia: undercoverage.
- Italy and Slovakia: excluding short-cycle tertiary.
- Poland: for short-cycle tertiary, data were negligible or 0 for graduates and students from abroad.
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.