SDGs & me: Climate action

The Sustainable Development Goal 'Climate Action' (SDG 13) seeks to achieve a climate-neutral world by mid-century and to limit global warming to well below 2°C — with an aim of 1.5°C — compared with pre-industrial times. It aims to strengthen countries’ climate resilience and adaptive capacity, with a special focus on supporting least-developed countries.
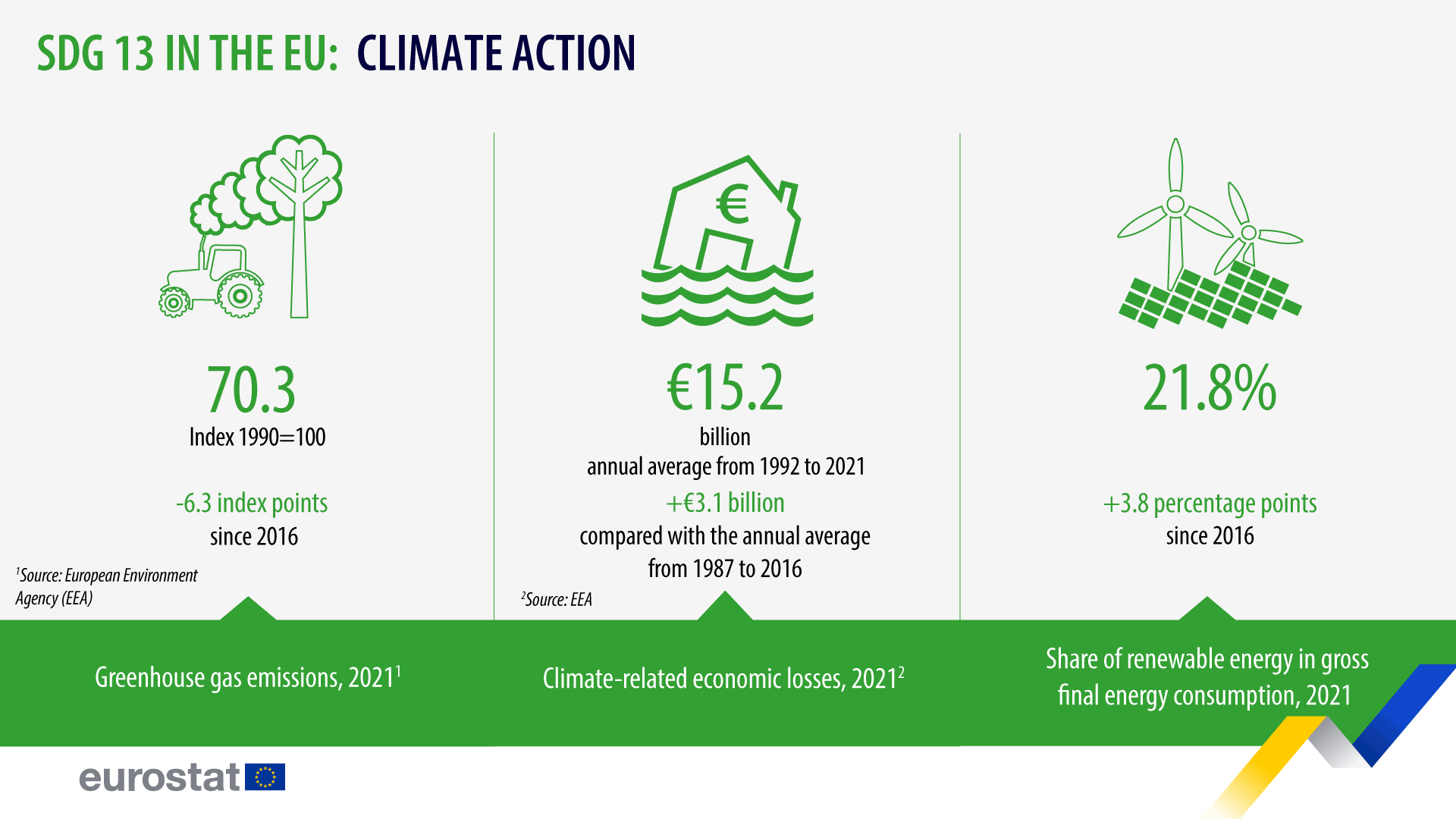
Monitoring SDG 13 in the EU context focuses on progress made in climate mitigation and adaptation efforts in reducing climate impacts and financing climate action. The EU has set into law a target to reach climate neutrality with no net greenhouse gas (GHG) by 2050. This means reducing GHG emissions as much as possible while offsetting the residual emissions by removing carbon dioxide (CO2), for example, through natural carbon sinks and using carbon-removal technologies. On its way to the 2050 target, the EU has committed itself to reducing net GHG emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared with 1990 levels.
Some of the indicators that monitor SDG 13 Climate Action are the following:
Would you like to learn more?
You can find out more about the EU’s progress towards the SDGs with the following products:
- The publication Sustainable development in the European Union – Monitoring report on progress towards the SDGs in an EU context – 2023 edition which monitors progress towards the SDGs in an EU context.;
- the visualisation tool - SDGs & me - to help you explore trends of specific indicators and compare your countries to others;
- the visualisation tool - SDG country overview - to compare your country for each SDG with the EU average;
- and the recording of the webinar on the EU’s progress, held on 25 May.
If you’d like to learn more on sustainable energy, you can also take part in the European Sustainable Energy Week 2023, being held from 20-22 June. Take part online or onsite in Europe’s biggest annual conference dedicated to renewables and energy efficiency.
For more information
- Publication on Sustainable development in the European Union – Statistical annex to the EU voluntary review – 2023 edition
- Set of Statistics Explained articles on sustainable development in the EU
- Thematic section on the Sustainable Development Goals
- Database on the Sustainable Development Goals
- Statistics for the European Green Deal
- EU Voluntary Review on progress in the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.