Labour market
Background information
Labour market data are an important set of indicators for assessing the cyclical situation and macroeconomic and social policy making. Both the unemployment and labour cost indices are important in compiling key indicators for the analysis of long-term economic equilibria and the movements around them. For example, through the Beveridge curve (relationship between the unemployment rate and the job vacancy rate) and the Phillips curve (relationship between inflation and unemployment).
Information in the database
This section covers the following topics:
Unemployment
According to the International Labour Organisation (ILO), unemployed persons are those aged 15 to 74 who:
- were not employed during the reference week
- are currently available for work
- have been actively seeking for work during the past four weeks, and
- are ready to begin working immediately or within two weeks.
Data are presented in thousands of persons, as percentages, and as shares of the labour force, for example for the unemployment rate. Data can be broken down by sex and age and is presented both unadjusted and seasonally adjusted.
Labour cost
The quarterly labour cost index (LCI) is an indicator that measures the cost pressure arising from the production factor ‘labour’. The data covered by the LCI relate to total average hourly labour costs (with and without bonuses), as well as to the labour cost categories ‘wages and salaries’ and ‘employers’ social security contributions plus taxes paid minus subsidies received by the employer.
Data are provided in nominal terms and broken down by cost items and economic activity. Labour cost index statistics are also available after adjustment for calendar and/or seasonal effects and as percentage changes.
Job vacancies
A job vacancy is defined as a paid post that is newly created, unoccupied, or about to become vacant, for which the employer is taking active steps and is prepared to take further steps to find a suitable candidate from outside the enterprise concerned. The employer also intends to fill the position either immediately or within a specific period.
The job vacancy rate (JVR) measures the proportion of total posts that is vacant according to the definition of job vacancy above, expressed as a percentage as follows:
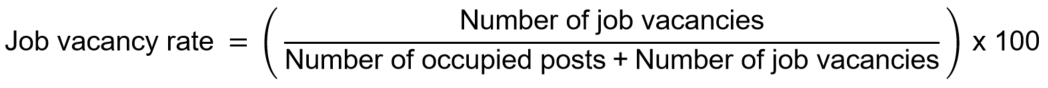
Eurostat publishes quarterly and annual data on job vacancy statistics.
