Preventive care: 6% of EU’s health expenditure in 2021
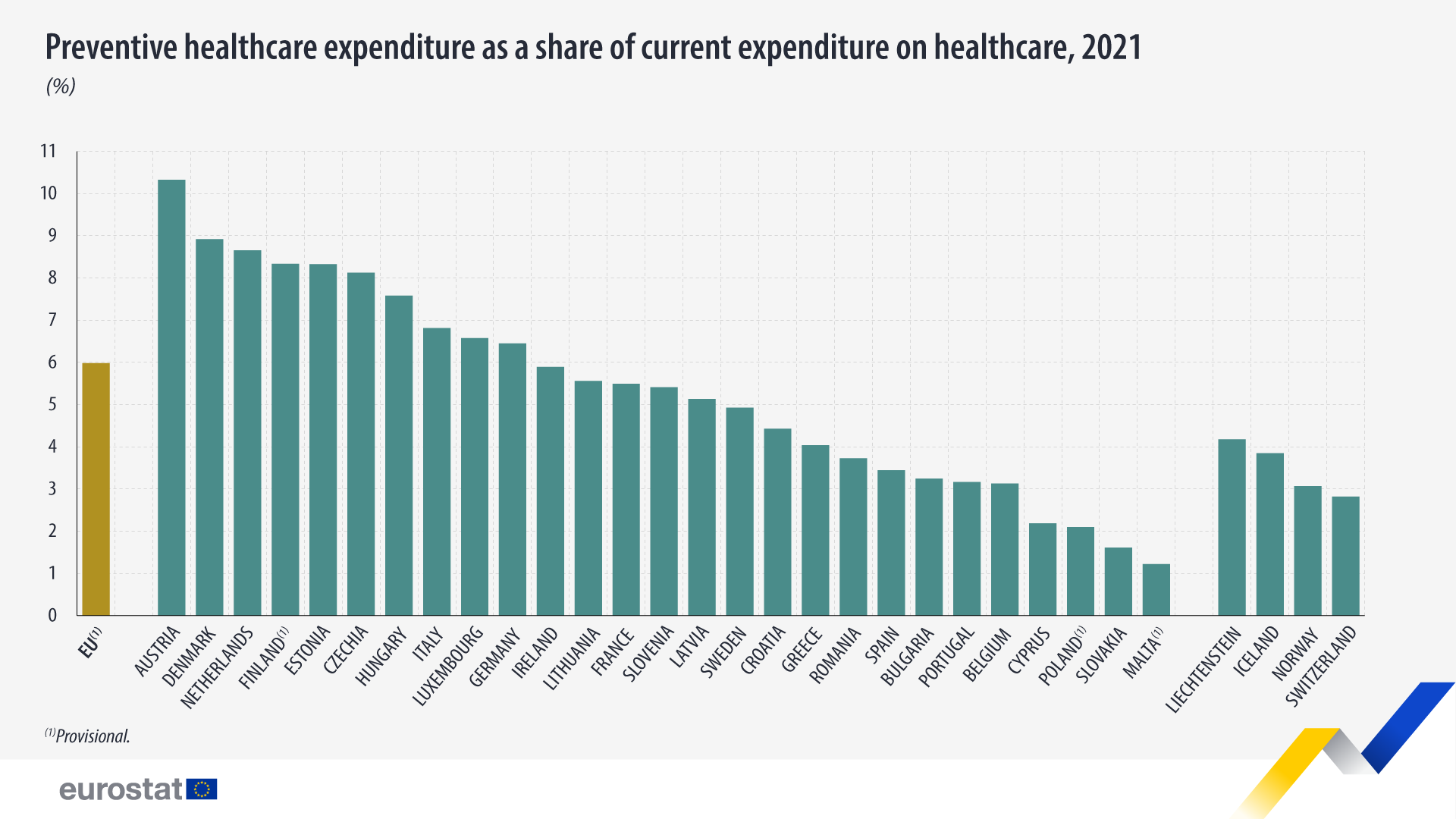
In the EU, public and private expenditure on preventive care accounted for 6.0% of total health expenditure in 2021.
In 2019 and in 2020, it accounted for 2.9% and 3.5%, respectively. This growth reflects the impact of preventive care measures activated to face the COVID-19 pandemic, in particular for the category ‘Immunisation programmes’ which includes vaccination campaigns that started in 2021. Generally, preventive care aims to avoid or reduce the number or severity of injuries and diseases, consequences, and complications.
The highest shares of preventive care expenditure were recorded in Austria (10.3% of total health expenditure), Denmark (8.9%) and the Netherlands (8.7%). In contrast, the lowest share was recorded in Malta (1.2%), followed by Slovakia (1.6%) and Poland (2.1%).
Source dataset: hlth_sha11_hc
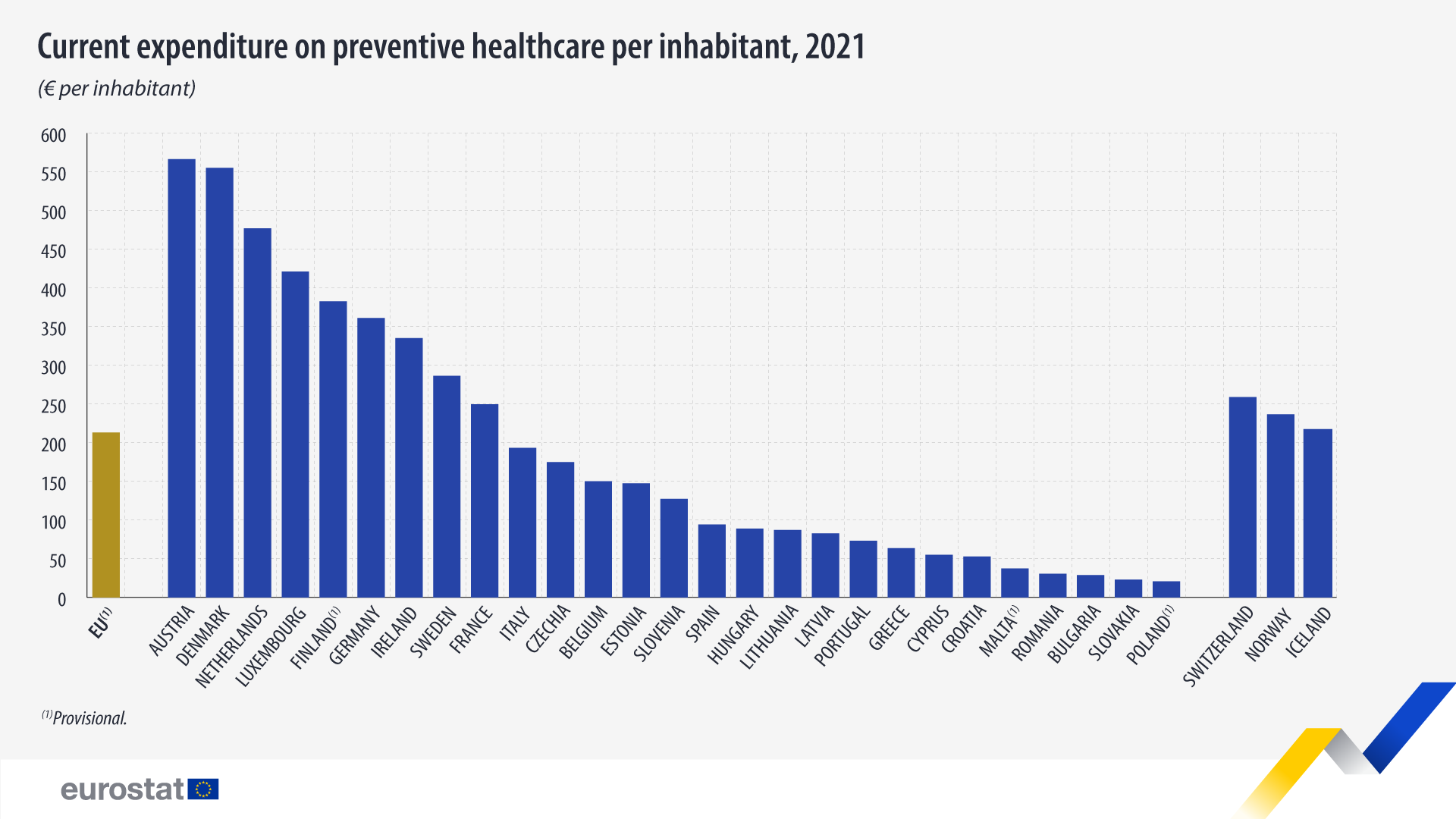
Relative to population size, in 2021, among EU countries, preventive care expenditure was highest in Austria (€566.4 per inhabitant), Denmark (€555.1) and the Netherlands (€476.9). Meanwhile, it was lowest in Poland (€20.6), Slovakia (€23.0) and Bulgaria (€28.7).
Source dataset: hlth_sha11_hc
For more information
- Statistics explained article on preventive health care expenditure
- Database on health
- Thematic section on health
Methodological notes
‘Current healthcare expenditure’ quantifies the economic resources dedicated to health functions, excluding capital investment. Healthcare expenditure is primarily concerned with healthcare goods and services that are consumed by people resident in the country, irrespective of where that consumption takes place (it may take place abroad) or who is paying for it. As such, exports of healthcare goods and services (i.e., services provided to non-residents) are excluded, whereas imports of healthcare goods and services for final use are included.
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.