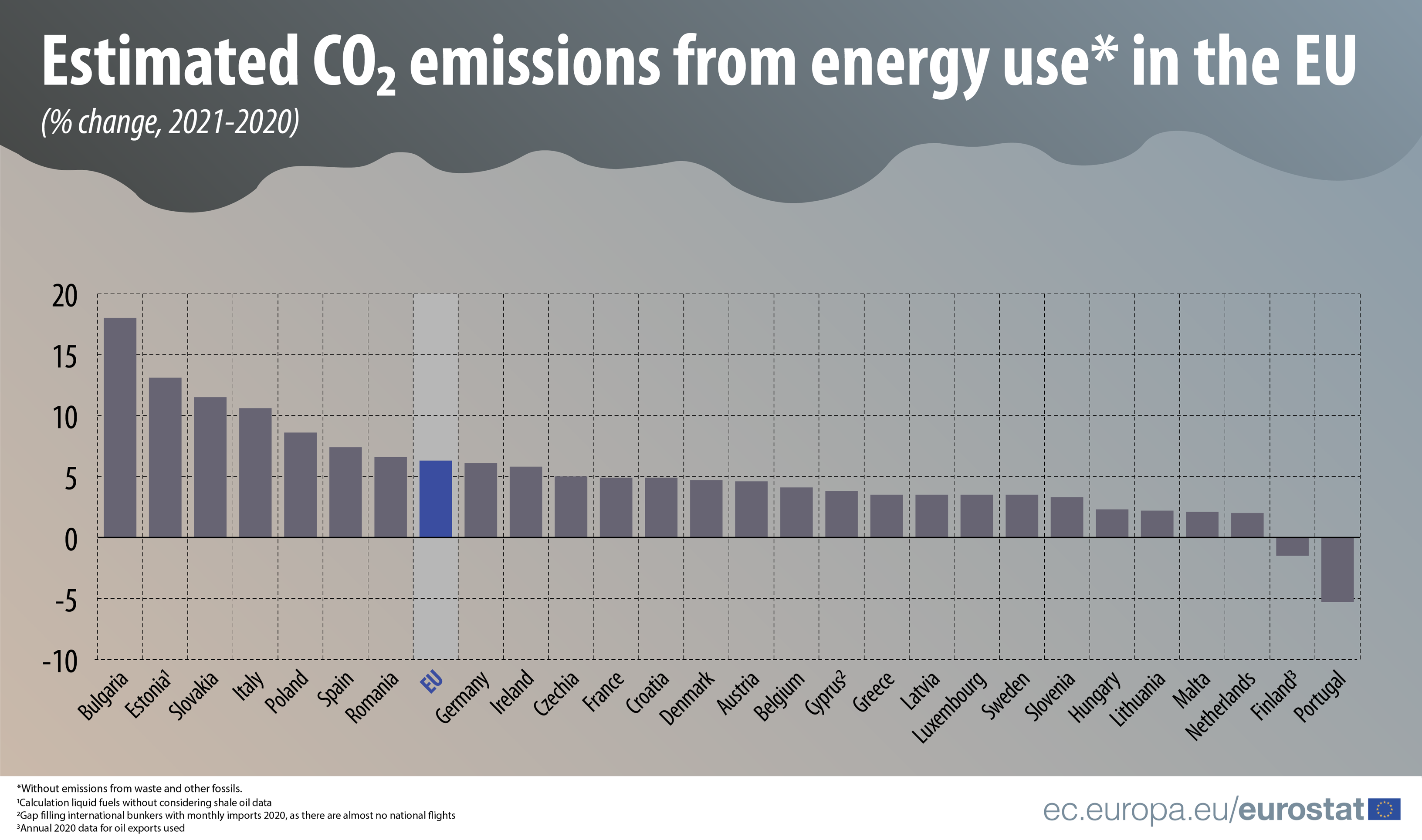
In 2021, when most of the COVID-19 containment measures were lifted by the EU Member States, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from fossil fuel combustion in the EU (mainly oil and oil products, natural gas, coal and peat) increased by 6.3% compared with the previous year. CO2 emissions from energy use are a major contributor to global warming and account for some 75% of all man-made greenhouse gas emissions in the EU. Climate conditions (e.g. cold/long winter or hot summer), economic growth, size of the population, transport and industrial activities are some factors that influence emissions.
CO2 emissions from fossil fuels originate in the country where the fuels are burned for electricity generation, transport, steel production etc., which consequently impacts imports and exports of energy products. For example, importing coal for electricity generation leads to an increase in emissions in the importing country. In contrast, electricity imports do not affect the importing country’s emissions, as these are reported in the exporting country where electricity was produced.
Source dataset: special data extraction
Biggest increases in CO2 emissions from energy use in Bulgaria, Estonia, Slovakia and Italy, decreases in Portugal and Finland
According to Eurostat estimates, CO2 emissions grew in 2021 in almost all EU Member States, with the largest increase in Bulgaria (+18.0%), followed by Estonia (+13.1%), Slovakia (+11.4%) and Italy (+10.6%). The only two countries with an estimated decrease in CO2 emissions are Portugal (-5.5%) and Finland (-1.5%).
In 2021, the increase in CO2 emissions was mainly due to the rising use of solid fossil fuels (which contributed to over 50% of the increase). Liquid fossil fuels were responsible for over 29% of the increase, whereas 21% can be attributed to natural gas. The reduced use of peat slightly alleviated the increase in CO2 emissions.
For more detailed information see the excel table with estimated CO2 emission developments per country.
For more information:
- Statistics Explained article on electricity generation from non-combustible renewables
- Dedicated section on environment
- Database on environment
- Statistics for the Green Deal dashboard
- Shedding light on energy in the EU — 2022 interactive edition
- European Environment Agency overview of the key types of greenhouse (GHG) emission estimates
Methodological notes:
- Early estimates of CO2 emissions from energy use for 2021 published in this news article are computed by Eurostat based on aggregated monthly energy statistics for fossil fuels (oil and oil products, natural gas, coal and peat) for the years 2020 and 2021. These monthly data are official data provided by Member States to Eurostat. The comparison of the two years gives a year-on-year change by fuel (increase/decrease by x%). This year-on-year change is then applied to official (GHG) inventory data Member States provided to UNFCCC for the reference year 2020 and results in the amount of CO2 emitted (in kt) in 2021 by fossil fuel and by country.
- CO2 emission data published here may slightly differ from those published nationally. More information is available in the methodological note.
- Data on CO2 emissions from energy use presented in this article do not include CO2 emissions resulting from the combustion of non-renewable waste.
- Country notes: Estonia: monthly data for shale oil is not taken into account as it is not consumed in the country. Cyprus: data on jet kerosene consumption in international aviation were gap filled by Eurostat. Finland: annual data for 2020 oil products exports was used instead of aggregated 2020 monthly data, because monthly data on oil products exports turned out to be unrealistic according to FI Statistical Office.
To contact us, please visit our User Support page.
For press queries, please contact our Media Support.