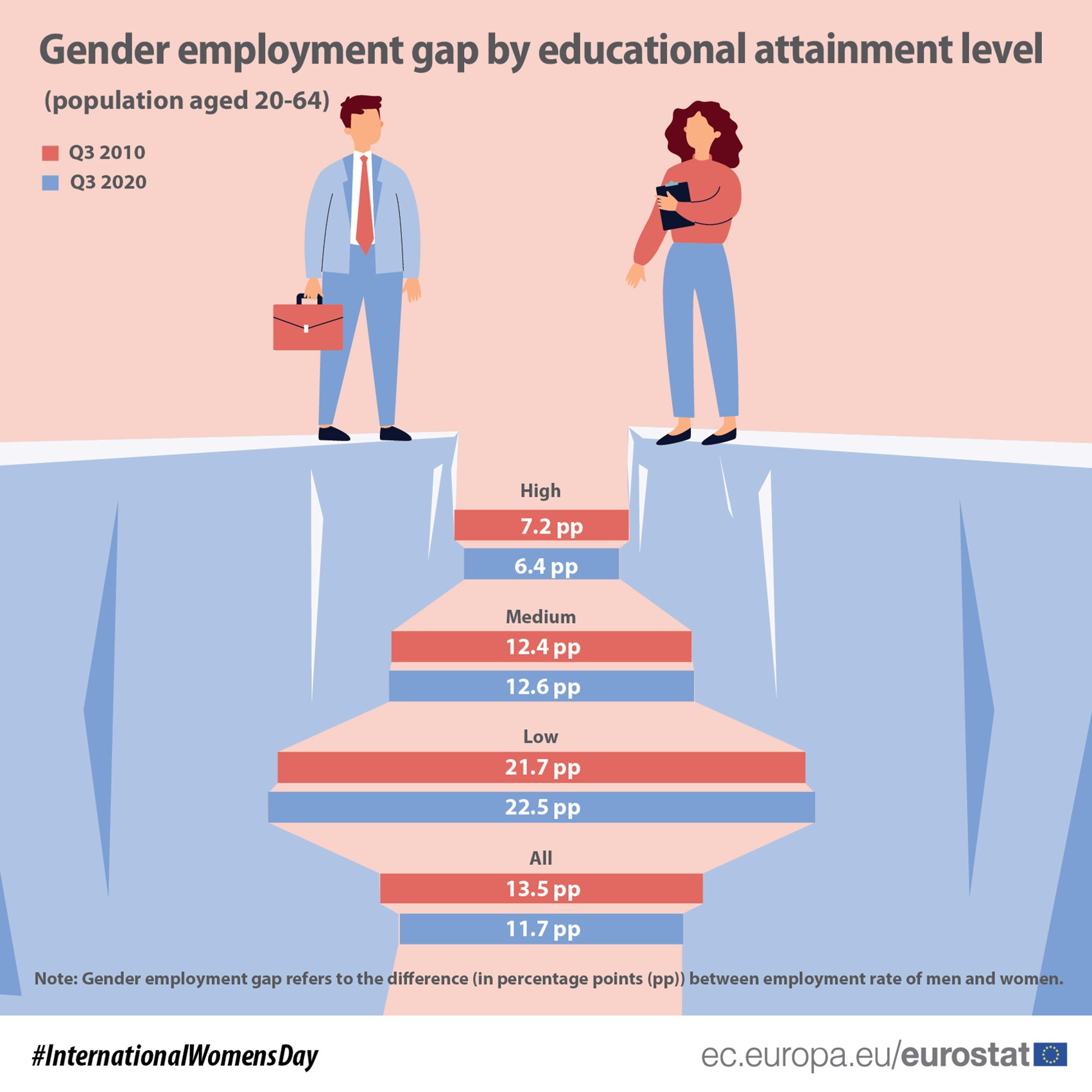
In the third quarter of 2020, the EU employment rate (for people aged 20-64) was 66.6% for women and 78.3% for men, corresponding to a gender gap of 11.7 percentage points (pp). This gender employment gap in favour of men was seen across all levels of education. However, the lower the education level, the wider the gap was between the employment rates for men and women.
86.9% of men and 80.5% of women with a high educational level were employed. In contrast, the employment rate for men with a low educational level was 65.9%, while for women it was 43.4%. Correspondingly, the gender employment gap between men and women with low educational attainment level was 22.5 pp, more than triple the employment gap among highly educated men and women (which was 6.4 pp).
In addition, over three-quarters of men with a medium level of education (78.5%) were employed, compared with under two-thirds of women (65.9%). This corresponds to a gender employment gap of 12.6 pp.
Source dataset: lfsq_ergaed
Over the last decade, the gender employment gap decreased from 13.5 pp in the third quarter of 2010 to 11.7 pp in the third quarter of 2020. Similarly, the employment gap between men and women with a high education level decreased from 7.2 pp in the third quarter of 2010 to 6.4 pp in the third quarter of 2020.
In contrast, the gender employment gap for those with a low education level increased from 21.7 pp in the third quarter of 2010 to 22.5 pp in the third quarter of 2020, while for those with a medium level of education from 12.4 pp to 12.6 pp.
This article is part of a series of articles published in the run-up to the International Women's Day.
For more information:
- Statistics Explained articles: Employment - quarterly statistics and Employment in detail - quarterly statistics.
- Germany: Due to technical issues with the introduction of the new German system of integrated household surveys, including the Labour Force Survey (LFS), the achieved sample for Q1-Q3 2020 is not large enough to allow for dissemination of the German figures. However, these are included in the computations of the EU aggregate. For more information: see here.
- Eurostat news article on women in management and knowledge-intensive services
To contact us, please visit our User Support page.
For press queries, please contact our Media Support.