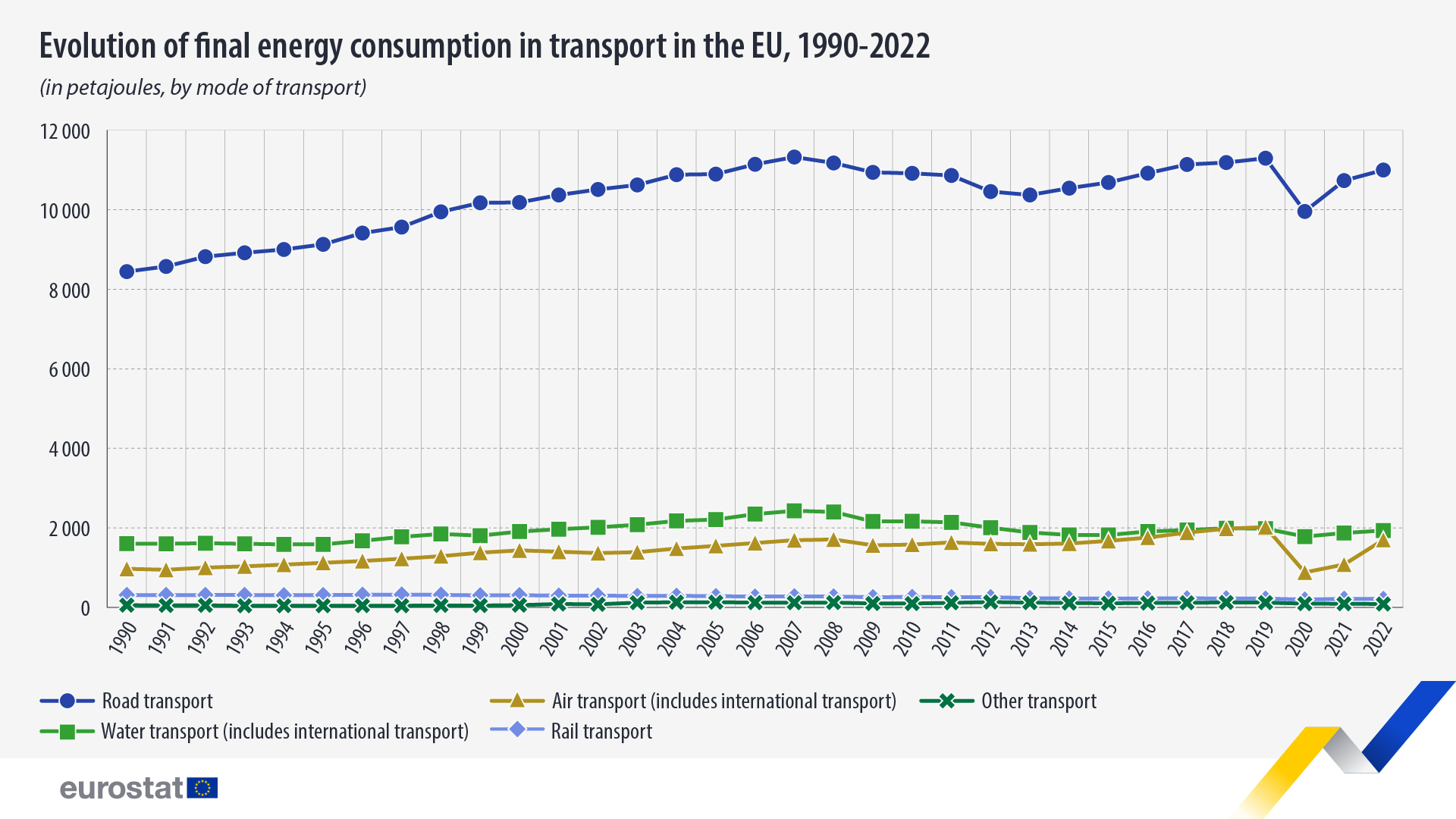
Energy consumption in transport at pre-pandemic levels

In the EU, in 2022, transport activities accounted for 31% of the final energy consumption, which made it the highest consumer of final energy, ahead of households (27%) and industry (25%).
Road transport was the largest energy consumer, responsible 74% of all energy consumption in transport, or 10 996 petajoules (PJ). Water transport accounted for 13% of all energy consumed in transport (1 935 PJ), followed by air (11%; 1 700 PJ) and rail transport (1%; 214 PJ).
Compared with 2021, air transport recorded the highest increase in energy consumption, with a striking 57% rise. In 2022, energy consumption levels in air transport were approaching the pre-pandemic figures, following sharp declines in 2020 and 2021.
Source dataset: nrg_bal_c
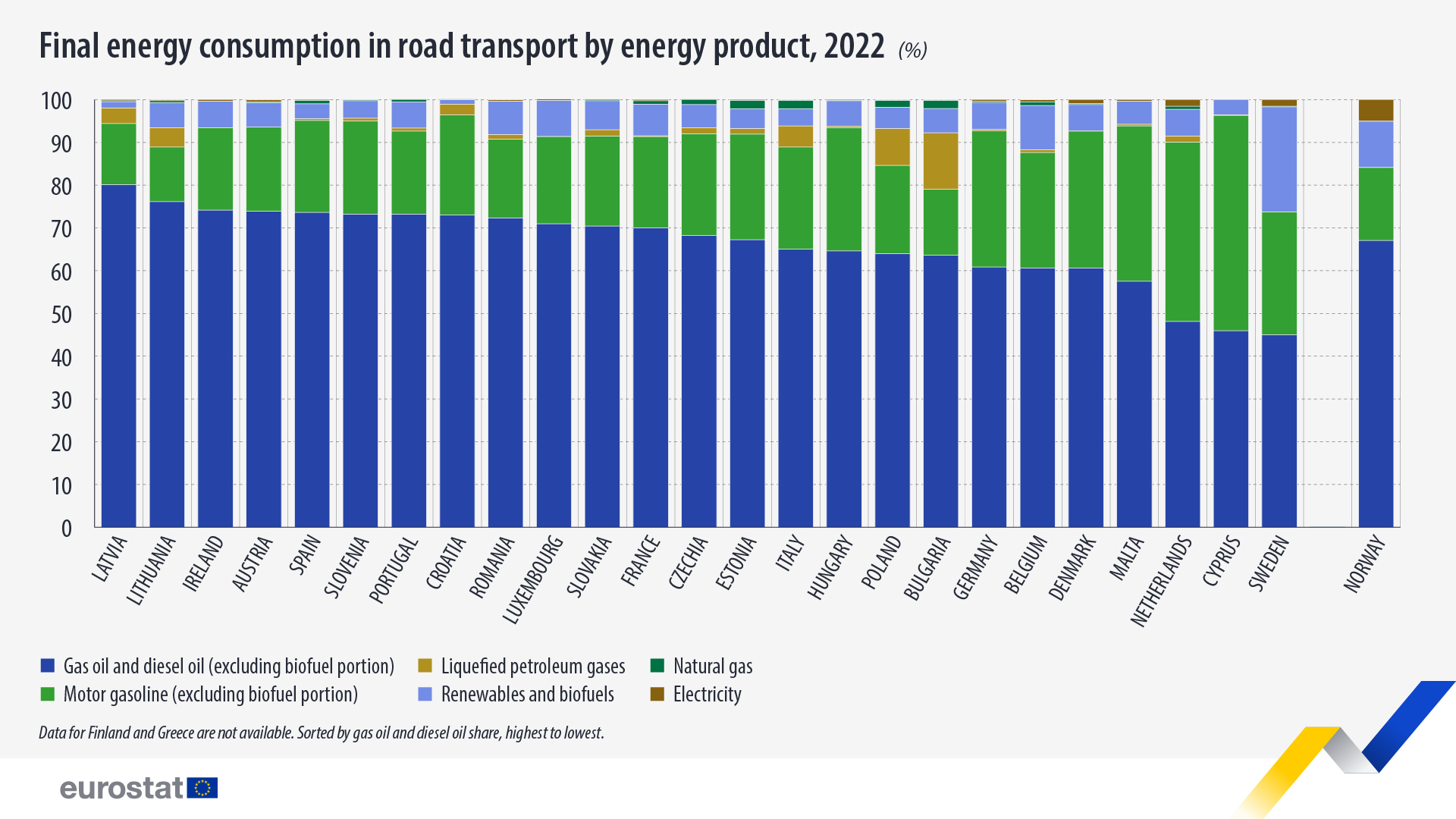
Gas/diesel oil and motor gasoline remained the leading energy sources in road transport
In 2022, gas/diesel oil (excluding the biofuel portion) was the main source of energy in road transport in the EU, with a 65% share. Motor gasoline (excluding the biofuel portion) followed at 25%, ahead of renewables and biofuels (6%), liquefied petroleum gases (2%), natural gas (1%) and electricity (0.3%).
In most EU countries, gas/diesel oil was the primary source of energy for road transport, though there were noticeable differences between the countries. The highest shares were reported in Latvia (80%) and Lithuania (76%), followed by Ireland, Austria, and Spain, each at 74%. In contrast, the lowest shares were recorded in Sweden (45%), Cyprus (46%) and the Netherlands (48%).
The share of motor gasoline was highest in Cyprus (50%), the Netherlands (42%), and Malta (36%). The lowest shares were reported in Lithuania (13%), Latvia (14%) and Bulgaria (15%).
Source dataset: nrg_d_traq
For more information
- Statistics Explained article on final energy consumption in transport
- Thematic section on energy statistics
- Database on energy statistics
- Webinar on energy statistics
- Shedding light on energy in Europe – 2024 edition
Methodological notes
- ‘Transport’ covers the energy used in all transport activities irrespective of economic sector in which the activity occurs (as defined by statistical classification of economic activities in the European Community (NACE)). It includes energy used for transport by households and by business activities, including in the industry and services sectors.
- Data on disaggregated final energy consumption in transport for 2022 are available for all EU countries, except Finland, and partially for Greece, Spain and Romania. Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2023/2199 of 17 October 2023 granted derogations for the entire collection to Spain, Romania and Finland for reference years 2022 and 2023. Under these granted derogations, Spain and Romania were still able to send data points. The Implemented Regulation also granted partial derogations to Greece for several families of fuels for reference years 2022, 2023 and 2024.
- For the full list of energy products, please refer to Annex A to Regulation (EC) No 1099/2008 on energy statistics. In this Annex and in energy statistics, ‘gas/diesel oil’ includes on-road diesel oil for diesel compression ignition engines of cars and trucks. In the context of this news item, Eurostat expects a majority of ‘gas/diesel oil’ to be taken by on-road diesel oil.
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.