The International Day of Forests is celebrated every year on 21 March to raise awareness of the importance of all types of forests.
Forests represent around 40% of total land area in the European Union (EU), with the largest shares in Finland, Sweden, Slovenia and Estonia. Not only do they play an essential role for biodiversity and are an important source of renewable energy, but they are also valuable for removing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the atmosphere.
In 2014, forests in the EU absorbed 433 million tonnes of CO2-equivalent, which corresponds to around 10% of total GHG emissions (4 420 mio. tonnes), compared to less than 7% (390 mio. tonnes) in 1990.
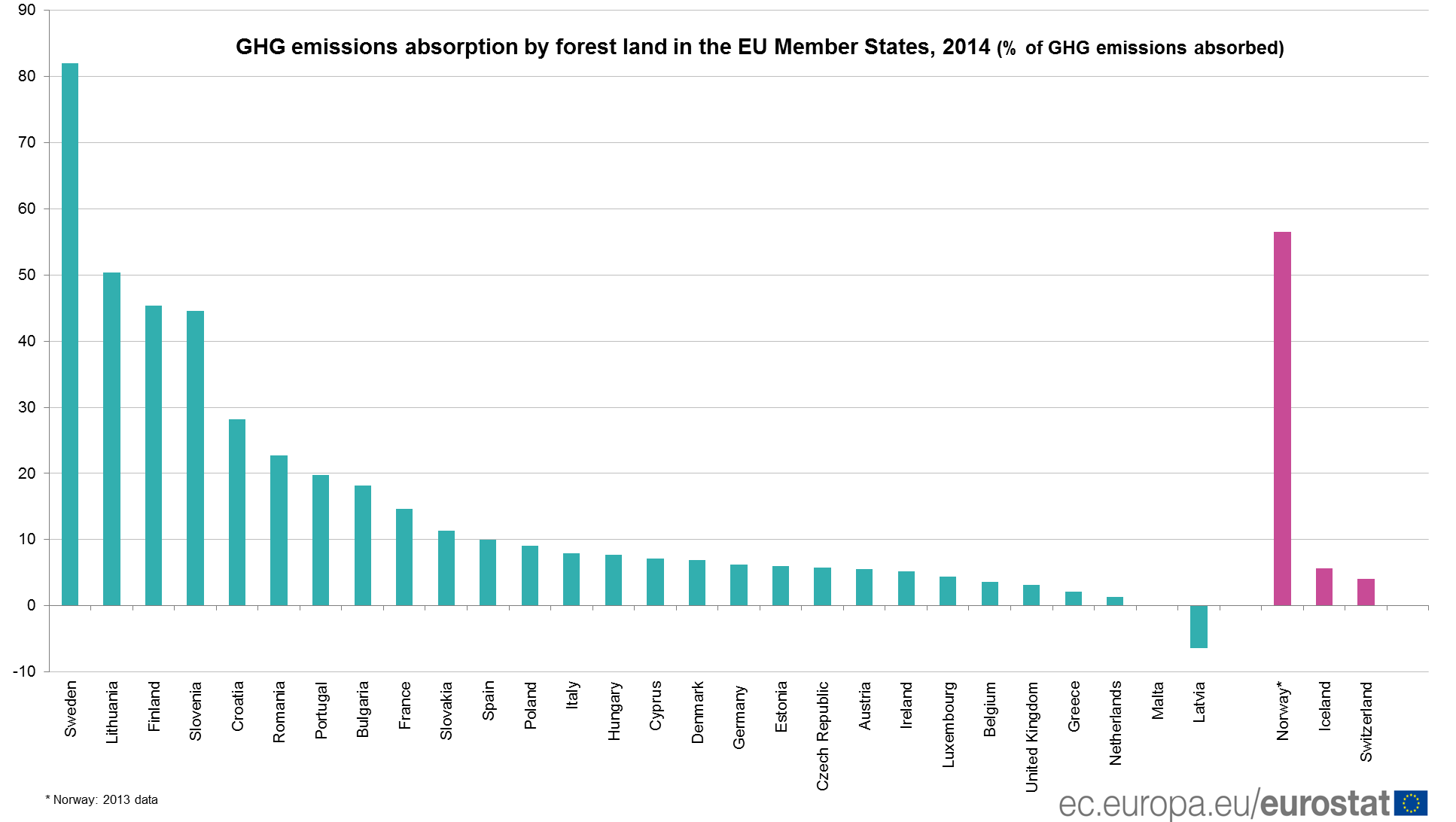
Highest shares of removals relative to Member States’ GHG emissions in Sweden
Compared with the GHG emissions of each Member State, forest land soaks up over 80% of CO2-equivalent in Sweden (82.0%) and over 50% in Lithuania (50.4%), followed by Finland (45.4%) and Slovenia (44.5%).
The contribution that forests make to the reduction of GHG emissions is not yet included in the EU GHG emission targets (see European Commission land use and forestry proposal for 2021-2030).
For more information
Eurostat website sections on environmental and forestry statistics.Data source for GHG emissions: European Environment Agency. The dataset is available on Eurostat website.
Data source for forests: FAO/Forest Europe. The dataset is available on Eurostat website.