Data extracted on 21 March 2025
Planned article update: February 2026
Highlights
In 2023, total government expenditure in the EU amounted to 49.0% of gross domestic product (GDP).
- Click on the picture to access the interactive data visualisation
This article analyses global trends in the structure of general government expenditure breakdown by their main socio-economic function (according to the Classification of the Functions of Government - COFOG).
Eurostat collects data on general government expenditure by economic function according to the international Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) in the framework of the European System of National Accounts (ESA2010).
This article is part of an online publication on general government expenditure by function.
General overview
In 2023, EU general government total expenditure stood at 49.0% of GDP, an increase as compared to 2019 when it stood at 46.6% of GDP, but a strong decrease compared to 2020 and 2021, when it stood at 52.9% of GDP and 51.1% of GDP, respectively and a slight decrease compared to 2022, when it stood at 49.2% of GDP. In 2023, the general government total expenditure to GDP ratio was was no longer significantly influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic and government measures to mitigate its effects. On the other hand, the level of the EU general government total expenditure was still influenced by government measures aimed at mitigating the impact of increasing energy prices. The decrease in the ratio to GDP compared with the previous year (49.2%) was mainly a consequence of increases in GDP, while growth in total expenditure was still observed (€8 427 billion in 2023 compared with €7 516 billion in 2022; an increase of €485 billion and a growth of 6.1% compared with 2022).
Based on the latest available expenditure data by economic function for 2023, at EU level, more than half was devoted to the functions 'social protection' (39.3% of total expenditure) and 'health' (14.8% of total expenditure), which equalled 19.2% and 7.3% of GDP respectively. The other functions of government spending with a large share of government expenditure are 'general public services' (12.0% of total expenditure or 5.9% of GDP), 'economic affairs' (11.8% of total expenditure or 5.8% of GDP) and 'education' (9.6% of total expenditure or 4.7% of GDP).
The functions 'public order and safety' (3.5% of total expenditure or 1.7% of GDP), 'defence' (2.7% of total expenditure or 1.3% of GDP), 'recreation, culture and religion' (2.4% of total expenditure or 1.2% of GDP), 'housing and community amenities' (2.4% of total expenditure or 1.2% of GDP) and 'environmental protection' (1.7% of total expenditure or 0.8% of GDP) had more limited weights at EU level in 2023.

EU general government expenditure stood at 49.0% of GDP in 2023
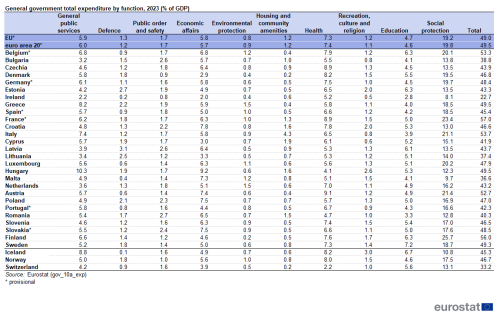
EU general government expenditure amounted to 49.0% of GDP in 2023. As a ratio to GDP in 2023, the highest levels of government expenditure were found in France (58.4% of GDP), followed by Italy (54.9% of GDP), Austria (53.0 % of GDP), Greece (52.9 % of GDP), Finland (52.6% of GDP) and Belgium (52.2 % of GDP), while the lowest levels were found in Ireland (20.6% of GDP), Lithuania (36.2% of GDP), Malta (37.7% of GDP) and Cyprus (37.9% of GDP). Switzerland (32.8% of GDP) recorded the lowest level among the EFTA countries.
General government expenditure by function
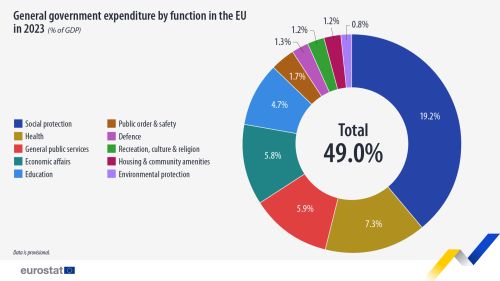
In the EU countries as well as EFTA countries reporting data, 'social protection' remained the most important function of government expenditure in 2023. In 2023, government social protection expenditure in the EU amounted to €3 309 billion (an increase by €187 billion compared to 2022) and was equivalent to 19.2% of GDP (see Table 1), compared to 19.3% of GDP in 2022. At EU level, the main contributor to the 2023 decrease of government social protection expenditure related to 'social exclusion not elsewhere classified', comprising for example support to households for increasing energy prices as well as support to refugees. In contrast, expenditure on 'old age' as a ratio to GDP increased from 10.3% of GDP in 2022 to 10.4% of GDP in 2023. The share of social protection expenditure in total expenditure remained stable at 39.3% of total expenditure in 2022 and in 2023. Over the period 1995 to 2023, the share of social protection expenditure in total expenditure at EU level increased from 36.5% of total expenditure to 39.3% of total expenditure.
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
At EU level, the next most important functions in terms of government expenditure were 'health' and 'general public services', amounting to €1 251 billion or 7.3% of GDP and €1 011 billion or 5.9% of GDP respectively in the EU in 2023. 'Economic affairs' (€991 billion or 5.8% of GDP) and 'education' (€806 billion or 4.7% of GDP) followed. The remaining functions – 'public order and safety' (€291 billion or 1.7% of GDP), 'defence' (€227 billion or 1.3% of GDP), 'recreation, culture and religion' (€201 billion or 1.2% of GDP), 'housing and community amenities' (€199 billion or 1.2% of GDP) and 'environmental protection' (€142 billion or 0.8% of GDP) - together represented 6.2% of EU GDP in 2023.
Ratio of social protection expenditure highest in Finland and France, lowest in Ireland
While social protection represented the most important area of general government expenditure in 2023 for all the EU countries, a wide variation was observed among the EU and EFTA countries. Government social protection expenditure as a percentage of GDP varied from 8.1% of GDP in Ireland, 9.7% in Malta, 12.3% in Hungary and 12.8% in Romania as well as 8.8% of GDP in Iceland, to 25.7% of GDP in Finland, 23.4% in France, 21.4% in Austria and 21.1% in Italy.
Government expenditure on health highest in Austria, on economic affairs highest in Hungary, on education highest in Sweden
In 2023, Austria (9.1% of GDP), Czechia and France (both 8.9% of GDP) recorded the highest ratios of government expenditure to GDP devoted to health among the EU members. The highest ratios of government expenditure to GDP on economic affairs in 2022 were recorded in Hungary (9.2%), ahead of Croatia (7.8%). The highest ratios of government expenditure to GDP on general public services were observed in Hungary (10.3%), ahead of Greece (8.2%). For education, the highest ratios to GDP were registered in Sweden (7.2%) and Finland, Belgium and Estonia (all 6.3%).
Evolution of general government total expenditure by function
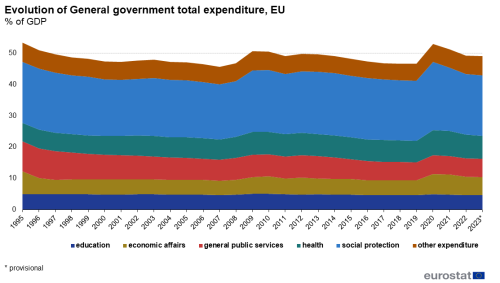
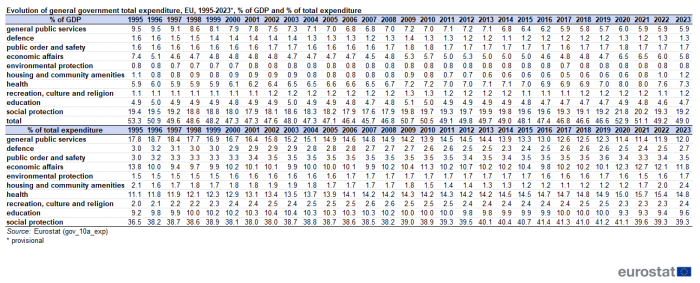
Between 1995 and 2007, total general government expenditure decreased as a ratio to GDP from 53.3% of GDP in 1995 to 45.7% of GDP in 2007. This decrease was mainly reflected in the functions 'general public services' and 'social protection' as well as 'economic affairs', the latter due to a one-off event in 1995. During the first three years of the economic and financial crisis (2007-2009), government expenditure as a percentage of GDP grew in the EU. It increased from 45.7% of GDP in 2007 to 50.7% in 2009, which was partially due to a lower GDP. Apart from an increase between the years 2011 and 2012 (from 49.1% of GDP to 49.8% of GDP), it steadily decreased to 46.6% of GDP in 2018 and in 2019. This gradual decrease was partly the result of the fiscal consolidation measures, renewed economic growth and counter-cyclical reactions of government expenditure. In recent years, one-off expenditure to support financial institutions has been decreasing.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic and government measures to mitigate its effects, total general government expenditure in the EU increased strongly in 2020 (52.9% of GDP) compared to 2019. This was a consequence of decreases in the GDP between 2019 and 2020 as well as increases in total expenditure. At EU level, in 2020, general government total expenditure increased for all the major functions, but increases were concentrated in 'social protection' (of which a major part for 'unemployment'), 'economic affairs' and 'health'. In 2021, general government total expenditure decreased as a ratio to GDP to 51.1% of GDP.
At EU level in 2022, total general government expenditure was 49.2% of GDP, a decrease compared to 2021 and mainly a consequence of increases in GDP, while growth in total expenditure was still observed. At EU level, in 2022, general government total expenditure increased in absolute terms for all the major functions. While in 2022, general government expenditure was less impacted by measures to mitigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, a strong influence of government measures to mitigate the impact of rising energy prices could be observed.
At EU level in 2023, total general government expenditure was 49.0% of GDP, a decrease compared to 2022 and again mainly a consequence of increases in GDP, while growth in total expenditure was still observed. Among the major functions decreases in the ratios to GDP were observed notably for health (-0.3 percentage points - pp. of GDP), general public services and economic affairs (both -0.2pp. of GDP) and social protection (-0.1 pp. of GDP), while increases in the ratio were observed for housing and community amenities (+0.1pp. of GDP) as well as defence and education (both +0.1pp. of GDP).
In absolute terms, at the level of the EU, general government total expenditure increased for all the major functions. There was a +€187 billion increase in social protection. General public services also registered a strong increase (+€66 billion), as did education (+€58 billion) and housing and community amenities (+€41 billion). The strongest relative increases were observed for housing and community amenities (+26.0%, from €158 billion in 2022 to €199 billion in 2023), and defence (+12.3%, from €202 billion in 2022 to €227 billion in 2023).

Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
Not all the functions of government expenditure evolved the same between 2007 and 2023. Some of the functions have a natural tendency to be counter-cyclical, even without a change in policy. For example, government expenditure on unemployment benefits (part of social protection) is more prone to have a natural counter-cyclical evolution than other functions, such as government expenditure on education. During an economic crisis, more people become unemployed, whereas the number of pupils and students is more affected by slower demographic changes.
Between 2007 and 2009, expenditure on 'unemployment' in the EU increased from 1.5% of GDP to 1.9%, decreasing to 1.3% of GDP in 2018 and 2019. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the government measures to mitigate its economic and social impact, this ratio increased to 2.2% of GDP in 2020. Between 2019 and 2020, at EU level, expenditure on unemployment increased from €180 billion to €298 billion, that is an increase of +€118 billion. In 2021, at EU level, expenditure on unemployment stood at €247 billion, compared to 2020 this represents a decrease of -€51 billion. In 2022, expenditure on unemployment decreased by a further - €58 billion to €189 billion and amounted to 1.2% of GDP. In 2023, expenditure on unemployment increased by €11 billion to stand at €200 billion and 1.2% of GDP.
Social protection expenditure as a whole increased from 17.6% of GDP (2007) to 19.8% (2009). Social protection expenditure decreased from 19.7% of GDP in 2016 to 19.2% of GDP in 2019 - together with the drop in expenditure on general public services (6.2% of GDP in 2016 decreasing to 5.7% of GDP in 2019), it is the main driver of the decrease in total expenditure in this period. In terms of the share of total expenditure, the share of 'social protection' expenditure was 38.2% in 2008 thereafter increasing to 41.4% of total expenditure in 2016, followed by a gradual decrease to 41.1% of total expenditure in 2020, and then an important decrease to 39.6% of total expenditure in 2021 and further decline to 39.3% of total expenditure in 2022 and in 2023. In terms of absolute amounts, EU total expenditure on social protection increased from €2 955 billion in 2020 to €3 309 billion in 2023.
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
Expenditure related to 'economic affairs' peaked in 1995 (13.8% of total expenditure) due to an assumption of debt relating to a former German holding company. In 2010, the high level of capital transfers to support financial institutions at the height of the financial crisis also contributed to a higher relative share of expenditure on 'economic affairs'(11.3% of total expenditure). The government measures to mitigate the economic and social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the form of subsidies, other current and capital transfers caused the share of general government expenditure on 'economic affairs' in total expenditure to increase to 12.3% in 2020 and to 12.1% in 2021. Still influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic and government measures to mitigate its effects, but to a lesser extent than in 2021. and also influenced by measures to mitigate the economic impact of rising energy prices, the share of general government expenditure on 'economic affairs' in total expenditure declined to 12.1% in 2022 and 11.8% in 2023. Expenditure on 'economic affairs' increased from €663 billion in 2019 to €991 billion in 2023, representing one of the strongest relative increase among the main functions of government expenditure since 2019. In terms of COVID measures, a number of subsidies to support businesses through pandemic related closures as well as some furlough schemes are recorded within this function. In addition, a number of the measures to mitigate the impact of rising energy prices are also reflected in this function.
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
Relatively stable shares of total expenditure over 1995-2023 are noted for 'public order and safety', 'environmental protection' and 'recreation, culture and religion'.
A steady increase over the period from 1995 to 2023 is noted for 'health', where the shares in total expenditure increased from 11.1% of GDP in 1995 to 14.8% of total expenditure in 2023. However, between 2021 and 2023, a decrease from the peak of 15.7% of total expenditure in 2021 is observed.
Expenditure on 'education' increased from 9.2% of total expenditure in 1995 to 10.0% of total expenditure in 2019-2021. However, the relative share of expenditure on 'education' decreased in 2020 and 2021 to 9.3% of total expenditure due to a lesser impact of the COVID-19 pandemic for this function and before increasing slightly again to 9.6% of total expenditure in 2023.
Decreases in the share of total expenditure over 1995 to 2023 are (also) noted for 'defence' (3.0% of total expenditure in 1995, 2.5% of total expenditure in 2022 and 2.7% of total expenditure in 2023) and general public services (17.8% of total expenditure in 1995 and 12.0% of total expenditure in 2023).
Detailed data by function
The figures at EU level mask disparate situations in the EU and EFTA countries - more detail is given in the articles below.
All these different functions are developed in 10 statistical articles as follows:
- Expenditure on 'general public services'
- Expenditure on 'defence'
- Expenditure on 'public order and safety'
- Expenditure on 'economic affairs'
- Expenditure on 'environmental protection'
- Expenditure on 'housing and community amenities'
- Expenditure on 'health'
- Expenditure on 'recreation, culture and religion'
- Expenditure on 'education'
- Expenditure on 'social protection'
Composition of general government total expenditure by function
The COFOG classification allows for an analysis of general government total expenditure by its socio-economic purpose - in other words "why" government spent money. An analysis by ESA transaction allows for an analysis of how government spent money.
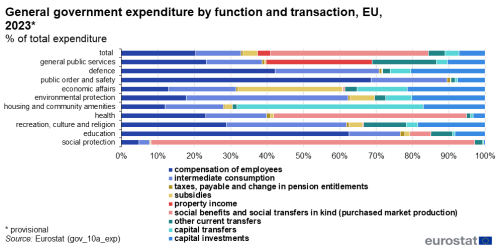
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
The most important component of government total expenditure are social benefits (in cash) and social transfers in kind ( - purchased market production). Social cash benefits are paid to households in order to relieve them of social risks or needs. Examples of social transfers are pension payments, unemployment benefits and child allowances. In 2023 in the EU, social benefits (in cash) and social transfers in kind ( - purchased market production) made up 43.4% of government total expenditure or €3 662 billion. The majority of social transfers in kind are classified in the function 'social protection', with significant amounts also recorded in 'health' and to a lesser extent 'education'.
Compensation of employees made up 20.4% of government expenditure in the EU in 2023 and amounted to €1 717 billion. It consists of wages and salaries of government employees as well as employers' social contributions. The largest amounts of compensation of employees were assigned to 'education', followed by 'health', 'general public services' and 'public order and safety'.
Intermediate consumption made up 12.4% of government expenditure in the EU in 2023 and amounted to €1 045 billion. It consists of government purchases of goods and services, excepts where these are regarded as capital formation. Important amounts were assigned to the functions 'health', 'general public services', 'economic affairs', 'education' and 'social protection'.
As regards other current transfers expenditure, these amounted to €387 billion and made of just over 4.6% of total expenditure in the EU in 2023. Two important kinds of other current transfers - current international cooperation as well as own resource contributions to the EU budget are recorded within the function 'general public services'. Important amounts were also allocated to 'social protection' and 'education'.
In 2023, at the level of the EU, subsidies (4.0% of total expenditure; €337 billion) and capital transfers - including investment grants – (€322 billion; 3.8% of total expenditure) were concentrated in the function 'economic affairs', with important amounts of capital transfers also observed in 'housing and community amenities'.
Property income expenditure (€296 billion and 3.5% of total expenditure) - consisting mainly of interest payments - was concentrated in the function 'general public services' (and the group 'public debt transactions' in particular).
Capital investments (gross capital formation) made up 7.2% of general government total expenditure in the EU in 2023. They were concentrated in the division 'economic affairs', which includes notably the group 'transport'.

Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
Source data for tables and graphs
The detailed tables ![]() are available here.
are available here.
Data sources
Reporting of data to Eurostat
Annual government finance statistics (GFS) data are collected by Eurostat on the basis of the European System of Accounts (ESA 2010) transmission programme. Member States are requested to transmit, among other tables, table 1100, 'Expenditure of general government by function' eleven months after the end of the reference period. Table 1100 provides information about expenditure of the general government sector divided into main COFOG functions and ESA 2010 categories. The transmission of the COFOG I level breakdown (divisions) for the general government sector and its subsectors is compulsory for the years 1995 onwards, whereas information on the COFOG II level (COFOG groups) is provided on a compulsory basis for the general government sector from the reference years 2001 onwards. The main reference year used in this publication is 2023 as the latest year available at EU level.
Data was extracted on 21 March 2025.
Provisional data
While a significant effort was undertaken to harmonise the recording of government measures to alleviate the impact of increasing energy prices, a full harmonisation was not yet achieved, please refer to country notes.
Data for the EU and euro area aggregates (2023), Belgium (2023), Germany (2021-2023), Spain (2023), France (all years) and Portugal (2023), Slovakia (all years) is provisional.
Definition of general government and its subsectors
The data relate to the general government sector of the economy, as defined in ESA 2010, paragraph 2.111: 'The general government sector (S.13) consists of institutional units which are non-market producers whose output is intended for individual and collective consumption, and are financed by compulsory payments made by units belonging to other sectors, and institutional units principally engaged in the redistribution of national income and wealth’.
Classification of functional expenditure of government
The Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) classifies government expenditure into ten main categories (divisions known as the 'COFOG I level' breakdown): general public services; defence; public order and safety; economic affairs; environmental protection; housing and community affairs; health; recreation, culture and religion; education; social protection. These divisions are further broken down into 'groups' (COFOG II level).
Further information is available in the Eurostat Manual on sources and methods for the compilation of COFOG Statistics.
Satellite accounts
Administrative expenditure data is additionally collected in so-called satellite accounts. In general, the amount of expenditure recorded in satellite accounts is expected to exceed the expenditure recorded under the respective COFOG division. More details on the comparability of COFOG data with satellite accounts data can be found in the COFOG manual.
Definition of general government total expenditure
Government total expenditure is defined in ESA 2010, paragraph 8.100 and chapter 20 by using as reference a list of ESA 2010 categories.
Government total expenditure comprises the following categories:
- P.2, 'intermediate consumption': the purchase of goods and services by government;
- P.5, 'gross capital formation' consists of: (a) gross fixed capital formation (P.51g); (b) changes in inventories (P.52); (c) acquisitions less disposals of valuables (P.53); where
- P.51g, 'gross fixed capital formation': consists of acquisitions, less disposals, of fixed assets during a given period plus certain additions to the value of non-produced assets realised by the productive activity of producer or institutional units. Fixed assets are tangible or intangible assets produced as outputs from processes of production that are themselves used repeatedly, or continuously, in processes of production for more than one year;
- D.1, 'compensation of employees': the wages of government employees plus non-wage costs such as social contributions;
- D.29, 'other taxes on production, payable',
- D.3, 'subsidies, payable',
- D.4, 'property income, payable', consists of : (a) 'interest, payable' (D.41) and (b) 'other property income, payable' (D.42+D.43+D.44+D.45), where
- D.41, 'interest': excludes settlements under swaps and forward rate arrangements, as these are treated as financial transactions in the ESA 2010;
- D.5, 'current taxes on income, wealth, etc, payable';
- D.62, social payments: cover social benefits and pensions paid in cash;
- D.632, 'social transfers in kind - purchased market production';
- D.7, 'other current transfers, payable';
- D.8, 'adjustments for the change in pension entitlements';
- D.9, 'capital transfers payable';
- NP, 'acquisitions less disposals of non-financial non-produced assets': public investment spending. Non-financial non-produced assets consist of land and other tangible non-produced assets that may be used in the production of goods and services, and intangible non-produced assets.
- Capital investments includes P.5 and NP.
- Other current expenditure includes D.29, D.5 and D.8.
Gross Domestic Product
Throughout this publication, the nominal GDP, i.e. GDP at current prices is used. The latest GDP available at time of publication is used.
Time of recording & symbols used
In the ESA 2010 system, recording is on an accrual basis, that is, when ‘economic value is created, transformed or extinguished, or when claims and obligations arise, are transformed or are cancelled.'
":" not available
"pp" percentage points
More data and information
For more country-specific notes, e.g. on missing data, please refer to the metadata published on Eurobase. The authors can be contacted at ESTAT-GFS@ec.europa.eu
Context
In the framework of the European System of National Accounts (ESA 2010), Eurostat collects data on general government expenditure by economic function according to the international Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) – see methodological note.
Explore further
Other articles
Database
- Government statistics (gov)
- Government finance statistics (EDP and ESA 2010) (gov_gfs10)
- Annual government finance statistics (gov_10a)
- Government revenue, expenditure and main aggregates (gov_10a_main)
- General government expenditure by function (COFOG) (gov_10a_exp)
- Main national accounts tax aggregates (gov_10a_tax_ag)
- Annual government finance statistics (gov_10a)
- Government finance statistics (EDP and ESA 2010) (gov_gfs10)
Thematic section
Selected datasets
- Government statistics (t_gov)
- Annual government finance statistics (t_gov_10a)
Methodology
- Government revenue, expenditure and main aggregates (ESMS metadata file — gov_10a_main_esms)
- General government expenditure by function (COFOG) (ESMS metadata file — gov_10a_exp_esms)
- Manual on sources and methods for the compilation of COFOG statistics - Classifications of the Functions of Government - 2019 edition
- Manual on government deficit and debt — implementation of ESA 2010 — 2022 edition


