Government expenditure on social protection
Data extracted on 29 February 2024
Planned article update: February 2025
Highlights
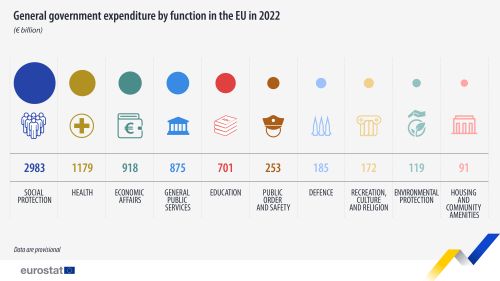
General government expenditure in the EU on social protection stood at €3 098 billion or 19.5 % of GDP in 2022.
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
This article analyses data on general government total expenditure on 'social protection' (according to the Classification of the Functions of Government - COFOG). It is part of a set of statistical articles based on general government expenditure by function.
Eurostat collects data on general government expenditure by economic function according to the international Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) in the framework of the European System of National Accounts (ESA 2010).
Full article
Expenditure on 'social protection'
Expenditure on 'social protection' remained by far the most important COFOG division in 2022 in the EU and in all reporting EU Member States and EFTA countries. This reflects government's core function to redistribute income and wealth, financed by compulsory payments. Unsurprisingly, the expenditure category dominating this division is 'social benefits and social transfers in kind (purchased market production)'. Social benefits are paid to households to alleviate social risks and needs. Examples include unemployment benefits and pension payments. In 2022 in the EU, social benefits and social transfers in kind (purchased market production) made up around 88 % of expenditure in the social protection COFOG division.

Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp)
In the EU in 2022, expenditure on social protection stood at €3 098 billion, equivalent to 19.5 % of GDP and 39.2 % of total expenditure.
By far the most significant group in this division, 'old age' (10.4 % of GDP), relates mainly to pension payments.
Expenditure in 'sickness and disability' (2.8 % of GDP), the second largest group, represents mainly social payments in cash or in kind related to social insurance schemes.
In the EU in 2022, the groups 'family and children' (1.9 % of GDP), 'survivors' (1.5 % of GDP) and 'unemployment' (1.2 % of GDP) also accounted for a significant part of expenditure. The group 'survivors' contains mainly pension payments to survivors of a deceased insured person.
'Housing', comprising mainly social protection payments to households to help with the cost of housing as well as the operation of social housing schemes, accounted for 0.3 % of GDP.
Expenditure related to 'social exclusion not elsewhere classified' accounted for 1.1 % of GDP at EU level in 2022 - this contains benefits to persons socially excluded, e.g. on low income, refugees, suffering from substance abuse, etc. Non-means tested assistance to households to alleviate the impact of high energy prices is also recorded in this group. This, together with the increase in refugees following Russia's war of aggression against Ukraine, accounts for an increase of expenditure in 2022.
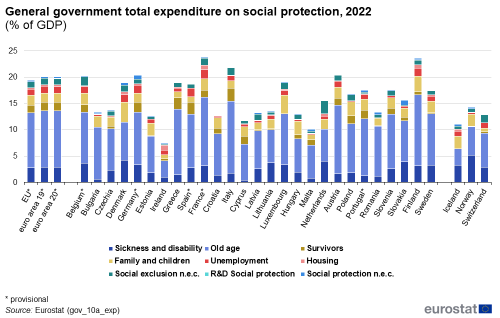
Government 'social protection' expenditure as a ratio to GDP varied across EU Member States from 7.5 % to 23.8 %
Social protection represented the largest area of general government expenditure in 2022 in all EU Member States. The ratio of government social protection expenditure to GDP varied across EU Member States from 7.5 % of GDP in Ireland to 23.8 % in France.
In 2022, six EU Member States – France (23.8 % of GDP), Finland (23.6 % of GDP), Italy (21.9 % of GDP), Austria (20.6 % of GDP), Germany (20.4 % of GDP) and Belgium (20.3 % of GDP) – devoted at least 20 % of GDP to social protection. At the other end of the scale, Ireland (7.5 % of GDP), Malta (10.1 % of GDP), Cyprus (11.8 % of GDP), Estonia (12.7 % of GDP) and Croatia (12.9 % of GDP), as well as Iceland (11.1 % of GDP) and Switzerland (12.9 % of GDP) among the EFTA countries, each spent less than 13 % of GDP on social protection.
'Social protection' expenditure by type of transaction
In 2022 at the EU level, 88 % of expenditure on 'social protection' was in the form of social (cash) benefits and social transfers in kind (purchased market production). This category comprises payments of retirement or survivors’ pensions, unemployment allowance, benefits connected with absence from work as a result of ill health, accident, maternity, payment of family, education or other allowances in respect of dependants. 5 % of expenditure in this function was in the form of compensation of employees, e.g. wages and salaries of staff administrating social protection schemes, 3 % was in the form of intermediate consumption (purchases of goods and services) and 3 % related to other current transfers, for example to non-profit institutions serving households or for non-means tested assistance to households.
Evolution of 'expenditure on social protection'
Compared to 1995, expenditure on 'social protection' has increased at the EU level as a share of total expenditure from 36.6 % of total expenditure in 1995 to 39.2 % of total expenditure in 2022. Compared to the period between 2016 and 2020 with the notably higher share (above 41 % on average), in 2021 (39.7 %) and 2022, in the EU, the share social protection in total expenditure stood at a comparatively low level.
As a percentage of GDP, expenditure on 'social protection' remained at a high level in 2022 (19.5 % of GDP), still influenced by government expenditure measures to mitigate the effects of the pandemic, although to a lesser extent than in 2020 (21.9 % of GDP) and 2021 (20.4 %), however government measures to mitigate the impact of increasing energy prices strongly influenced the level of expenditure on 'social protection' in 2022. The decrease in the ratio compared to the previous year was mainly due to the increase in the nominal GDP, which overweighed the effect of the increase in total expenditure in nominal terms in this division from €2 985 billion in 2021 to €3 098 billion in 2022.
Over the period between 1995 and 2022, the expenditure on 'social protection' as a ratio to GDP increased from 19.4 % of GDP in 1995 to 19.5 % of GDP in 2022. The strongest annual increases of the ratio were reported in 2020 (2.6 percentage points) and in 2009 (1.9 pp). This was a consequence of decreases in the GDP in both periods as well as increases in total expenditure on 'social protection' to mitigate the effects of the financial crisis and the COVID-19 pandemic, respectively.
After a notable increase from 1.4 % of GDP in 2008 to 1.9 % in 2009, gradually decreasing in the following years until 2019 (1.3 % of GDP), expenditure on 'unemployment' in the EU sharply increased in 2020 (2.2 % of GDP) due to the government measures to mitigate the economic and social impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The ratio remained high in 2021 (1.7 % of GDP), still impacted by the government measures, but declined to 1.2 % of GDP in 2022, below the pre-pandemic level. Between 2019 and 2022, at the EU level, expenditure on unemployment increased from €180 billion in 2019 to €297 billion in 2020 and decreased to €247 billion in 2021 and €188 billion in 2022. This evolution is notably due to increased assistance during the COVID-19 pandemic, notably furlough schemes designed to prevent wide-spread unemployment.
Between 2021 and 2022, among the more detailed social protection functions, the strong decreases at EU level on 'unemployment' and 'old age' as a ratio to GDP were only partly compensated by smaller increases in expenditure on 'social exclusion n.e.c.'.
Not all the functions of government expenditure evolved the same in the period analysed. Some of the functions have a natural tendency to be counter-cyclical, even without a change in policy. For example, government expenditure on unemployment benefits (part of social protection) is more prone to have a natural counter-cyclical evolution than other functions, such as government expenditure on education. During an economic crisis, more people become unemployed, whereas the number of pupils and students is more affected by long-term demographic changes.
Source data for tables and graphs
The detailed tables ![]() are available here.
are available here.
Data sources and availability
Reporting of data to Eurostat
Annual government finance statistics (GFS) data are collected by Eurostat on the basis of the European System of Accounts (ESA 2010) transmission programme. Member States are requested to transmit, among other tables, table 1100, 'Expenditure of general government by function' twelve months after the end of the reference period. Table 1100 provides information about expenditure of the general government sector divided into main COFOG functions and ESA 2010 categories. The transmission of the COFOG I level breakdown (divisions) is compulsory for the years 1995 onwards, whereas information on the COFOG II level (COFOG groups) at general government level is provided on a compulsory basis for the reference years 2001 onwards. The main reference year used in this publication is 2022 as the latest year available at EU level.
Data was extracted on 29 February 2024.
Provisional data
While a significant effort was undertaken to harmonise the recording of government measures to alleviate the impact of increasing energy prices, a full harmonisation of data for the reference year 2022 was not yet achieved.
Data for the EU and euro area aggregates (2022), Belgium (2022), Germany (2020-2022), Spain (2022), France (2021-2022) and Portugal (2022) is provisional.
Definition of general government and its subsectors
The data relate to the general government sector of the economy, as defined in ESA 2010, paragraph 2.111: 'The general government sector (S.13) consists of institutional units which are non-market producers whose output is intended for individual and collective consumption, and are financed by compulsory payments made by units belonging to other sectors, and institutional units principally engaged in the redistribution of national income and wealth’.
Classification of functional expenditure of government
The Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) classifies government expenditure into ten main categories (divisions known as the 'COFOG I level' breakdown): general public services; defence; public order and safety; economic affairs; environmental protection; housing and community affairs; health; recreation, culture and religion; education; social protection. These divisions are further broken down into 'groups' (COFOG II level).
For 'social protection', the groups are
- 'sickness and disability',
- 'old age',
- 'survivors',
- 'family and children',
- 'unemployment' ,
- 'housing',
- 'social exclusion n.e.c.',
- 'R&D social protection',
- 'social protection n.e.c.'
Further information is available in the Eurostat Manual on sources and methods for the compilation of COFOG Statistics.
Satellite accounts
Administrative expenditure data is additionally collected in so-called satellite accounts. In general, the amount of expenditure recorded in satellite accounts is expected to exceed the expenditure recorded under the respective COFOG division. More details on the comparability of COFOG data with satellite accounts data can be found in the COFOG manual.
Definition of general government total expenditure
Government total expenditure is defined in ESA 2010, paragraph 8.100 by using as reference a list of ESA 2010 categories. More detail is provided in the overview article on Government expenditure by function – COFOG.
Gross Domestic Product
Throughout this publication, nominal GDP, i.e. GDP at current prices is used.
Time of recording & symbols used
In the ESA 2010 system, recording is on an accrual basis, that is, when ‘economic value is created, transformed or extinguished, or when claims and obligations arise, are transformed or are cancelled.'
":" not available
"pp" percentage points
More data and information
For more country-specific notes, e.g. on missing data, please refer to the metadata published on Eurobase. The authors can be contacted at ESTAT-GFS@ec.europa.eu
Context
In the framework of the European System of National Accounts (ESA 2010), Eurostat collects data on general government expenditure by economic function according to the international Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) – see methodological note.
Direct access to
- Government expenditure by function - online publication
- Government expenditure by function – COFOG - overview article
- Government statistics (t_gov)
- Annual government finance statistics (t_gov_10a)
- Government statistics (gov)
- Government finance statistics (EDP and ESA2010) (gov_gfs10)
- Annual government finance statistics (gov_10a)
- Government revenue, expenditure and main aggregates (gov_10a_main)
- General government expenditure by function (COFOG) (gov_10a_exp)
- Main national accounts tax aggregates (gov_10a_tax_ag)
- Annual government finance statistics (gov_10a)
- Government finance statistics (EDP and ESA2010) (gov_gfs10)
- Government revenue, expenditure and main aggregates (ESMS metadata file — gov_10a_main_esms)
- General government expenditure by function (COFOG) (ESMS metadata file — gov_10a_exp_esms)
- Manual on sources and methods for the compilation of COFOG statistics - Classifications of the Functions of Government - 2019 edition
- Manual on government deficit and debt — implementation of ESA 2010 — 2022 edition