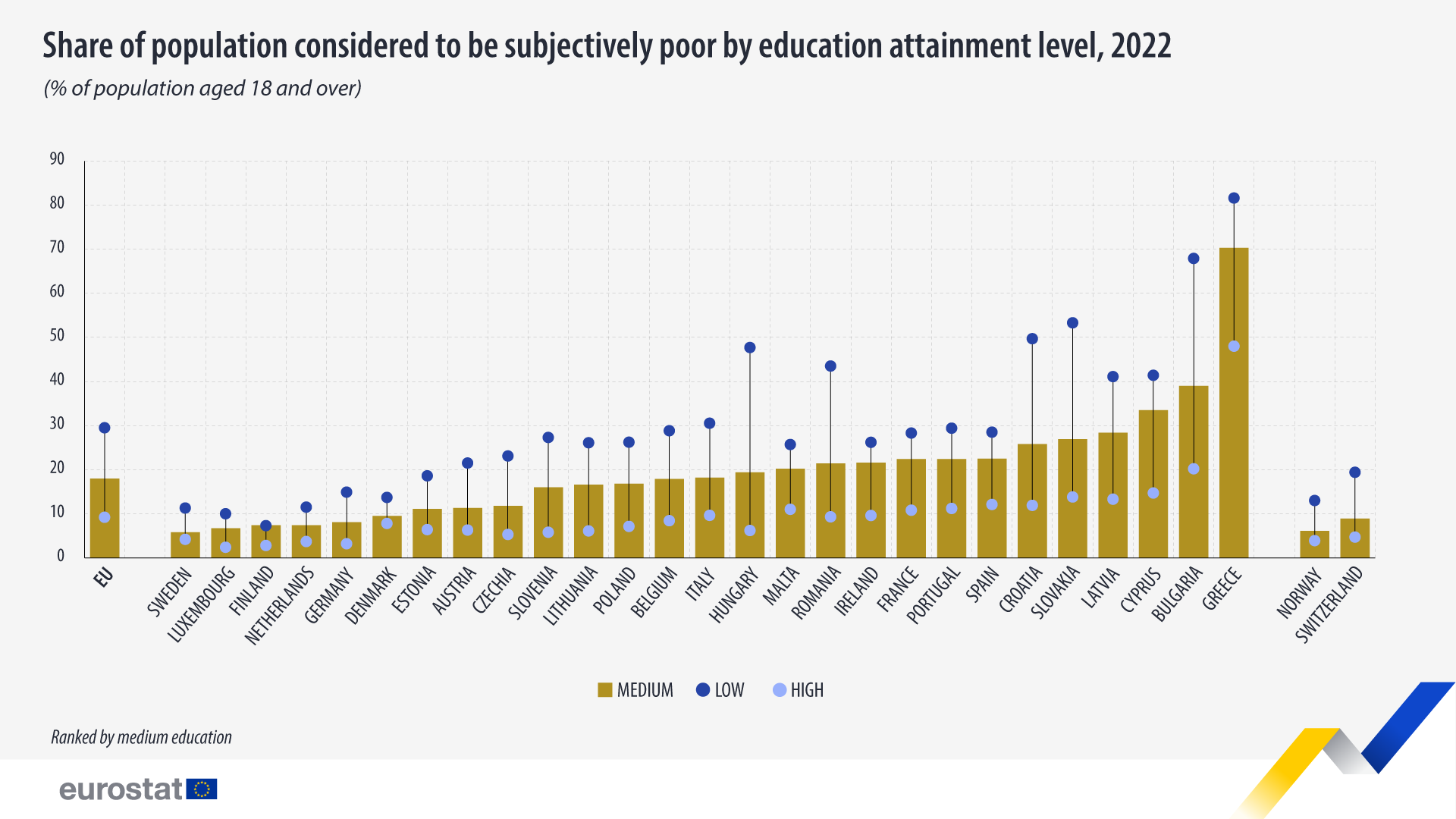
Subjective poverty highest among lower educated

In 2022, almost one third (29.5%) of the EU population with a low educational attainment level (International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED), levels 0-2) was considered poor. The rate was more than 3 times lower (9.2%) for people with high education (ISCED levels 5-8) while the share for people with a medium educational attainment level (ISCED levels 3 and 4) was 18.0%.
26 EU members reported higher rates of people with a low education level who are considered poor, compared with people with medium and high education levels. Finland was the exception, with a slightly higher rate among people with a medium education level.
Source dataset: ilc_sbjp02
Among the EU countries, Greece had the highest share of people with a low education level (four fifths; 81.6%) considered poor. This was followed by Bulgaria (67.9%) and Slovakia (53.3%). The lowest numbers were registered in Finland (7.3%), Luxembourg (10.0%) and Sweden (11.3%).
Most of the EU members reported significant differences between high and low-educated population groups. The difference was at least 20 percentage points (pp) in 12 countries. The most notable differences were in Bulgaria (47.7 pp), Hungary (41.5 pp) and Slovakia (39.5 pp) and the lowest in Finland (4.5 pp), Denmark (5.9 pp) and Sweden (7.1 pp).
For more information
- Statistics Explained article subjective poverty statistics
- Thematic section on Income and living conditions
- Database on Income and living conditions
Methodological notes
- Subjective poverty is an individual’s perception of his/her financial and material situation. It is a concept based on results from the EU’s statistics on income and living conditions (EU-SILC), a data collection which is conducted across EU members, as well as in most of the EFTA and candidate countries. The aim of this indicator is to assess the respondents’ perception of the difficulties experienced by the household in making ends meet. The assessment considers the households’ material wellbeing situation including income, expenditure, debt and wealth.
- International Standard Classification of Education ISCED levels 0-8:
- ISCED 0: Early childhood education (‘less than primary’ for educational attainment)
- ISCED 1: Primary education
- ISCED 2: Lower secondary education
- ISCED 3: Upper secondary education
- ISCED 4: Post-secondary non-tertiary education
- ISCED 5: Short-cycle tertiary education
- ISCED 6: Bachelor’s or equivalent level
- ISCED 7: Master’s or equivalent level
- ISCED 8: Doctoral or equivalent level
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.