Temporary employment: demographics and parenthood factors

In 2022, 24 million people worked under a temporary contract in the EU (12% of total employed people aged 15-64). Among them, one-fourth (6 million) were aged 15-29 and no longer in formal education (23% of total employed people aged 15-29 not participating in formal education).
There were significant variations in the share of employed people aged 15-29 not participating in formal education with temporary contracts in EU countries. The highest share of temporary workers in this category was recorded in Portugal (40 %), followed by Spain (39%) and Italy (38%). On the other end, the lowest shares were recorded in Lithuania and Latvia (both 3%), Romania (4%) and Estonia (5%).
Source dataset: LFS ad-hoc extraction
Impact of education level and parenthood
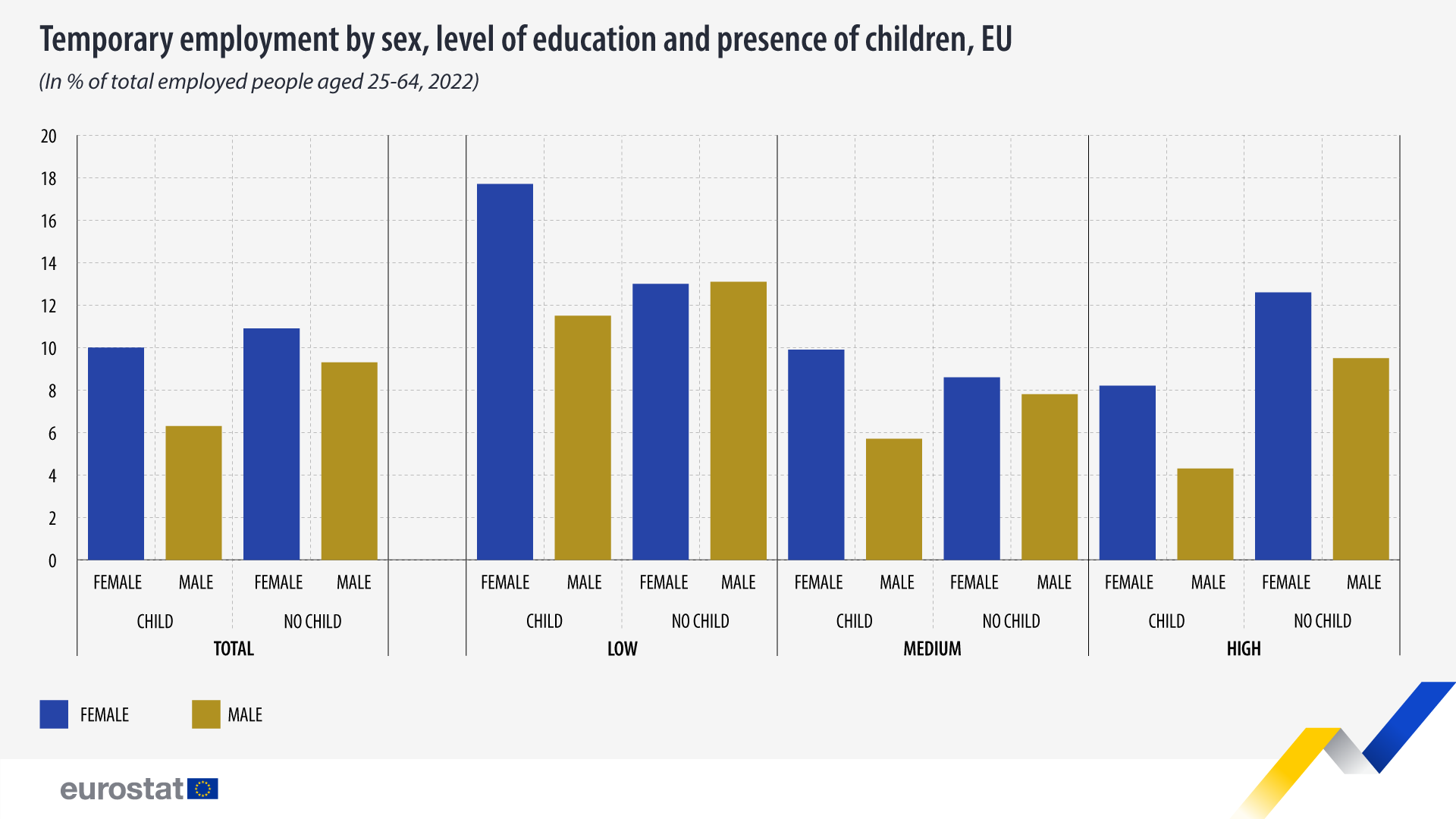
The shares of temporary workers among employed men and women aged 25-64 vary by education level and presence of children. The 25-64 age group is considered, to enable comparison across education levels.
The highest share of temporary workers in this group was found among women with a low level of education and children (18%). Three categories rank second: men and women with a low level of education and without children as well as women with a high level of education and without children (all 13%).
Source dataset: LFS ad-hoc extraction
In contrast, the lowest shares were recorded among men with a high level of education and children (4%) and men with a medium level of education and children (6%).
For more information
- Statistics Explained article on temporary employment
- Thematic section on employment and unemployment (LFS)
- Database on employment and unemployment (LFS)
- Statistics 4 Beginners on the labour market
Methodological notes
- Temporary employment: work under a fixed-term contract. A job may be considered temporary employment (and its holder a temporary employee) if both employer and employee agree that its end is decided by objective rules (usually written down in a work contract of limited life). These rules can be a specific date, the end of a task, or the return of another employee who has been temporarily replaced.
- Participation in education: participation in formal education and training (student or apprentice) in the last 4 weeks.
- Educational attainment levels are classified according to the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED): low level of education refers to ISCED levels 0-2 (less than primary, primary and lower secondary education), medium to ISCED levels 3 and 4 (upper secondary and post-secondary non-tertiary education) and high to ISCED levels 5-8 (tertiary education). The level of educational attainment means the highest level of education successfully completed.
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.