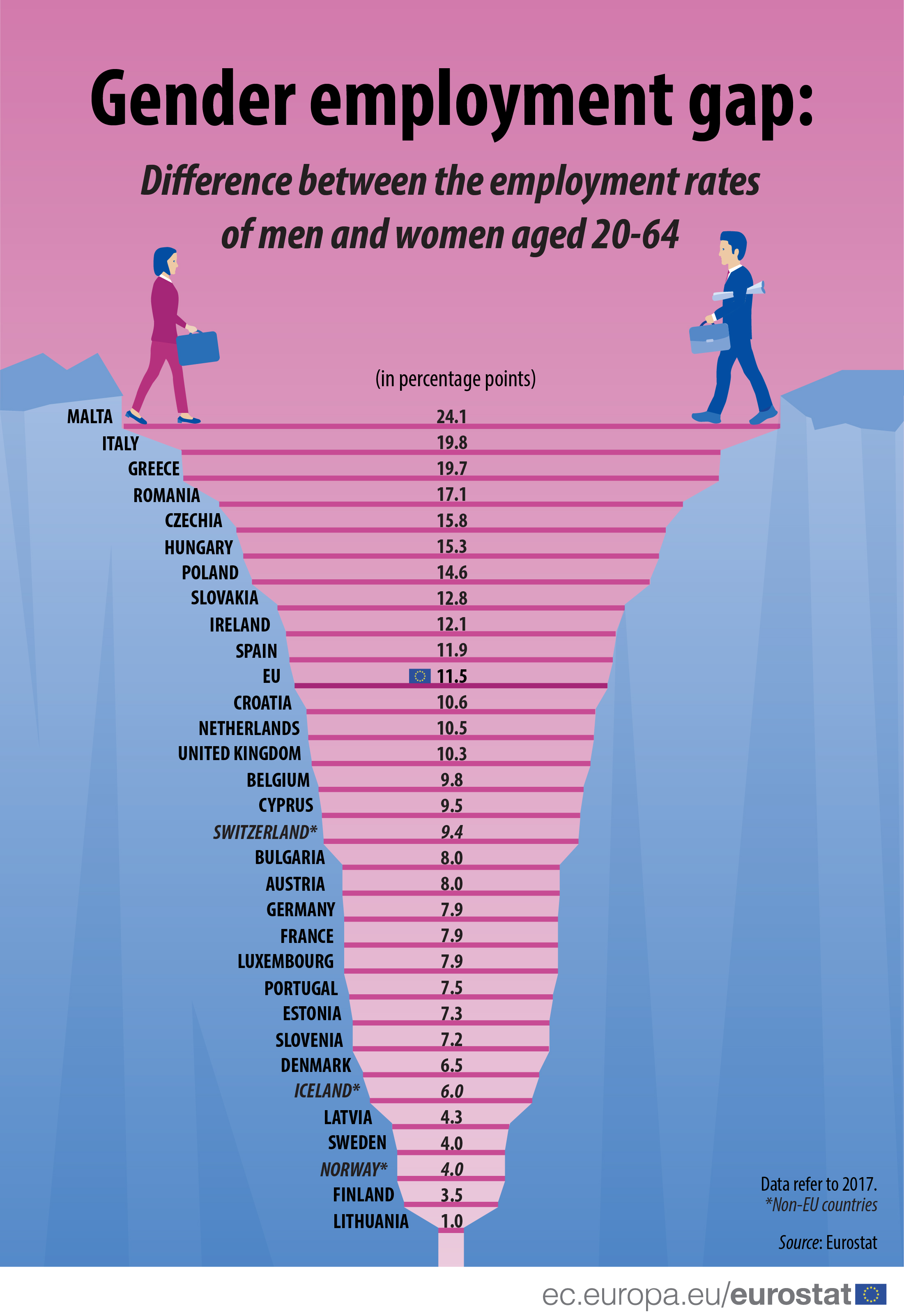
In 2017, the employment rate of women aged 20 – 64 (66.5%) was 11.5 percentage points (pp) lower than that of men aged 20 - 64 (78.0%) in the European Union (EU). In other words, the gender employment gap in the EU stood at 11.5 pp.
Among the EU Member States, the gender employment gap was lowest in Lithuania (1.0 pp), Finland (3.5 pp), Sweden (4.0 pp) and Latvia (4.3 pp).
At the opposite end of the scale, the largest employment gap between men and women was observed in Malta (24.1 pp), followed by Italy (19.8 pp) and Greece (19.7 pp).
The source dataset is accessible here.
Decreasing trend in majority of the EU Member States
Compared with five years ago, the gender employment gap decreased in the EU by 0.7 pp (from 12.2 pp in 2012 to 11.5 pp in 2017). A decrease occurred in 16 EU Member States.
Between 2012 and 2017, the largest decreases in the employment gap between men and women were recorded in Malta (-7.3 pp) and Luxembourg (-6.5 pp), followed by Slovakia (-2.7 pp) and Germany (-2.6 pp).
However, the gender employment gap rose over this period in 11 EU Member States. The highest increase was recorded in Hungary (+4.2 pp), followed by Ireland (+3.5 pp) and Bulgaria (+2.4 pp).
The gender employment gap remained stable in Slovenia (with a gap equal to 7.2 pp in both 2012 and 2017).
Additional gender based statistics are available in the Statistics Explained article “Gender statistics”.
To contact us: estat-user-support@ec.europa.eu