Gross available energy is the quantity of energy needed to meet the energy needs of a country or a region.
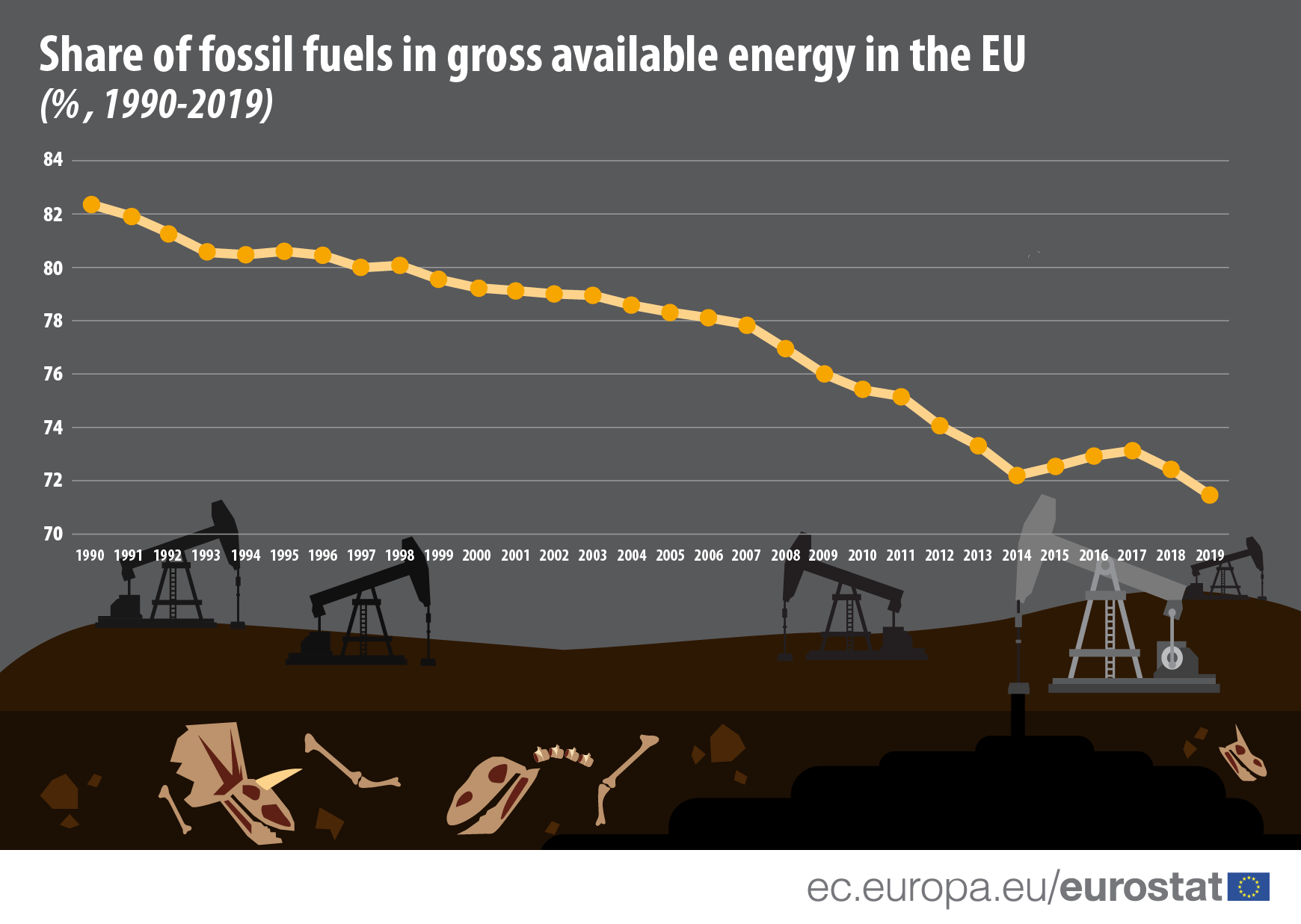
In 2019, fossil fuels made up 71% of the gross available energy in the European Union (EU) of 27 Member States. This percentage has decreased significantly over the last decades, due to the increase in renewable energy. Since 1990, the first year for which data are available, the percentage of fossil fuel used in the EU has decreased by 10.9 percentage points (pp).
Source dataset: nrg_ind_ffgae
In the EU, we still rely largely on fossil fuels for our overall national energy supply, illustrated by the ratio of fossil fuels in gross available energy. Total national energy supply includes energy transformation (such as electricity generation from fossil fuels), distribution losses fossil products used for non-energy purposes (for example lubricants), fossil fuels used for transport (fuel purchased within the EU, even if it was used elsewhere).
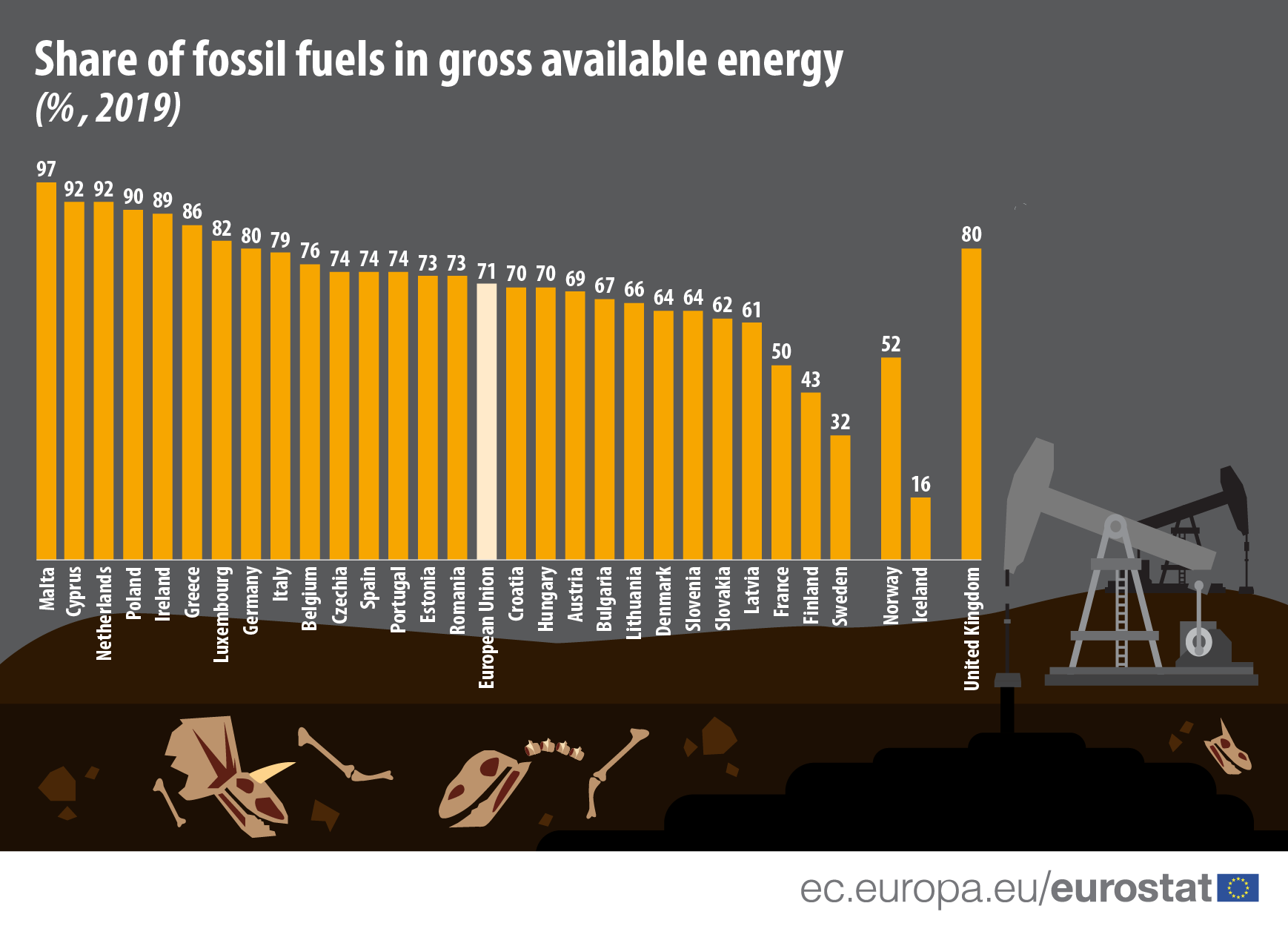
In 2019, Malta (97%) was the EU Member State with the highest share of fossil fuels in gross available energy followed by Cyprus and the Netherlands (both 92%), Poland (90%), Ireland (89%), Greece (86%) and Luxembourg (82%). Most of the other Member States had shares between 60% and 80%. Only Sweden (32%), Finland (43%) and France (50%) had shares below 60%.
Source dataset: nrg_ind_ffgae
Of the EU in the last 10 years, only Lithuania has increased its share of fossil fuels in gross available energy by 10 pp (from 56% in 2009 to 66% in 2019). The largest decrease by 19 pp was measured in Denmark (83% to 64%), closely followed by Estonia (86% to 73%) and Finland (56% to 43%; both by 13 pp).
Comparing 2019 to 2018, only two EU Member States, Latvia and Austria, increased their share of fossil fuels in gross available energy, each by 1 pp. Eight countries’ figures remained the same. Among the other countries, the largest decreases were in Estonia with 12 pp, Slovakia with 4 pp, followed by Belgium and Denmark, each with 3 pp.
Methodological note:
Fossil fuels include coal and coal products, natural gas, crude oil and petroleum products, peat and peat products, oil shale and oil sands, non-renewable municipal/industrial waste).
Gross available energy means the overall supply of energy for all activities on the territory of the country. This also includes energy transformation (including generating electricity from combustible fuels), distribution losses and use of fossil fuel products for non-energy purposes (e.g. in the chemical industry). It also includes fossil fuel used for transport, including fuel purchased within the country that is used elsewhere (e.g. international aviation, international maritime bunkers and, in the case of road transport “fuel tourism”).
To contact us, please visit our User Support page.
For press queries, please contact our Media Support.