An estimated 315 000 of the 3.1 million gigawatt-hour of gross electricity generated in 2016 in the European Union (EU) came from wind power. In other words, wind accounted for 10% of the total electrical energy produced in the EU in 2016. This is five times more than in 2005 (2%). As such, wind is the fourth source of electricity in the EU, after conventional thermal (49%), nuclear (26%) and hydro (12%) energy.
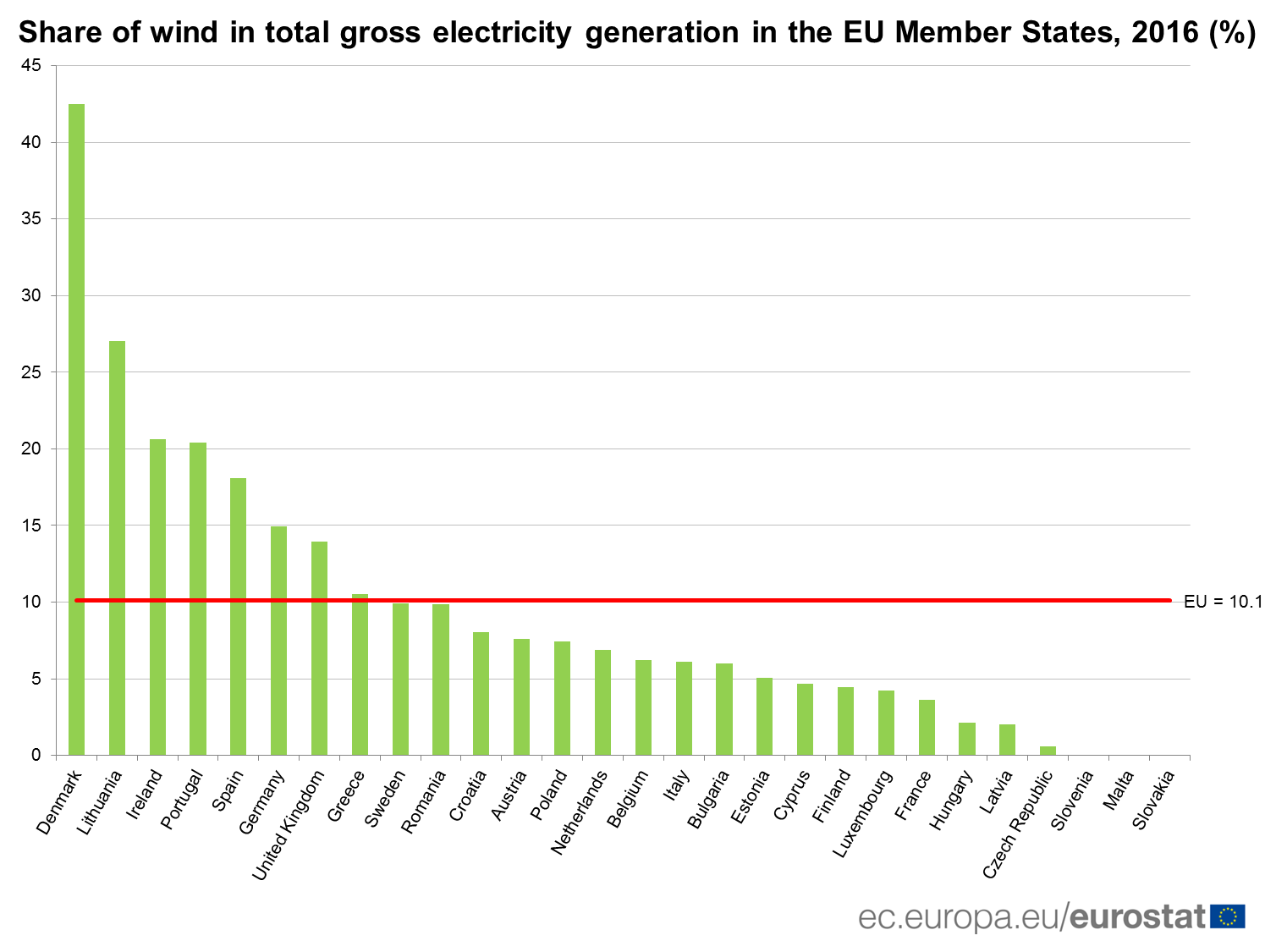
In the EU Member States, Denmark recorded by far the highest proportion of wind in total gross electricity generation with 43% in 2016. It was followed by Lithuania (27%), Ireland (21%), Portugal 20%), Spain (18%) and the United Kingdom (14%).
At the opposite end of the scale, the contribution of wind to the production of electricity was insignificant in Malta, Slovenia, Slovakia and the Czech Republic (all with a share below 1%) and very marginal in Latvia and Hungary (both 2%) as well as in France, Luxembourg and Finland (all around 4%).
Wind electricity generation grows fastest in Lithuania and Denmark
Compared with 2005, the contribution of wind to total gross electricity generation has increased in all the EU Member States that use wind as source of electricity. The highest rises were observed in Lithuania (from 0% to 27%, or + 27 percentage points – pp) and Denmark (+24 pp), ahead of Portugal (+17 pp), Ireland (+16 pp), the United Kingdom (+13 pp), Spain and Germany (both +11 pp).
This news item marks EU sustainable energy week, taking place from 19-25 June 2017.
For more information:
Eurostat website section dedicated to energy statistics.
Eurostat digital publication on energy.