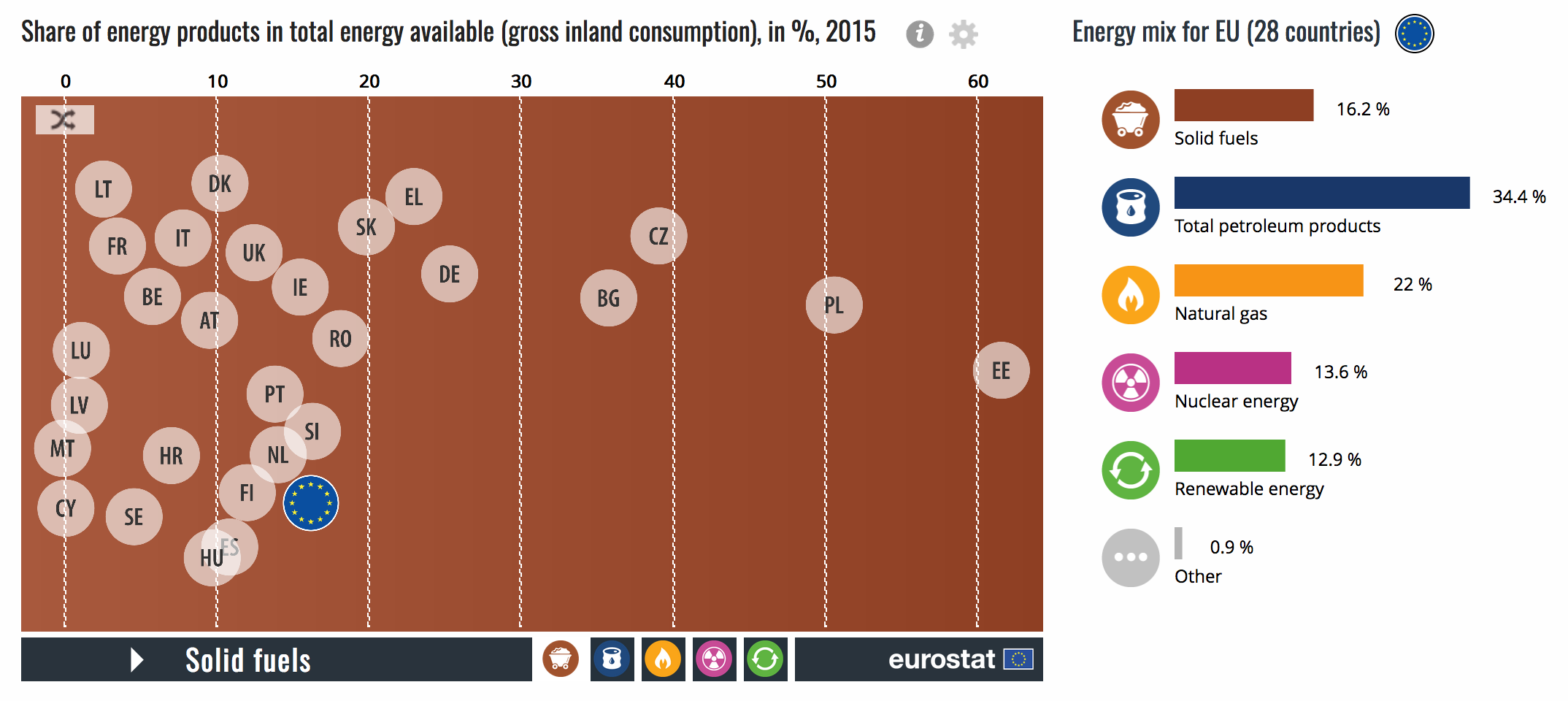
2.1 Where does our energy come from?
The energy available in the European Union comes from energy produced in the EU and from energy imported from third countries. In 2015, the EU produced around 46 % of its own energy, while 54 % was imported.
Imports and production form together the sources of energy available in the EU
In order to get a good overview of the total energy available in the EU, energy production should always be put in context with imports.
In 2015, the energy mix in the EU, meaning the range of energy sources available, was mainly made up by five different sources: Petroleum products (including crude oil) (34 %), natural gas (22 %), solid fuels (16 %), nuclear energy (14 %) and renewable energy (13 %).
The shares of the different energy sources in the the total energy available vary considerably between Member States. Petroleum products (including crude oil) (including crude oil) account for a significant share of total energy available in Cyprus (93 %), Malta (85 %) and Luxembourg (63 %), while natural gas makes up around a third or more in the Netherlands, Italy and the United Kingdom. Over half of the energy available in Estonia (62 %) and Poland (51 %) comes from solid fuels (mainly coal), while nuclear energy accounts for 45 % in France and 32 % in Sweden. Renewable energy makes up 42 % in Sweden and 35 % in Latvia.