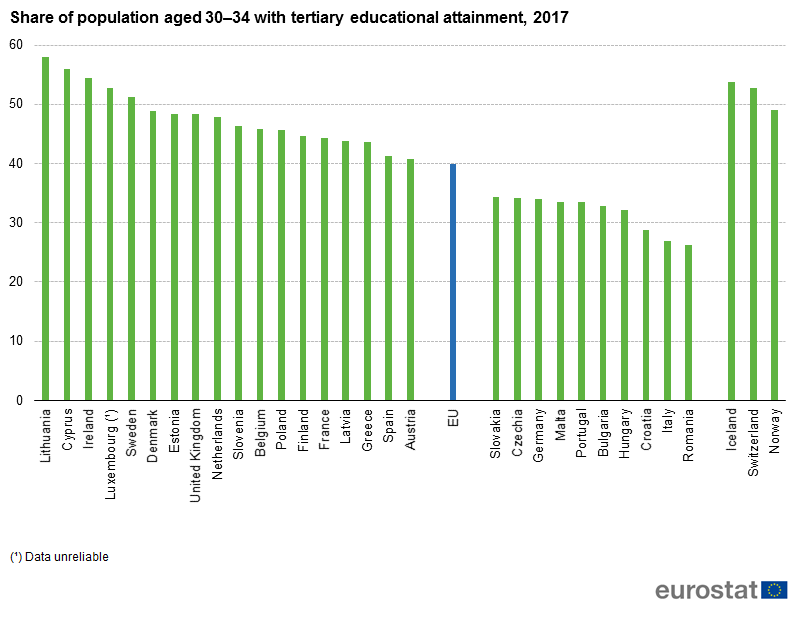
In the European Union (EU), 40% of people aged 30-34 had a tertiary level of education in 2017.
In 2017, whilst 45% of women in the EU aged 30-34 had completed tertiary education, the proportion was 35% for men. The share of men with tertiary education has increased over the last ten years but at a slower pace than for women, leading to a broader gender gap.
Highest share of tertiary education attainment in Lithuania
In five EU Member States, at least half of those aged 30-34 had a tertiary level of education, with the highest shares in Lithuania (58%), Cyprus (56%) and Ireland (55%). In contrast, the lowest proportions of those having a completed tertiary education were recorded in Romania (26%), Italy (27%) and Croatia (29%).
The source dataset is accessible here.
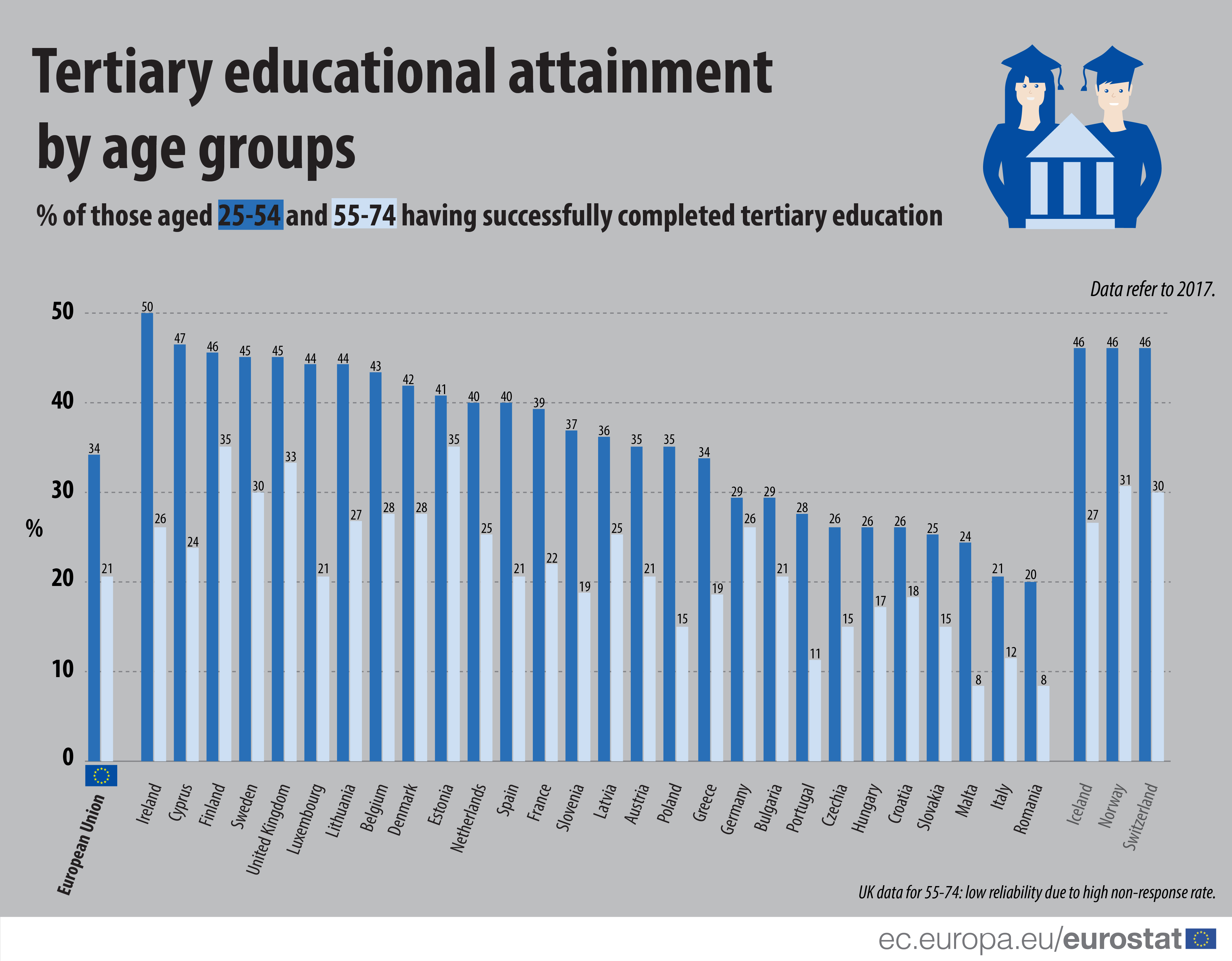
In 2017, 1 in 3 people aged 25–54 in the EU had tertiary educational level (34%), compared with 1 in 5 of those aged 55–74 (21%). The patterns of educational attainment levels of the population have changed significantly: on average, younger people attain higher levels of education than older ones.
The source dataset is accessible here.
This article is published on the International Day of Education (24 January) to acknowledge education’s contribution to peace and development.
More information on educational attainment in the EU can be found in a Statistics Explained article on Educational attainment statistics.
To contact us: estat-user-support@ec.europa.eu