Archive:Housing statistics
- Data from June 2009, most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
Access to good quality and affordable accommodation is a fundamental need and right. Ensuring this need is still a significant challenge in a number of European Union (EU) countries. Housing deprivation is one of the examples of poverty and social exclusion in society. In order to monitor the social inclusion process, new housing indicators have been adopted by the Indicators Sub-Group of the Social Protection Committee in 2009, that is, an indicator of overcrowding and two indicators measuring housing affordability.
Main statistical findings
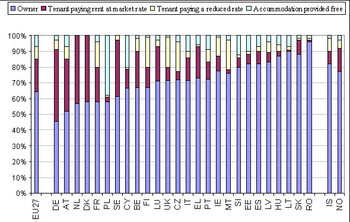
Tenure status
In 2007, 65% of households in the EU-27 owned their dwelling, 21% paid rent at market rate, 8% paid rent at a reduced rate and 7% of households occupied free accommodation. More than half of households owned their dwelling in all Member States with the highest proportions in Romania (96%), Lithuania and Slovakia (both 89%) and Hungary (87%). The lowest percentages of households owing their dwelling were observed in Germany (46%), Austria (52%), the Netherlands (56%) and Denmark, France and Poland (all 58%).
Type of dwelling
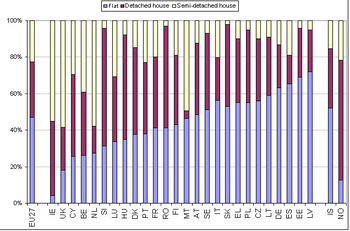
In the EU-27 in 2007, 46% of households lived in flats, 30% in detached houses and 22% in semi-detached houses. The share of households living in flats was highest in Latvia (72%), Estonia (69%), Spain (66%) and Germany (62%). The percentage of households living in detached houses was largest in Slovenia (65%), Hungary (57%), Romania (56%) and Denmark (48%), while for semi-detached houses, the share was highest in the United Kingdom (59%) and Ireland and the Netherlands (both 55%).
Housing quality
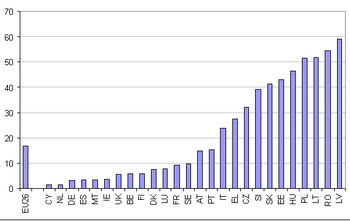
The overcrowding rate describes the percentage of people living in households which are considered as overcrowded. It depends on the household size as well as the age and the family situation of the household members. In 2007 17% of the EU-27 population lived in overcrowded households. Among Members States, the highest percentages of people living in overcrowded households were registered in Latvia (59%), Romania (54%), Lithuania and Poland (both 52%). By contrast, Cyprus and the Netherlands (both 2%) recorded the lowest percentage.
Housing affordability
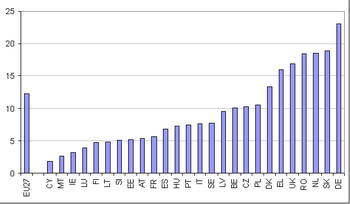
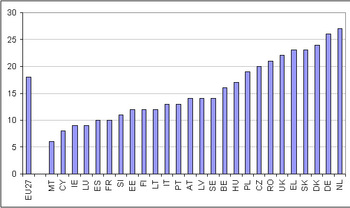
In order to measure housing affordability, two indicators have been recently adopted, namely, the 'Share of population whose housing cost burden exceeds 40% of the disposable income' and the median of the distribution of the 'Share of housing cost in the disposable income' indicator, which is the proportion of disposable income spent on housing by half of the population.
In the EU-27 in 2007, 12% of the European citizens spent on housing 40% or more of their disposable income. This EU average masks significant differences between Member States. At one extreme, countries with the lowest share of the population whose housing cost exceeds 40% of the disposable income were Cyprus (2%), Malta and Ireland (both 3%) as well as Luxembourg (4%). At the other extreme, the share was around 18-19% in Romania, the Netherlands and Slovakia. Finally, the highest value was reached in Germany with 23%.
The median of the housing costs burden distribution - which is measured with the share of housing costs in disposable income - reached 18% in 2007. The median of the distribution, however, varied largely across Europe and ranged from 6% up to 27%. The lowest values were recorded in Malta, Cyprus, Ireland and Luxembourg with 50% of individuals living in households for which the housing costs represented less than 10% of the total disposable income. On the contrary, 50% of the population in Romania, the United Kingdom, Greece, Slovakia, Denmark, Germany and the Netherlands lived in households for which the housing costs represented more than 20% of the total disposable income.
Data sources and availability
The data presented in this section are extracted from micro-data from EU statistics on income and living conditions (EU-SILC) and refers to 2007, when EU-SILC covered all 27 EU Member States plus Norway and Iceland. There is no data yet for Bulgaria.
Context
At the Laeken European Council in December 2001, Heads of State and Government endorsed a first set of common statistical indicators of social exclusion and poverty that are subject to a continuing process of refinement by the Indicators Sub-group (ISG) of the Social Protection Committee (SPC). These indicators are an essential element in the Open Method of Coordination (OMC) to monitor the progress of Member States in the fight against poverty and social exclusion.
The 2001 SPC report on indicators to monitor the social inclusion process recommended 'improving comparable information and reporting on decency of housing, housing costs and homelessness'. The 2006 SPC report on indicators reserved a slot in the social inclusion portfolio for the housing dimension.
In order to provide underlying data for indicators, the EU-SILC (Community Statistics on Income and Living Conditions) instrument was implemented. The EU-SILC, organised under a Framework Regulation (1177/2003) of the European Parliament and the Council, is now the reference source for statistics on income and living conditions and for common indicators for social inclusion in particular.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
Main tables
- Income and living conditions
- Non-monetary poverty and social exclusion
- Share of households with/without financial burden due to housing costs
- Share of households that cannot afford a car
- Rooms per person
- Share of households living in overcrowded houses
- Proportion of population living in households considering that they suffer from noise
- Share of households owning their accommodation
- Share of households living in a house
- Non-monetary poverty and social exclusion
Database
- Income and living conditions
- Non-monetary poverty and social exclusion
- Households and living conditions
- Housing
- Non-monetary poverty and social exclusion
Dedicated section
- Household Budget Surveys
- Income, Social Inclusion and Living Conditions
- Indicators of the social inclusion strand
Other information
- Regulation (EC) 1177/2003 of European Parliament and Council of 16/6/2003 and published in the Official Journal of 3/7/2003
- Regulation (EC) 1553/2005 of European Parliament and Council of 7/9/2005 and published in the Official Journal of 30/9/2005
- Regulation (EC) 1791/2006 of European Parliament and Council of 20/10/2006 and published in the Official Journal of 20/12/2006