Foreign language learning increases among EU students

The majority of pupils in primary and secondary education in the EU study at least one foreign language: in 2021, this consisted of 86.3% of pupils in primary education, 98.5% of students in lower secondary and 91.0% in upper secondary education.
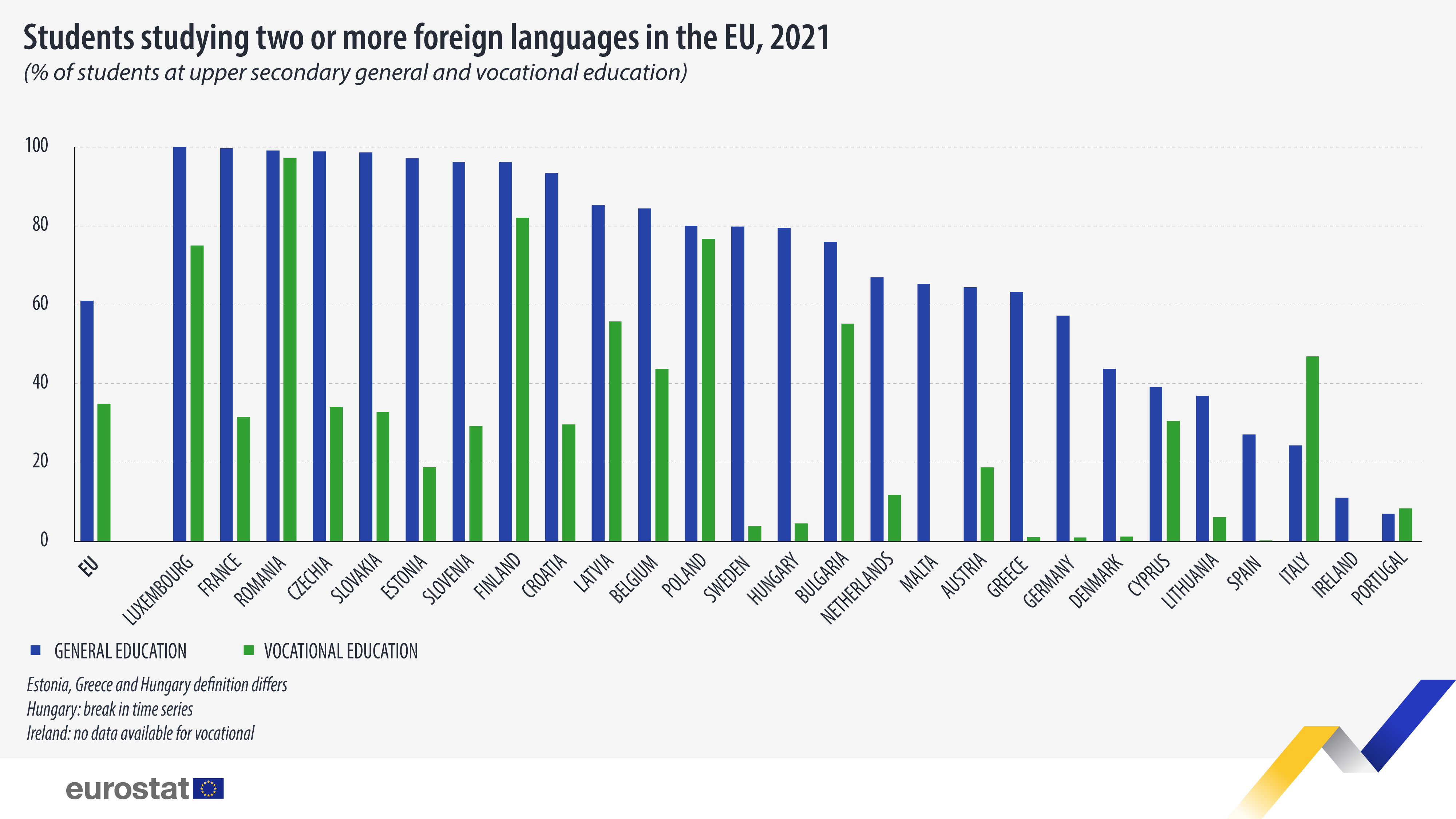
In 2021, 61.0% of students in upper secondary general education (ISCED level 34) studied two or more foreign languages as compulsory subjects or as compulsory curriculum options, +2.6 percentage points (pp) more than in 2013 (58.4%). In upper secondary vocational education (ISCED level 35), this share was 34.9%, +0.8 pp than in 2013 (34.1%).
In Luxembourg and France, all students in upper secondary general education studied two or more foreign languages. Czechia, Romania and Slovakia also registered a large share of students studying two or more languages (all 99%). These EU countries were followed closely by Estonia (97%), Slovenia and Finland (both 96%).
Source dataset: educ_uoe_lang02
When it comes to upper secondary vocational education, Romania was the only EU country where almost all students (97%) studied two or more foreign languages in 2021. Finland (82%) followed, with Poland (77%) and Luxembourg (75%) coming next.
English leads in both general and vocational upper secondary education
In 2021, English was the most studied foreign language at the upper secondary general and vocational education level in the EU, with 96.8% and 78.6% of students learning it, respectively.
In terms of general education, Spanish ranked second (26.8%), followed by French (22.3%), German (21.8%) and Italian (3.2%). In addition, Russian was the non-EU language most commonly learned in the EU (2.8%), especially in Estonia (66%) and Latvia (59%), followed by Lithuania (28%) and Bulgaria (25%).
In vocational education, the German language came in second (17.9%), followed by French (16.4%), Spanish (7.0%) and Russian (2.2%). In this case, Russian was mostly learned in Latvia (42%), Bulgaria (30%) and Cyprus (15%).
Source dataset: educ_uoe_lang01
This article is being published on the occasion of the European Day of Languages. This event, celebrated every year since 2001 on the 26th of September, aims to promote Europe's linguistic and cultural diversity and to encourage lifelong language learning for better cultural understanding.
For more information
- Statistics Explained set of articles on Education and training in the EU - facts and figures
- Thematic section on education and training
- Database on education and training
- Metadata on education and training. Detailed footnotes to data are available in the Annexes section.
Methodological notes
- Only foreign languages studied as compulsory subjects or as compulsory curriculum options are included. The study of languages when the subject is offered in addition to the minimum curriculum is excluded.
- The data refer to all modern spoken living languages that are taught as foreign languages. The learning of classical languages such as Ancient Greek and Latin is not included though they are the source of many modern languages and therefore can facilitate language learning in general.
- Belgium: the official state languages are Dutch, French and German. Luxembourg: French and German are both official national languages and are taught as foreign languages. Finland: depending on their mother tongue, students have to choose between Finnish and Swedish. Both are considered foreign languages for the purpose of education statistics, but only when they are studied as a second language.
- Relevant updated information on the joint UIS (UNESCO Institute of Statistics)/OECD/Eurostat (UOE) data collection and Quality reports compiled at the country level can be found in the Education administrative metadata file. Quality reports include an annex on Provisions for language learning.
- Ireland: 2021 data not available for vocational upper secondary education.
- Estonia: definition differs at ISCED 35 (under-coverage). Excludes some ISCED11_354 programme language learning.
- Greece: change in legislation. Second foreign language made compulsory in upper secondary from the school year 2020/21
- Hungary: break in time-series.
- Italian: definition differs for general upper secondary education.
- Spanish, German, English, French and Russian: definition differs for vocational upper secondary education.
If you have any queries, please visit our contact us page.