Road freight transport statistics - cabotage
Data extracted in October 2023.
Planned article update: November 2024.
Highlights
Cabotage accounted for 4.5 % of national road freight transport for hire and reward in the EU in 2022, a decrease of 0.4 percentage points compared with 2021.
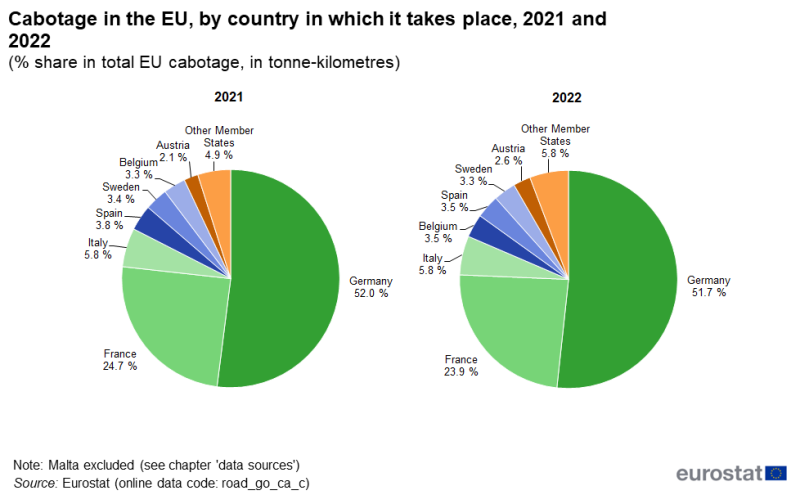
More than half of the cabotage in the EU in 2022 was performed in Germany (51.7 %).
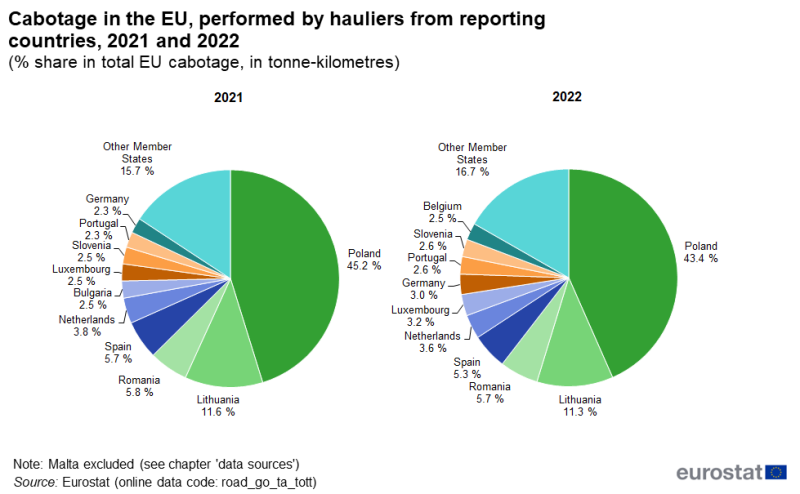
Polish hauliers performed 43.4 % of all EU cabotage in 2022.
Road freight cabotage transport, EU, 2018-2022
This article presents the road freight cabotage transport in the European Union (EU) up to and including 2022. The trends in cabotage are presented both from the perspective of the hauliers performing cabotage in other countries, and from the perspective of the countries where this cabotage takes place. Cabotage is defined as freight transport carried out in one country by hauliers registered in another country. As national transport markets within the EU are not yet fully liberalised, the level of cabotage (together with cross-trade, i.e. transport between two countries that are carried out by hauliers from a third country), may be seen as a sign of market integration.
This article, together with the articles 'Road freight transport statistics', 'Road freight transport by vehicle characteristics', 'Road freight transport by type of goods' and 'Road freight transport by journey characteristics' present a complete overview of road freight transport in Europe.
Full article
Road freight cabotage transport decreased in 2022
From the perspective of a reporting country and its hauliers, cabotage is considered as international transport as it takes place on the territory of another country. From the perspective of the country in which the transport takes place, it could be considered as national transport for hire and reward since goods are transported by foreign trucks from one location to another within the country.
As road cabotage transport represents only a small part of road freight transport for hire and reward in the national territory and as data are collected on the basis of sample surveys, the accuracy of data on cabotage is generally lower than the accuracy of other transport variables. The percentage standard error of cabotage transport varies significantly from country to country, both in tonne-kilometres (tkm) and in tonnes.
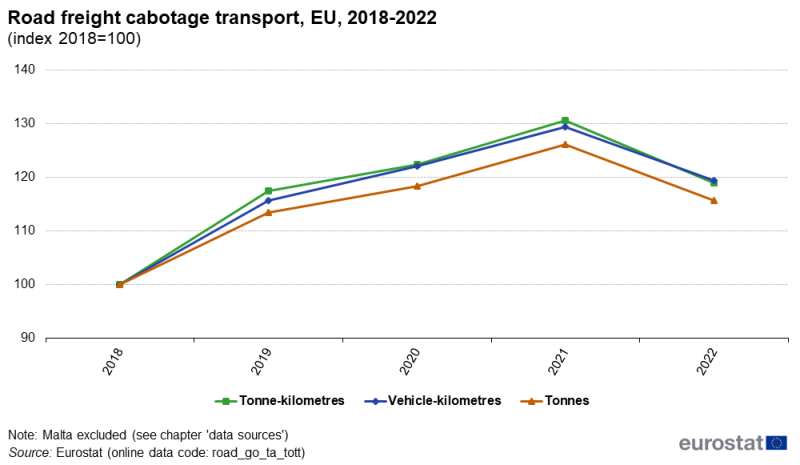
Figure 1 shows the road freight cabotage transport in the EU in terms of million tonne-kilometres, thousand tonnes and million vehicle-kilometres (vkm), as indices based on 2018=100. Since 2018, cabotage transport has grown continuously and with similar trends for the three units, except for a decline for all three indices in 2022.
Cabotage transport measured in million tonne-kilometres and million vehicle-kilometres reached in 2022 an index value of 19 % above the 2018 figures, while the transport measured in thousand tonnes increased by 16 %.
(2018=100)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ta_tott)
Cabotage accounted for 4.5 % of national road freight tonne-kilometres for hire and reward in the EU in 2022
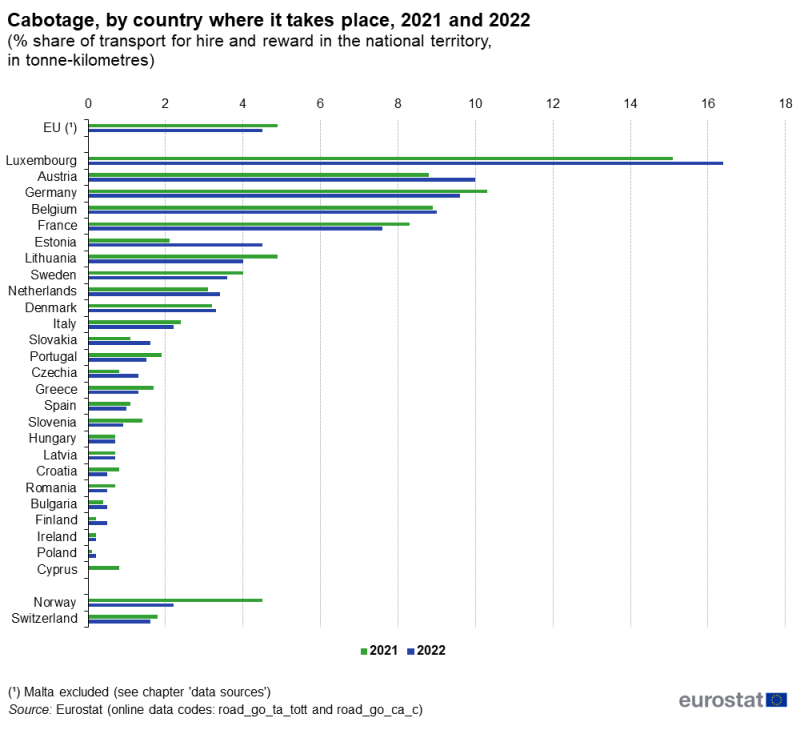
The ‘cabotage penetration rate for hire and reward transport’ is the main indicator used to assess the extent of cabotage within the national transport markets in the EU. It is defined as the share of cabotage transport in the total national transport of a country (sum of national transport for hire and reward and cabotage transport). Thus, it does not consider any transport that companies do on their own account, using their own trucks and lorries.
The cabotage penetration rate in the EU decreased from 4.9 % in 2021 to 4.5 % in 2022 (see Figure 2).
In 2022, the highest cabotage penetration rate among the EU Member States was recorded in Luxembourg with 16.4 %, far ahead of Austria (10.0 %), Germany (9.6 %) and Belgium (9.0 %). Together with France (7.6 %), these were the only Member States having a cabotage penetration of more than 7 % in the period 2021-2022. The cabotage penetration grew considerably in Estonia: in 2022, at 4.5 %, it was 2.4 percentage points (pp) higher than in 2021.
In stark contrast, Lithuania recorded a decrease in the cabotage penetration rate in its national transport market, from 4.9 % in 2021 to 4.0 % in 2022, this being the highest decrease recorded in 2022. Poland, which is one of the major road transport providers in the EU, recorded a cabotage penetration rate of 0.1 % in 2021 and 0.2 % in 2022. Ireland, Finland, Bulgaria, Romania, Croatia, Latvia and Hungary also recorded cabotage penetration of less than 1 % in their national transport markets in the period 2021-2022.
(% share of transport for hire and reward in the national territory, in tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ta_tott), (road_go_ca_c)
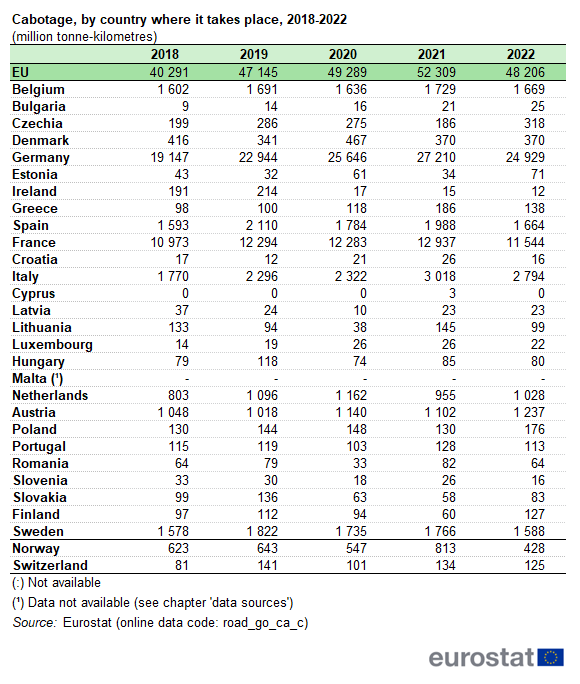
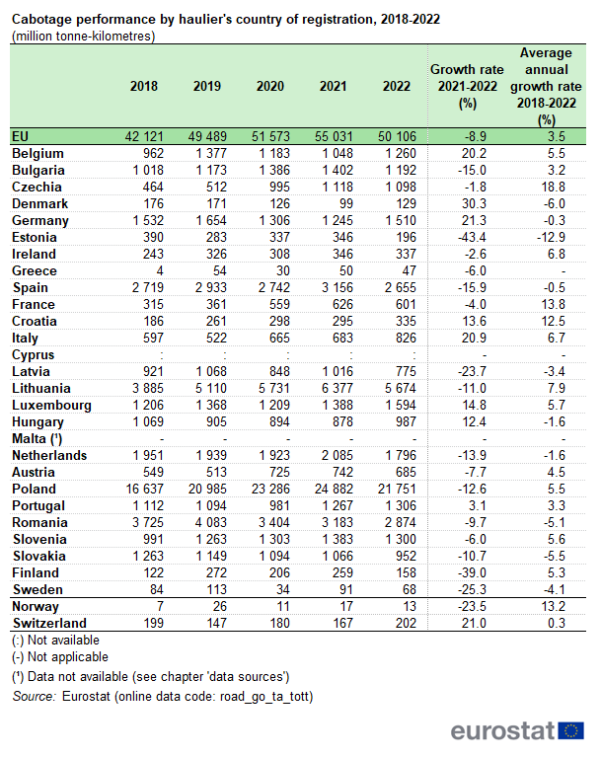
In terms of transport performance measured in tonne-kilometres, cabotage in the EU has been increasing almost continuously since 2018, with only a small fall in 2022, reaching 52.3 billion tonne-kilometres in 2021 from 40.3 billion tonne-kilometres in 2018, and decreasing to 48.2 billion tonne-kilometres in 2022 (see Table 1). Germany remained the country with the highest level of cabotage performance in its national transport market, rising from almost 19.1 billion tonne-kilometres in 2018 to 27.2 billion in 2021, followed by a decrease to 24.9 billion in 2022. France, with the second highest level of cabotage performance, grew from 11.0 billion tonne-kilometres in 2018 to 12.9 billion in 2021, dropping to 11.5 billion tonne-kilometres in 2022. The level of cabotage performance in other Member States’ territories was much smaller, with Italy growing from 1.8 billion tonne-kilometres in 2018 to 3.0 billion in 2021, decreasing to 2.8 billion tonne-kilometres in 2022; while Belgium and Spain recorded both 1.6 billion tonne-kilometres in 2018 and 1.7 billion tonne-kilometres in 2022, their highest peak being in 2021 (1.7 billion tonne-kilometres and 2.0 billion tonne-kilometres, respectively). For all other Member States, the cabotage performance was below 2 billion tonne-kilometres for the period 2018-2022.
(million tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ca_c)
Cabotage is not always performed by hauliers from neighbouring countries
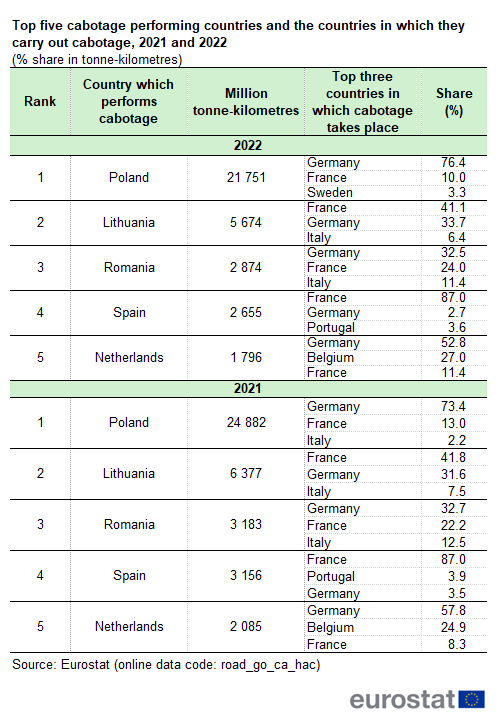
Table 2 shows in which countries the top five cabotage performers, i.e., Poland, Lithuania, Romania, Spain and the Netherlands, mainly carry out cabotage transport (in tonne-kilometres). Until a few years ago, most cabotage transport was carried out in neighbouring countries. This has changed in recent years, in particular for hauliers from Poland, Lithuania and Romania.
Hauliers from Poland continued to carry out by far the largest share of cabotage transport in the EU. In 2021, Poland accounted for 45.2 % of freight cabotage for hire and reward in the EU, falling to 43.4 % in 2022 (see Figure 3). About three quarters of the cabotage performed by Polish hauliers in the other EU Member States takes place in Germany: in 2021, Germany accounted for 73.4 % of Polish cabotage performance, increasing to 76.4 % in 2022. Polish hauliers also carried out some cabotage in France, Sweden and Italy, although to a lesser degree. Cabotage in France represented 13.0 % of total Polish cabotage in 2021 and 10.0 % in 2022, with Italy being the third largest with 2.2 % in 2021, while Sweden took over this place in 2022 with 3.3 %.
Lithuania was the second largest provider of cabotage transport, with 11.6 % of the total EU cabotage in 2021 and 11.3 % in 2022. Lithuania performed most of its cabotage in countries with which it had no land borders. Just over 40 % was performed in France (41.8 % in 2021, 41.1 % in 2022), with somewhat less being performed in Germany (31.6 % and 33.7 % respectively), and with Italy being in the third place (7.5 % and 6.4 %, respectively).
Romania was the third largest provider of cabotage transport, with 5.8 % in 2021 and 5.7 % in 2022. The same two transport markets, Germany and France, were also the main countries for cabotage by Romanian hauliers. In both 2021 and 2022, Germany had the highest share at 32.7 % and 32.5 %, respectively, with France following at 22.2 % and 24.0 % in these two years.
Spain was the fourth largest provider of cabotage transport, with 5.7 % in 2021 and 5.3 % in 2022, while the Netherlands had lower shares, with 3.8 % in 2021 and 3.6 % in 2022. In contrast, for hauliers from Spain and the Netherlands, their neighbouring countries were the main markets for cabotage. For Spanish hauliers, France accounted for 87 % of all cabotage in both 2021 and 2022. For Dutch hauliers, more than half (57.8 % in 2021; 52.8 % in 2022) of their total cabotage was performed in Germany, and around a quarter in Belgium (24.9 % in 2021; 27.0 % in 2022).
(% share in tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ca_hac)
(% share in total EU cabotage, in tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ta_tott)
Half of the EU cabotage transport is carried out in Germany
In 2021, 52.0 % of the cabotage transport in the EU (in tonne-kilometres) was performed in the German national territory, falling to 51.7 % in 2022. Approximately one quarter of the cabotage transport in the EU was carried out in France, with 24.7 % in 2021, decreasing to 23.9 % in 2022. (see Figure 4).
(% share in total EU cabotage, in tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ca_c)
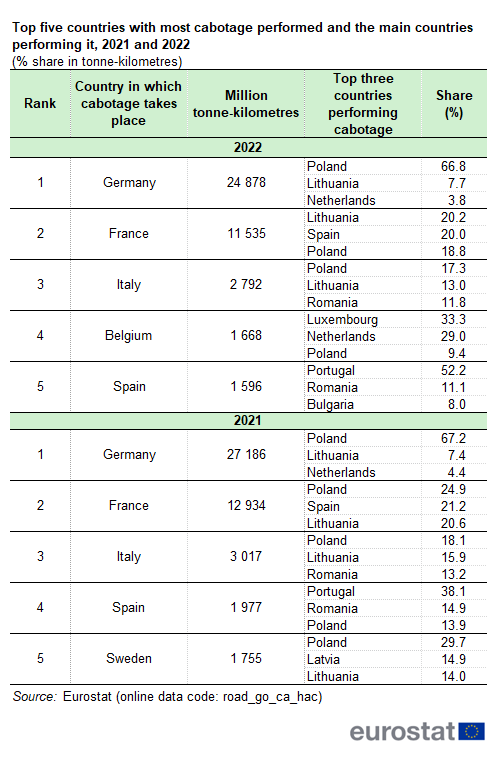
Table 3 shows the five countries where the highest cabotage in the EU was performed (in tonne-kilometres) and the nationality of the three hauliers that performed the largest parts of this cabotage.
As mentioned, the highest number of cabotage tonne-kilometres was performed in Germany in both 2021 and 2022. Polish hauliers performed two thirds of all cabotage in Germany in both years, with 67.2 % and 66.8 %, respectively. Lithuania was the second largest cabotage provider, but with far lower shares: 7.4 % in 2021 and 7.7 % in 2022.
France recorded the second highest volume of cabotage, measured in tonne-kilometres. The three largest cabotage performers in France – Poland, Spain and Lithuania – switched positions from 2021 to 2022: in 2021, Poland accounted for the highest share (24.9 %), ahead of Spain (21.2 %) and Lithuania (20.6 %); while in 2022, Lithuania performed the highest share (20.2 %), ahead of Spain (20.0 %) and Poland (18.8 %).
For cabotage in Italy, Polish hauliers retained the highest share in 2021 and 2022, with 18.1 % and 17.3 %, respectively. Lithuania had the second highest share, with 15.9 % in 2021 and 13.0 % in 2022, followed by Romania with 13.2 % and 11.8 %, respectively.
Spain fell from the fourth place in the top five countries with the most cabotage performed in 2021 to the fifth place in 2022, while Belgium rose to the fourth place in 2022 being outside of the top five in 2021. In Spain, Portugal accounted for more than one third of the cabotage in 2021 (38.1 %), while it performed half of all cabotage in 2022 (52.2 %). In Belgium, Luxembourg performed one third of the cabotage in 2022 (33.3 %) closely followed by the Netherlands (29.0 %). In Sweden, in 2021, Polish hauliers accounted for 29.7 % of all cabotage.
(% share in tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ca_hac)
Highest relative growth in cabotage by Czech, French and Croatian hauliers since 2018
From 2018 to 2022, cabotage performance grew in 14 of the 25 Member States for which data are available. The highest average annual growth rates in cabotage performed were observed for Czechia (+18.8 %), France (+13.8 %) and Croatia (+12.5 %), ahead of Lithuania (+7.9 %) and Ireland (+6.8 %).
In contrast, the highest average falls in the period 2018-2022 were recorded for Estonia (-12.9 %), Denmark (-6.0 %), Slovakia (-5.5 %), Romania (-5.1 %) and Sweden (-4.1 %) (see Table 4).
For six Member States, in 2022, the cabotage activity reached its lowest level since 2018: Estonia, Spain Latvia, the Netherlands, Romania and Slovakia. The highest increases in cabotage transport between 2018 and 2022 were recorded by Poland (+5.1 billion tonne-kilometres), Lithuania (+1.8 billion tonne-kilometres) and Czechia (+0.6 billion tonne-kilometres). At the other end of the scale, the highest decreases were recorded by Romania, (-0.9 billion tonne-kilometres) and Slovakia (-0.3 billion tonne-kilometres).
(million tonne-kilometres)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ta_tott)
The trend in volume (in tonnes) of goods transported in cabotage was similar to the trends in tonne-kilometres. Polish hauliers carried by far the largest volume of goods in cabotage in 2022, followed by Dutch hauliers (see Figure 5). The highest relative rise between 2021 and 2022 was registered by Danish hauliers (+55 %) and Italian hauliers (+42 %), although Denmark transported low volumes in absolute terms. At the other end of the scale, Greece (-93 %) and Finland (-71 %) recorded the highest decreases from 2021 to 2022.
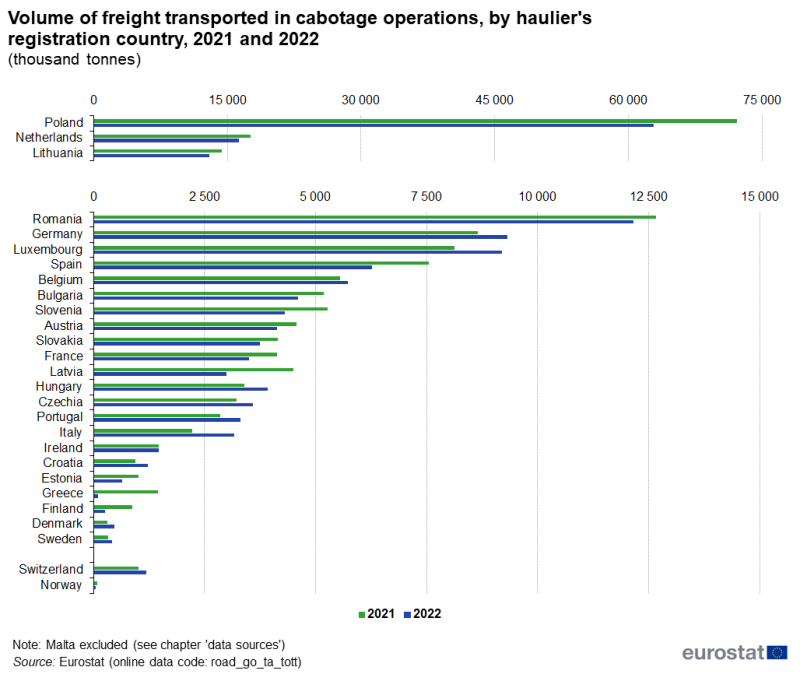
(thousand tonnes)
Source: Eurostat (road_go_ta_tott)
Source data for tables and graphs
Context
Data presented in this publication were collected in the framework of Regulation (EU) No 70/2012 on statistical returns in respect of the carriage of goods by road (recast). These data are based on sample surveys carried out in the reporting countries, i.e. the EU Member States, Norway, Switzerland and Montenegro, and record the freight transport undertaken by road vehicles registered in these countries.
Reporting countries use their own national surveys for the collection of data based on returns from road hauliers. The results are microdata referring to vehicles and their linked journeys, providing detailed information on goods transported. At the European level, common aggregation procedures that might diverge from national practices have been used. Differences might therefore occur between the figures in this publication and national values. For the distinction between national and international transport, journey related information is used at European level, which might cause differences in corresponding values from those countries that are using goods-related information for these statistics.
Country specific notes
Croatia: While Croatia had no obligation prior to accession in 2013, it started reporting data for the reference year 2008.
Malta: Regulation (EU) No 70/2012 does not apply to Malta, as long as the number of Maltese-registered goods road transport vehicles licensed to engage in international transport does not exceed 400 vehicles.
Finland: National and international surveys have been harmonised and follow a common methodology from Q1 2011 onwards, leading to a break in time series in 2011.
Sweden: A break in series was produced in 2014 following a change in methodology. On the basis of a specific survey, Sweden corrected the European road freight survey results for trucks participating in the sample which were not in use over the surveyed period.
Methodological notes
EU totals calculated in this publication refer to road freight transport reported by the EU Member States, excluding Malta which is currently exempt from reporting road freight statistics.
Total transport
Total transport includes national transport, international transport of goods loaded in the reporting countries, international transport of goods unloaded in the reporting countries, cross-trade and cabotage
Cabotage
Definition and history: Cabotage is declared by Member States for hauliers registered in their country that performed transport on the national territory of another country. From the point of view of the reporting country, it is considered as international transport, from the point of view of the movements of goods, it could be considered as national transport.
With the aim of increasing transport efficiency and reducing the number of empty journeys, cabotage transport was gradually introduced in 1990 through authorisation quotas (quantitative restrictions) and further liberalised in 1998 in the 15 EU Member States at that time (hauliers are allowed up to three cabotage operations within 7 days following an incoming international carriage). The cabotage regime was extended to the EFTA states (except Switzerland) following the creation of the EEA (European Economic Area). Cabotage between the EU (referring to the prior composition of 15 Member States) and the Member States that joined the EU in 2004 was liberalised in May 2009 and in January 2012 for Bulgaria and Romania. Cabotage for Croatian hauliers is allowed in some EU Member States since July 2015 and was then extended to all Member States.
Cabotage penetration rate: Share of cabotage transport in total national transport, where total national transport is the sum of national transport (for hire and reward) and cabotage transport (in that country).
Data reliability: As road cabotage transport represents only a small percentage of total road transport and as data are collected on the basis of sample surveys, the importance of cabotage could sometimes either be over- or underestimated. Percentage standard error (PSE, 95% confidence interval) of cabotage transport is typically 5-40% for tonnes and 5-30% for tonne-kilometres. Furthermore, variability in cabotage transport performance often occurs due to ‘haulage contracts’ that have a limited validity. A haulier might thus perform cabotage transport operations in one year and lose this market to a transport operator registered in a different country the next year.
Data availability: The figures presented in this publication have been extracted from Eurostat’s free dissemination database and reflect the state of data availability in October 2023.
In this article:
- 1 billion = 1 000 000 000
- "- "not applicable
- ": "not available
Direct access to
- Transport, see:
- Road transport (t_road)
- Transport, see:
- Road transport (road)
- Road freight transport measurement (road_go)
- Key figures on European transport — 2022 edition - Statistical book
- Eurostat regional yearbook — 2022 edition - Statistical book
- Energy, transport and environment statistics — 2020 edition - Statistical book
- Road freight transport measurement (ESMS metadata file)
- Glossary for transport statistics — 5th edition — 2019 — Manuals and guidelines
- Methodologies used in road freight transport surveys in Member States, EFTA and candidate countries — 2021 edition — Manuals and guidelines
- Road freight transport methodology — Revised edition, August 2017 — Manuals and guidelines
- Regulation (EC) No 70/2012 on statistical returns in respect of the carriage of goods by road (recast)
- Regulation (EC) No 1304/2007 of 7 November 2007 amending Directive 95/64, Regulation (EC) No 1172/98, Regulations (EC) No 91/2003 and (EC) No 1365/2006 with respect to the establishment of NST 2007 as the unique classification for transported goods in certain transport modes
- A wider European legislative framework for international road freight transport is presented by Regulation (EC) No 1072/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 on common rules for access to the international road haulage market
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 202/2010 amending Regulation (EC) No 6/2003 concerning the dissemination of statistics on the carriage of goods by road