Surgical operations and procedures statistics
Data extracted in July 2024.
Planned article update: September 2025.
Highlights
There were over 1.10 million caesarean sections performed in the EU in 2022.
Large positive rates of change reported in recent years by most EU countries for keyhole surgery used to perform hysterectomies, repairs of inguinal hernias and appendectomies.
In nearly all EU countries, there has been a fall in recent years in the use of in-patient procedures for cataract surgery.
Cataract surgery, 2022
This article presents an overview of European Union (EU) statistics related to surgical operations and procedures. It provides information for a selection of the most common surgical operations and procedures in addition to details on the fastest growing and fastest declining operations and procedures over the last 10 years. These operations and procedures are classified according to the International Classification of Diseases – clinical modification (ICD-9-CM).
This article is one of a set of statistical articles concerning health status in the EU which forms part of the online publication on Health in the European Union - facts and figures.
Full article
Number of surgical operations and procedures
The 2 most common surgical operations and procedures performed in EU hospitals (for which data are collected) were cataract surgery and caesarean sections
Tables 1 and 2 indicate how frequently a selection of the most common surgical operations and procedures were conducted in 2022. In both tables, the data are presented relative to the size of the population (per 100 000 inhabitants). For several of these operations and procedures, such as cholecystectomies (the surgical removal of the gallbladder), additional information is given on the frequency with which these are carried out laparoscopically; a minimally invasive surgical technique used to diagnose and treat conditions that involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a camera and specialised instruments to perform procedures. This approach typically results in less pain, reduced recovery time, and minimal scarring compared with open surgery. It is also known as keyhole surgery..

(per 100 000 inhabitants)
Source: Eurostat (hlth_co_proc3)
Cataract surgery (ICD-9-CM codes 13.1 to 13.8), the extraction of the lens from an eye, was conducted 4.73 million times in 2022 across the EU countries (Malta and the Netherlands, 2021 data; Greece, no recent data available), making this the most common of the surgical operations and procedures presented in this article. In 16 of the EU countries, cataract surgery was performed over 1 000 times per 100 000 inhabitants in 2022 (2021 data for the Netherlands; see Figure 1 for details of coverage), peaking at 1 493 times per 100 000 inhabitants in France. By contrast, cataract surgery was performed less often than 500 times per 100 000 inhabitants in Romania.
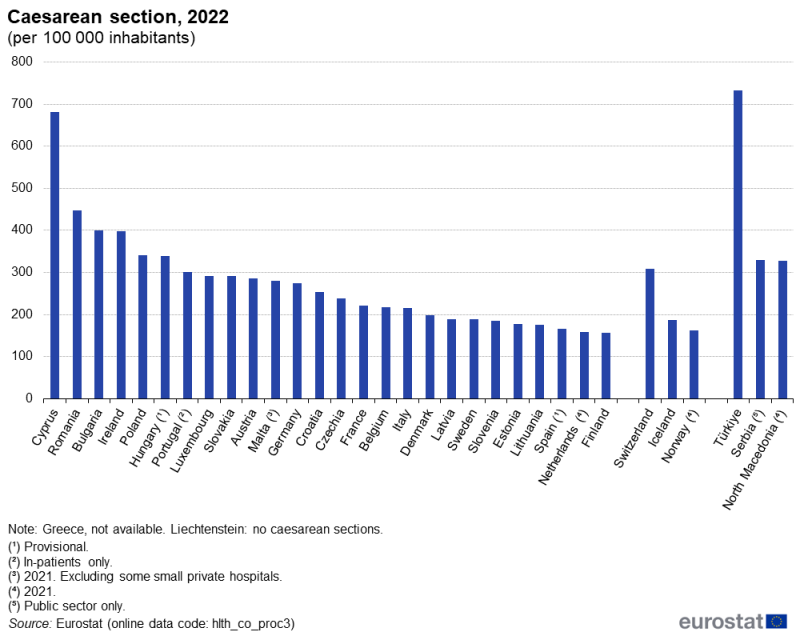
At least 1.10 million caesarean sections performed in the EU
Another common procedure was a caesarean section (ICD-9-CM codes 74.0 to 74.2, 74.4 and 74.99); the delivery of 1 or more babies through an incision in a mother’s abdomen and uterus. In 2022, this procedure was performed at least 1.10 million times in the EU (Malta and the Netherlands, 2021 data; Portugal, in-patients only; Greece, no recent data available). A total of 230 200 caesarean sections were performed in Germany, while between 125 400 and 150 700 caesarean sections were performed in France, Italy and Poland.
In most of the EU countries, between 176 and 401 caesarean sections were performed per 100 000 inhabitants in 2022 (see Figure 2). This procedure was more frequent in Cyprus and Romania, with 681.6 and 446.9 caesarean sections performed per 100 000 inhabitants, respectively. It was less frequent in Spain (166.0), the Netherlands (157.9; 2021 data) and Finland (157.3).
Transluminal coronary angioplasties concern the opening up of blocked coronary arteries (ICD-9-CM codes 36.01, 36.02 and 36.05). In 2022, transluminal coronary angioplasties were most common, relative to population size, in Croatia, Germany and Bulgaria where they were performed on average 500.1, 379.3 and 378.4 times per 100 000 inhabitants, respectively. They were conducted between 156 and 342 times per 100 000 inhabitants in most of the remaining EU countries for which data are available, with Poland, Romania, Spain, Luxembourg and Portugal below this range.
Hip replacements (ICD-9-CM codes 81.51 to 81.53) were performed 326.2 times per 100 000 inhabitants in Germany in 2022 and between 282 and 302 times per 100 000 inhabitants in Austria, Denmark and Belgium; these were the highest frequencies among the EU countries for which data are available (see Table 1). Fewer than 100 hip replacements were performed per 100 000 inhabitants in Romania and Malta (2021 data).
Repairs of inguinal hernias involve covering the hernia defect with mesh from within the abdomen in order to patch it (ICD-9-CM codes 53.0 and 53.1). Repairs of inguinal hernia were typically undertaken between 142 and 231 times per 100 000 inhabitants in 2022, with Austria reporting a higher frequency (273.2 per 100 000 inhabitants), while Ireland and Romania reported lower frequencies (both below 116 per 100 000 inhabitants). A majority of these repairs were undertaken laparoscopically in Cyprus (with a peak of 99%), Germany, Denmark, Belgium, Austria, Czechia and the Netherlands (2021 data). This share was below 50% in the remaining EU countries for which data are available; it was below 10% in 3 EU countries: Portugal, Sweden and the lowest in Italy (at 6%).

(per 100 000 inhabitants)
Source: Eurostat (hlth_co_proc3)
In general, the frequency of cholecystectomies (ICD-9-CM codes 51.22 and 51.23) varied less between the EU countries than did most other procedures presented in Tables 1 and 2. The frequency of cholecystectomies in 2022 was highest in Cyprus and Lithuania, at 261.3 and 257.9 procedures per 100 000 inhabitants, respectively. It was lowest in Bulgaria (103.6 per 100 000 inhabitants) and Malta (39.2 per 100 000 inhabitants; 2021 data). The share of cholecystectomies that were performed laparoscopically varied little: the vast majority of cholecystectomies were performed laparoscopically, their share in 2022 ranging from 79% in Bulgaria to 96% in the Netherlands (2021 data).
The frequency of knee replacements (ICD-9-CM code 81.54) varied more between the EU countries than did hip replacements. Furthermore, with the exceptions of Cyprus and Malta (2021 data), total knee replacements were less common than hip replacements in 2022. More than 200 knee replacements per 100 000 inhabitants were performed in Germany, Denmark, Austria and Finland, compared with fewer than 50 per 100 000 inhabitants in Bulgaria and Romania.
The frequency of appendectomies, the removal of an (infected) appendix, (ICD-9-CM codes 47.0 and 47.1) varied less between the EU countries than did most other procedures presented in Tables 1 and 2. There was more variation in the frequency of laparoscopic appendectomies, which in 2022 was highest in Belgium, at 128.8 per 100 000 inhabitants. It was lowest in Italy, Poland, Romania and Bulgaria, where there were fewer than 50 laparoscopic appendectomies per 100 000 inhabitants. The share of appendectomies that were performed laparoscopically varied greatly, from 15% of the total number of appendectomies in Bulgaria to more than 90% in France, Belgium, the Netherlands (2021 data) and Denmark.
Another common procedure performed within the EU was hysterectomies, which is the removal of all or part of the uterus, (ICD-9-CM codes 68.3 to 68.7 and 68.9). Hysterectomies were most frequently performed in 2022 in Czechia (146.1 per 100 000 inhabitants). In all of the other EU countries the frequency ranged from 45.7 in the Netherlands (2021 data) to 127.4 in Lithuania. More than two thirds of all hysterectomies in Finland, Denmark and Estonia were performed laparoscopically. The share of hysterectomies performed laparoscopically was below one fifth in 5 EU countries, with the lowest share in Romania (7%).
The frequency of partial excisions of mammary glands (ICD-9-CM codes 85.20 to 85.23) varied quite considerably between the EU countries in 2022. In Belgium, this procedure was performed 141.4 times per 100 000 inhabitants, while in Poland it was performed 14.2 times per 100 000 inhabitants.
Increasing and decreasing surgical operations and procedures
Large increases reported for hysterectomies performed using keyhole surgery
A selection of surgical operations and procedures which have generally become more frequent during recent years is presented in Table 3; 3 of these concern laparoscopic techniques. Data are usually presented for 2012 and 2022: alternative years are presented for some countries – see Table 3 for the precise coverage.
[[Image:Selected high growth procedures performed in hospitals, 2012 and 2022 (per 100 000 inhabitants)_Health2024.png|thumb|centre|800px|Table 3: Selected high growth procedures performed in hospitals, 2012 and 2022
(per 100 000 inhabitants)
Source: Eurostat (hlth_co_proc3)|alt=A table showing the number per hundred thousand inhabitants of selected high growth procedures performed in hospitals. Data are shown for 2012 and 2022 for EU, EFTA and enlargement countries.]
Relative to population size, the frequency of laparoscopic hysterectomies increased in 21 of the 22 EU countries for which data are available, the exception being Slovenia which reported a decrease of 6.5 surgeries per 100 000 inhabitants between 2012 and 2022. There were 6 EU countries which reported the frequency of this procedure more than doubling during the period under consideration. Excluding Cyprus, which has a break in series, the largest relative increase was in Hungary where the frequency was approximately 6 times as high in 2022 as it had been in 2012, up from 3.0 to 18.4 procedures per 100 000 inhabitants.
Between 2012 and 2022, the frequency of laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernia increased in 21 of the 22 EU countries for which data are available. Finland was the only country to report a decrease, from 22.9 to 18.5 surgeries per 100 000 inhabitants. In 11 EU countries, the frequency of this procedure more than doubled during the period under consideration. Aside from countries where there is a break in series, the largest relative increases were observed in Portugal and Slovenia, the frequency being 9.8 times as high in 2022 as in 2012 in the former and 8.1 times as high in 2022 as in 2012 in the latter.
A total of 24 out of 25 EU countries for which data are available in Table 3 reported an increase in the frequency of cataract surgeries, the most common procedure among those shown in the table. The exception was Malta (2012–21), where the frequency declined by 31 %. Among countries without a break in series, the largest relative increase was in Portugal, where the frequency was 1.7 times as high in 2022 as in 2012.
Among the 22 EU countries for which data are available for 2012 and 2022, all but 1 reported an increase in laparoscopic appendectomies; the exception was Germany, where the frequency relative to the population size fell by 14 %. The frequency of this procedure more than doubled in 10 EU countries. Aside from countries where there is a break in series, the largest relative increase was observed in Malta (2012–21), where the frequency was 8.1 times as high in the most recent year as in the earlier year.
The frequency of total knee replacements (ICD-9-CM code 81.54) increased between 2012 and 2022 (see Table 3 for the precise coverage) in 19 of the 24 EU countries for which data are available. The largest increase was in Poland, where the frequency in 2022 was 3.6 times as high as in 2012. The decrease in frequency observed in 5 EU countries was most substantial in Malta, down 47.4% between 2012 and 2021.
Tonsillectomies were performed with a decreasing frequency
A selection of surgical operations and procedures which have become less common in recent years is presented in Table 4. For 2 of these procedures, hysterectomies and appendectomies, the overall frequency has declined, despite the relatively fast growth in their performance using laparoscopic techniques. Data are generally presented for 2012 and 2022; alternative years are presented for some EU countries – see Table 4 for the precise coverage.

(per 100 000 inhabitants)
Source: Eurostat (hlth_co_proc3)
The removal of tonsils, a tonsillectomy (ICD-9-CM codes 28.2 to 28.4), remains a relatively common procedure despite a decline in its frequency. Among 24 EU countries for which data are available, the frequency of tonsillectomies fell in 22 countries between 2012 and 2022; the only increases were reported in Denmark and Cyprus (2013–22), both of which reported a break in series. The sharpest decline in the frequency of tonsillectomies was recorded in Malta (2012–21), down 73.9%.
For bypass anastomosis for heart revascularisation (ICD-9-CM code 36.1), which is a bypass operation that concerns 1 or more coronary arteries, 21 of the 24 EU countries for which data are available reported a decline in the frequency between 2012 and 2022. The frequency of carrying out bypass anastomosis for heart revascularisation increased in Cyprus, Ireland and Slovakia; note there is a break in series for Cyprus and Ireland. The frequency decreased by more than 50% in Malta (2012–21), Luxembourg and Denmark, with Denmark reporting the greatest decrease (down 60.8%); note there is a break in series.
A total of 25 EU countries have data available for both years for the frequency of hysterectomies. Cyprus (2013–22), Denmark, Ireland, Poland and Slovenia were the only EU countries to report an increase in the frequency of this procedure between 2012 and 2022, although there is a break in series in Cyprus, Denmark and Ireland. The frequency fell by more than 40% in Malta (2012–21), Latvia and the Netherlands; note there is a break in series for Latvia and the Netherlands.
Among the 26 EU countries for which data are available, 17 recorded a lower frequency of appendectomies in 2022 than in 2012. The frequency of this operation was down by 58.2% in Romania and 44.1% in Bulgaria during the period under consideration. Aside from countries with a break in series, the largest increases in the frequency of this procedure were observed in Croatia (up 9.1%) and Malta (up 8.6%; 2012–21).
Among 25 EU countries for which data are available, 17 reported decreases in the frequency of caesarean sections between 2012 and 2022. Aside from Cyprus (where there is a break in series), Croatia and Bulgaria recorded the largest increases, up 39.7% and 26.8%, respectively. There were 3 EU countries where the frequency of carrying out a caesarean section fell by more than a quarter, Italy (down 34.7%), Spain (down 31.9%; note that there is a break in series) and Lithuania (down 29.2%).
In-patient procedures: cataract surgery
Widespread fall in the use of in-patient procedures for cataract surgery
As already noted, 1 of the most common procedures conducted in the EU is cataract surgery. Several decades ago, this procedure required admission as an in-patient. Figure 3 shows that this is no longer the case in many of the EU countries (no data available for Greece). In 2022, less than 10.0% of procedures for cataract surgery were carried out as in-patient procedures in 20 of the EU countries. The lowest shares – less than 1.0% – were recorded in Portugal, Spain, Denmark, Slovenia, Cyprus and the Netherlands (2021 data). There were 2 EU countries where at least half of the procedures for cataract surgery in 2022 were performed on in-patients: Romania (53.0%) and Bulgaria (50.0%).

(%)
Source: Eurostat (hlth_co_proc3)
Between 2012 and 2022, the share of procedures for cataract surgery carried out on in-patients fell in nearly every EU country for which data are available. The exceptions were Finland and Estonia where low shares had already been recorded in 2012; while the shares increased between 2012 and 2022, they remained lower than in a majority of the other EU countries. In 18 EU countries, the share of these procedures carried out on in-patients fell by more than half. Aside from Cyprus (where there is a break in series), the largest relative decrease was in Luxembourg, where the share of cataract surgery carried out on in-patients fell from 36.9% in 2012 to 1.4% in 2022.
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
Key concepts
Surgical procedures are all types of medical interventions involving an incision with instruments mostly performed in an operating theatre, which normally involve anaesthesia and/or respiratory assistance. Surgical procedures can be performed as in-patient cases, day cases or out-patient cases.
Only the main procedure performed on a patient whether during a hospital stay, day case or out-patient treatment should normally be reported.
An in-patient is a patient who is formally admitted (or ‘hospitalised’) to an institution for treatment and/or care and stays for a minimum of 1 night or more than 24 hours in the hospital or other institution providing in-patient care. An in-patient or day care patient is discharged from hospital when formally released after a procedure or course of treatment (episode of care). A discharge may occur because of the finalisation of treatment, signing out against medical advice, transfer to another healthcare institution, or because of death.
Healthcare resources and activities
Statistics on healthcare resources and healthcare activities (such as information on surgical operations and procedures) are documented in the article Health in the European Union – facts and figures, which provides information on the scope of the data, its legal basis, the methodology employed, as well as related concepts and definitions.
For surgical operations and procedures, the International Classification of Diseases – clinical modification (ICD-9-CM) is used.
- Cataract surgery (13.1-13.8)
- Caesarean section (74.0-74.2; 74.4, 74.99)
- Transluminal coronary angioplasty (36.01, 36.02, 36.05)
- Hip replacement (81.51-81.53)
- Repair of inguinal hernia (53.0, 53.1)
- of which: laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernia (17.1, 17.2)
- Cholecystectomy (51.22, 51.23)
- of which: laparoscopic cholecystectomy (51.23)
- Total knee replacement (81.54)
- Appendectomy (7.0, 47.1)
- of which: laparoscopic appendectomy (47.01, 47.1)
- Hysterectomy (68.3-68.7; 68.9)
- of which: laparoscopic hysterectomy (68.31, 68.41, 68.51, 68.61, 68.71)
- Partial excision of mammary gland (85.20-85.23)
- Tonsillectomy (28.2-28.4)
- Bypass anastomosis for heart revascularisation (36.1)
For country specific notes, please refer to the annexes at the end of the national metadata reports accessible from links at the beginning of the European metadata report. In particular, note that
- data for Cyprus generally only concern public hospitals and exclude outpatients; however, coverage is complete for caesarean sections
- data for Malta exclude some small private hospitals
- data for Serbia only concern public hospitals.
The Healthcare non-expenditure statistics manual provides an overview of the classifications, both for mandatory variables and variables provided on a voluntary basis.
Symbols
Tables in this article use the following notation
| Value in italics | estimate or provisional data |
| Value is : | not available |
Context
For any particular type of surgical operation or procedure, the extent to which this is performed is influenced by a number of factors, including the size of the population and the prevalence or incidence of the underlying disease or injury among the population. Other factors include differences in medical practices between countries and the availability of financial, technical and human resources.
Direct access to
Online publications
Health status – selected diseases and related health problems
Healthcare activities
- Consultations
- Hospital discharges and length of stay
- Medicine use
- Cancer screening statistics
- Unmet needs for health care
Methodology
General health statistics articles
- Health (hlth)
- Health care (hlth_care)
- Health care activities (hlth_act)
- Operations, procedures and treatment (hlth_oper)
- Surgical procedures (hlth_co_proc3)
- Operations, procedures and treatment (hlth_oper)
- Health care activities (hlth_act)
- Healthcare non-expenditure statistics (ESMS metadata file – hlth_res_esms)