Archive:Agricultural output, price indices and income
- Data from September 2010, most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
This article gives an overview of recent changes in agricultural output, gross value added and prices in the European Union (EU), and takes a look at their effect on income from agricultural activity. Agricultural output decreased by as much as 11.9 % (in producer prices) in 2009, compared with 2008, when the output were still at a high level compared to the last ten years. Producer output prices, after removal of inflation, rose on average by 2.0 % per year in the EU-27 (without data from Germany, Cyprus and Ireland) between 2005 and 2009. In parallel to decreasing gross value added (-13.4% in basic prices), there was an average 11.6 % decline of real income across the EU in 2009, compared with 2008.
Main statistical findings
The agricultural industry of the EU-27 generated in total EUR 125 400 million of gross value added at producer prices in 2009, which represented a steep reduction of 14.0 % in relation to the previous year. Strong decreases in both the value of crop output (down 13.9 % to a value of EUR 171 000 million in 2009) and animal output (down 10.9 % to a value of EUR 133 000 million) were partly countered by a large decrease in the value of intermediate consumption of goods and services (down 10.5 % in 2009).
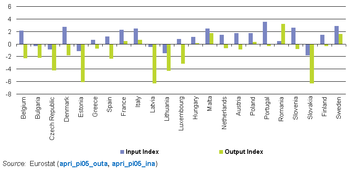
Values comprise a volume and price component. One important strand of latest changes in agricultural policy has been the move away from price support, so that prices more accurately reflect market forces and changes in supply and demand. Among the Member States, there were big differences in the development of deflated agricultural output prices during the period between 2005 and 2009; there were rises in the 7 Member States, the strongest increases being recorded for Romania (average growth of 3.2 % per year) and Malta (1.7 % per year), while reductions were posted in 16 of the Member States, the largest of which was in Latvia (-6.3 % per year), in Slovakia (-6.2 % per year) and in Estonia (-6.1 % per year) . Data were not yet available for 2009 for four countries
For the development in deflated agricultural input prices the picture were also different between countries. 17 Member States shows increasing input prices, while there was a decrease in 6 countries.
The development in output prices shows a 9 per cent increase from 2005 to 2009, but also a significant decrease from 2008 to 2009. Products with big fluctuations are in example cereals and milk.
Real net value added at factor cost of agriculture per unit of full-time labour (non-full time converted into annual work units), also termed as agricultural income indicator A, declined by an average 11.6 % across the EU in 2009, compared with 2008. There were stark contrasts among the Member States, with decreases over 20 % in Hungary, Luxembourg, Ireland, Germany and Italy, contrasting with small increases in Malta, Denmark, Finland, Cyprus, Belgium and Grece.
Data sources and availability
The Economic accounts for agriculture (EAA) comprise a production account, a generation of income account, an entrepreneurial income account and some elements of a capital account. For the output items of agriculture, Member States transmit to Eurostat values at basic prices, as well as their components (the value at producer prices, subsidies on products and taxes on products). For the items of intermediate consumption, values at purchaser prices (basic prices) are transmitted. The data for the production account and for gross fixed capital formation are transmitted in both current prices and the prices of the previous year.
Animal and crop output are the main product categories of agricultural output. The output of agricultural activity includes output sold (including trade in agricultural goods and services between agricultural units), changes in stocks, output for own final use (own final consumption and own-account gross fixed capital formation), output produced for further processing by agricultural producers, as well as intra-unit consumption of livestock feed products. The output of the agricultural industry is made up of the sum of the output of agricultural products and of the goods and services produced in inseparable non-agricultural secondary activities. Intermediate consumption represents the value of all goods and services used as inputs in the production process, excluding fixed assets whose consumption is recorded as fixed capital consumption.
Gross value added equals the value of output less the value of intermediate consumption, and is shown here measured at producer prices (the producer price excludes subsidies less taxes on products).
Agricultural income indicators (in the EAA) are presented in the form of:
- an index of real income of factors in agricultural activity per annual work unit (indicator A);
- the index of real net agricultural entrepreneurial income, per unpaid annual work unit (indicator B);
- net entrepreneurial income of agriculture (indicator C).
The concept of output, for animal and crop output, comprises sales, changes in stocks, and products used for processing and own final use by producers. EU agricultural price indices are obtained by a base-weighted Laspeyres calculation (2005=100), and are expressed both in nominal terms, and deflated using an implicit HICP deflator.
Context
One of the principal objectives of the Common agricultural policy (CAP) is to provide farmers with a reasonable standard of living. Although this concept is not defined explicitly, one of the measures tracked is income development from farming activities; economic accounts for agriculture (EAA) are one of the data sources that provide such income measures. This macro-economic set of data is used to analyze the production process of agricultural activity and the primary income generated by it. The EAA provide key insights into:
- the economic viability of agriculture;
- its contribution to a Member State’s wealth;
- the structure and composition of agricultural production and inputs;
- the remuneration of factors of production;
- relationships between prices and quantities of both inputs and outputs;
- responds to the need to have internationally comparable information.
In addition, the EAA data meets the requirement for internationally comparable information.
Eurostat also collects annual agricultural prices (in principle net of VAT) to compare agricultural price levels between Member States and study sales channels. Price indices, quarterly and annual, for agricultural products and the means of agricultural production, on the other hand, are used principally to analyse price developments and their effect on agricultural income.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Agriculture – Main statistics - 2007-2008 pocketbook
- Agricultural statistics – Main results 2006-2007 pocketbook
- EU Agricultural Income down 11.6% in 2009 - Issue number 18/2010
Main tables
- Economic Accounts for Agriculture (t_aact)
- Crop output - basic and producer prices (tag00054)
- Animal output - basic and producer prices (tag00055)
- Output of the agricultural industry - basic and producer prices (tag00102)
- Gross value added of the agricultural industry - basic and producer prices (tag00056)
- Indicator A of the income from agricultural activity (tag00057)
- Agricultural prices and price indices (t_apri)
Database
- Agriculture (agri), see:
- Economic Accounts for Agriculture (aact)
- Economic Accounts for Agriculture (aact_eaa)
- Economic accounts for agriculture - values at current prices (aact_eaa01)
- Economic accounts for agriculture - Values at n-1 prices (aact_eaa02)
- Economic accounts for agriculture - Values at constant prices (2005=100) (aact_eaa03)
Economic Accounts for agriculture - Values at real prices (aact_eaa04) - Economic accounts for agriculture - indices : volume, price, values (aact_eaa05)
- Economic accounts for agriculture - Agricultural income (indicators A, B, C) (aact_eaa06)
- Agricultural Labour Input Statistics (aact_ali)
- Agricultural Labour Input Statistics - absolute figures (aact_ali01)
- Agricultural Labour Input Statistics - indices (2005=100) (aact_ali02)
- Economic Accounts for Agriculture (aact_eaa)
- Agricultural prices and price indices (apri)
- Selling prices of agricultural products (absolute prices), land prices and rents (apri_ap)
- Price indices of agricultural products (apri_pi)
Source data for tables, figures and maps on this page (MS Excel)
Dedicated section
Methodology/Metadata
- Economic Accounts for Agriculture [ESMS metadata file - aact_esms]
- Selling prices of agricultural products (absolute prices), land prices and rents [ESMS metadata file - apri_ap_esms]
- Price indices of agricultural products [ESMS metadata file - apri_pi_esms]
Other information
- Handbook for EU agricultural price statistics (PDF)
- Regulation 138/2004 on the economic accounts for agriculture in the Community
External links
- European Commission - Agriculture and Rural Development - Food Prices
- The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Statistics