Archive:Youth unemployment
Planned article update: September 2022.
This article explains how youth unemployment in the European Union (EU) and its Member States is measured and how youth unemployment rates are affected by the transition of young adults from formal education to the labour market. Two factors are particularly relevant. First, the majority of 15-19 year olds are predominantly in formal education and there is a steep rise in participation in the labour market between the ages of 15 and 24. Second, young people in formal education are sometimes also employed or unemployed, so there is an overlap between the labour market and education.
This article focuses on measures of youth unemployment, and is a supplement to a companion article called "Participation of young people in education and the labour market" which further develops on the interplay between formal education and labour market participation. The latest Eurostat data on youth unemployment can be found here.
Full article
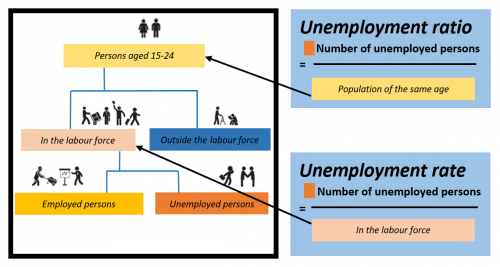
Definition of unemployment and youth unemployment indicators
A person's labour force status falls into one of three categories: employed, unemployed or outside the labour force. Eurostat uses the employment and unemployment definitions from the International Labour Organisation (ILO) . The labour force, which may also be referred to as active population, consists of employed and unemployed persons. An employed person is a person aged 15 and over who during the reference week performed work, even if just for one hour a week, for pay, profit or family gain, or alternatively had a job or business from which he/she was temporarily absent due to illness, holiday, industrial dispute or education and training. On the other hand, an unemployed person is not employed, currently available for work and actively seeking work. Thorough explanation of these concepts is available in an article on the EU-LFS methodology. The same definitions apply to young people just as they do to any other age group.
Figure 1 shows the EU population of young persons 15-24 years old divided into three groups based on their labour force status, and its evolution from 2005 to 2020. The graph presents for each year the number of young people that were employed, unemployed and outside the labour force. It appears from the graph that youth unemployment has been decreasing from 4.5 million in 2005 to 3.5 million in 2008. It began to rise in 2009, reaching 4.7 million in 2013 and hereafter gradually decreasing to a new low of 2.8 million in 2019. Furthermore, the number of young persons outside the labour force in the period 2005-2019 was the highest in 2005 reaching 31.6 million and the lowest in 2019 with 28.1 million. After the low levels in 2019, in 2020, both the population of unemployed and people outside the labour force increased to 2.9 and 28.9 million, respectively. In addition, the increase of 0.7 million in the number of people outside the labour force between 2019 and 2020 was the first increase in this sub-population recorded since 2005. Respectively, the number of young employed people dropped by 0.9 million from 2019 and 2020 and reached 14.6 million.
People are classified as being employed or unemployed irrespective of whether they are in formal education or not. In other words, Eurostat unemployment statistics, in line with ILO standards, do not exclude students from unemployment just because they are students. The same criteria that apply to the rest of the population also apply to them. This means that whether someone is in formal education or not is irrelevant for his/her status regarding employment or unemployment. However, participation in education of the population as a whole has an indirect effect on youth unemployment indicators.
The main indicator of youth unemployment is the youth unemployment rate for the age group 15-24. This uses the same standard definition as the unemployment rate for the population of working age. For a given age group, it is the number of those unemployed divided by the total number of people in the labour market (employed plus unemployed). In the EU in 2020, there were 2.9 million unemployed persons aged 15-24 and 17.5 million persons of that age group in the labour market, according to the EU labour force survey. This gives a youth unemployment rate of 16.8 %. For comparison, this rate in 2019 was 15.1 %. Nevertheless, the increase between 2019 and 2020 was more influenced by the reduction of the labour force due to the lower number of young employed people, than by the increase in the number of unemployed population.
Given that not every young person is in the labour market, the youth unemployment rate does not properly reflect the proportion of young adults who are unemployed. Youth unemployment rates are frequently misinterpreted in this sense. For example, when the youth unemployment rate equals 25 %, it does not mean that 'one quarter of the whole young population is unemployed' but it means that among the young people in the labour force (either employed or unemployed), one quarter is unemployed and three quarters are employed. Young people outside the labour market are not included (or not taken into account) in this rate, they are neither in the numerator nor in the denominator. Also, the youth unemployment rate may be high, as exemplified above, even if the number of unemployed persons is limited, the rate depending on the number of young persons who are employed. This issue is not present for the unemployment rate of the whole working age population due to the higher participation of that population in the labour market.
Another indicator of youth unemployment published by Eurostat is the youth unemployment ratio. This has the same numerator as the youth unemployment rate, but the denominator is the total population aged 15 to 24. It thus gives an unemployment-to-population measure. The size of the youth labour market (i.e. the size of the young labour force) only triggers minor effects in the youth unemployment ratio, contrary to the unemployment rate.
In 2020, in the EU there were 46.4 million persons aged 15-24, of whom 2.9 million were unemployed. This gives a youth unemployment ratio of 6.3 %. Figure 2 shows youth unemployment rates alongside youth unemployment ratios for 2020 for each country. Data is based on the EU labour force survey.
The youth unemployment ratio is by definition always smaller than the youth unemployment rate, typically less than half of it. This difference is entirely due to the different denominators. However, it is worth noticing that in some countries the values of the rate and ratio are closer to each other than in others, meaning that in some instances young people in the labour force relatively more closely overlap with the total population of the same age. See for example Malta, Denmark, Austria, Germany and the Netherlands, where the difference between the youth unemployment rate and the ratio is less than 5 percentage points (p.p.). By contrast, this difference in Greece, Spain and Italy, exceeds 20 p.p.
Figure 3 below shows the different denominators involved in the calculation of the youth unemployment rate and youth unemployment ratio. As can be seen, both indicators use the same numerator but the denominators differ.
Young persons' participation in the labour market
As explained above, unemployment rates and unemployment ratios differ because unemployment rates include in the denominator only the part of the population that is in the labour market. There is also a strong link between labour market participation and educational status, which becomes particularly clear when looking at young people's situation at different ages. This section analyses this issue in detail.
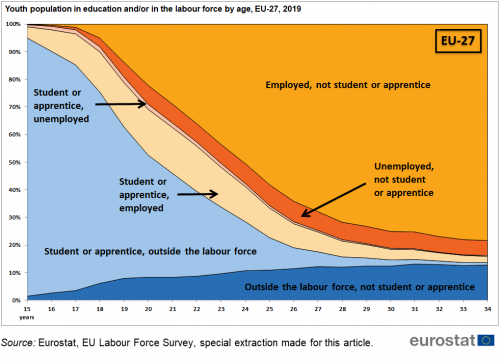
At 15 years of age, nearly 100 % of the population in the EU and its Member Sates are still at school. As the young grow older, many move into the labour market, becoming employed or unemployed, or remain outside the labour market. Not all young people make this transition at the same age, so there is a gradual rise in the number of the young people on the labour market. Figure 4 below shows the proportion of young people in formal education and/or on the labour market at each year of age (data for EU, 2020). The persons in formal education are colour-coded in light blue, and those not in education are colour coded in orange. There is a steep rise in the labour market participation, from 4 % at age 15 to 71 % at age 24. This steep increase explains the difference between the youth unemployment rates and youth unemployment ratios, introduced in the previous section. This is a distinctive feature of the young population and it has no equivalent at other ages, except for the gentle decrease in labour participation by older workers as they retire.
Figure 4 is based on EU labour force survey data and it counts all those who state they have been in formal education or training during the previous four weeks as being in education, and does not include people who participated exclusively in non-formal training sessions such as attending a course, a seminar or taking private lessons.
A second feature in Figure 4 is that many young people join the labour market before they finish their studies or they participate in formal education while already on the labour market. This means that people can be simultaneously in education and on the labour market. (It is noted that participation in the labour market, according to ILO definitions, occurs by working as little as 1 hour in the week, or looking and being available for such work). Otherwise said, those in formal education and those on the labour market are not always different groups as an overlap exists between the two groups. The transition from education to the labour market is not a simple switch of status but a complex overlap of different situations. This is developed further in the article Participation of young people in education and the labour market.
Figure 4 shows that in 2019, in the EU, there were 2.1 million young unemployed persons aged 15-24 that were not in education, and 0.8 million persons unemployed but in education. There were also many young persons employed while in education amounting to 5.9 million. As can be seen, there are more young employed persons in education than young unemployed persons (whether in education or not).
The effects of the 2008-2013 crisis on youth unemployment
Video 1 shows a sequence of charts such as Figure 4 with young persons 15-34 years of age in employment and/or formal education or none of the above, in the EU-27. The video covers all years ranging from 2005 to 2019 to capture the changes in the labour force status of the given population prior to, during and after the 2008-2013 crisis. An increase in youth unemployment was one of the outcomes of this economic crisis not only in countries that were severely affected such as Spain and Greece, but also the EU-27 as a whole. As indicated by the video, the number of young persons unemployed and not in education reached a highest peak in 2012 and 2013, decreasing considerably in the following years and reaching its lowest point in 2019. The proportion of the population simultaneously in education and on the labour market reached the highest point in 2008, gradually decreasing in the following years until increasing again in the last couple of years.
Context
Young people are a priority for the European Union’s social vision, and the crisis further highlighted the need to sustain the young human capital. In November 2009, the Council of Youth Ministers adopted the EU Youth Strategy for 2010-2018 which had two overall objectives: to provide more and equal opportunities for young people in education and in the labour market to promote the active citizenship, social inclusion for all young people. Recently, following the Council Resolution of 26 November 2018, the EU Youth Strategy 2019-2027 has been introduced with 11 European Youth Goals, among them quality employment set as one of the objectives.
The Open Method of Coordination supports the implementation of the strategy which should create favourable conditions for young people to develop their skills, fulfil their potential, work, and actively participate in society. In this framework youth statistics are an essential tool to support evidence-based policy-making in the various domains covered by the strategy.
Focus on young people has also been highlighted with the adoption of the Europe 2020 strategy back in June 2010. Quality education and training, successful labour market integration and more mobility of young people are key to unleashing all young people's potential and achieving the Europe 2020 objectives. Youth on the Move presents a framework of policy priorities for action at national and EU level to reduce youth unemployment by facilitating the transition from school to work and reducing labour market segmentation. Particular focus is put on the role of public employment services, promoting the Youth Guarantee scheme to ensure all young people are in a job, in education or in activation, creating a European Vacancy Monitor and supporting young entrepreneurs.
Direct access to
- All articles on labour market
- Education and training statistics introduced
- EU labour force survey (online publication)
- Participation of young people in education and the labour market (background article)