Archive:Extra-EU trade in manufactured goods
Data from April 2019
Planned update: April 2020
Highlights
In 2018, manufactured goods made up 82 % of all EU exports and 67 % of EU imports.
The United States and China were the main EU trading partners for manufactured goods in 2018.
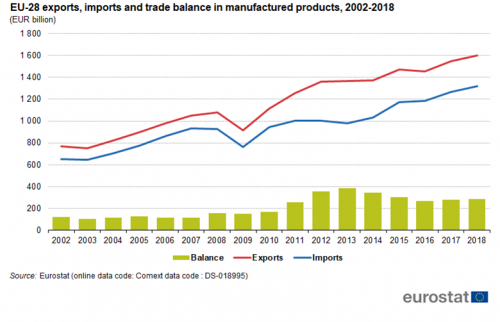
EU-28 exports, imports and trade balance in manufactured products, 2002-2018
This article focuses on the structure and evolution of the European Union (EU) international trade in manufactured goods: imports and exports at EU level.
This article is part of an online publication providing recent statistics on international trade in goods, covering information on the EU's main partners, main products traded, specific characteristics of trade as well as background information.
Full article
Manufactured goods dominate international trade
The Standard international trade classification (SITC) distinguishes four main categories (sections) of manufactured goods:
- chemicals (SITC 5);
- manufactured goods classified chiefly by material (SITC 6);
- machinery and vehicles (SITC 7);
- miscellaneous manufactured articles (SITC 8).
Categories 6 and 8 are often grouped together as 'other manufactured goods'. This grouping is also used in this article.
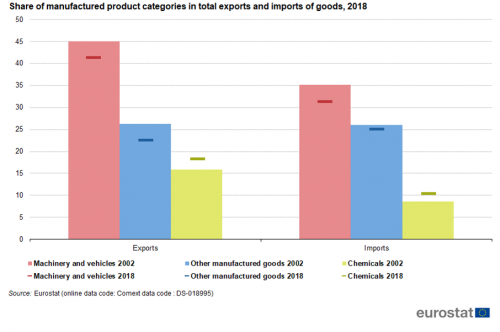
Manufactured goods are the main type of goods traded by the EU. In 2018 they made up 82 % of all EU exports. This was 5 percentage points (p.p.) less than in 2002. Comparing the three sectors of manufactured goods: 'Machinery and vehicles', 'Other manufactured goods' and 'Chemicals', between 2002 and 2018, we see that the first two both lost almost 4 p.p. while the latter gained 2 p.p. Regarding EU imports the share of manufactured goods was 31 % which was 3 p.p. lower than in 2002. Again 'Machinery and vehicles' lost 4 p.p. and 'Other manufactured goods' lost 1 % while 'Chemicals' gained 2 p.p.
Since 2002, imports and exports have doubled in value (see Figure 2). Since exports were higher than imports in 2002, this meant that, in absolute terms, exports grew more, leading to a record trade surplus of EUR 387 billion in 2013. Between 2013 and 2016, the trade surplus dropped to EUR 268 billion but then increased to EUR 286 billion in 2018.
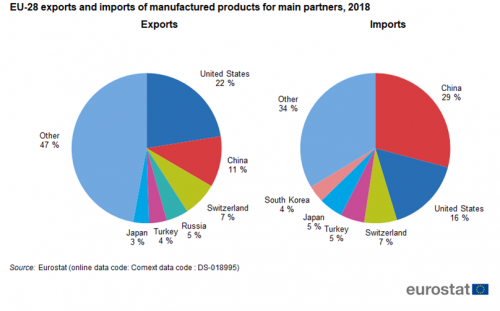
Five of the six main partners in exports of manufactured goods are also among the five main partners in imports (see Figure 3). These are the United States, China, Switzerland, Turkey and Japan. The remaining top six partner for exports was Russia, while for imports it was South Korea. In exports, the top six, headed by the United states (22 %), China (11 %) and Switzerland (7 %), accounted for slightly more than half of all exports of manufactured products. Imports were somewhat more concentrated with the top six, headed by China (29 %), the United States (16 %) and Switzerland (7 %), accounting for two thirds of all imports of manufactured products.
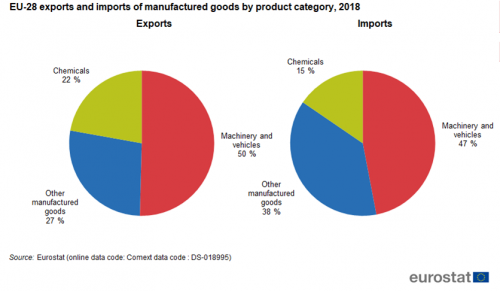
The three sectors that are distinguished in manufactured products have different shares in extra-EU exports and imports (see Figure 4). Both ’Machinery and vehicles’ and ’Chemicals’ have higher shares in exports while ’Other manufactured goods’ has a higher share in imports. Each of these three sectors is discussed in separate paragraphs below.
Machinery and vehicles largest sector in manufactured goods
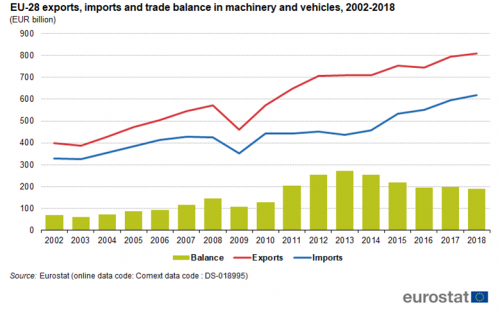
The most important sector in the international trade of manufactured products by the EU is ’Machinery and vehicles’. The EU exported EUR 809 billion (41 % of total EU exports) and imported almost EUR 619 billion (67 % of total EU imports) in this sector in 2018 (Figure 5). The sector also had the largest surplus in EU trade, with EUR 189 billion in 2018.
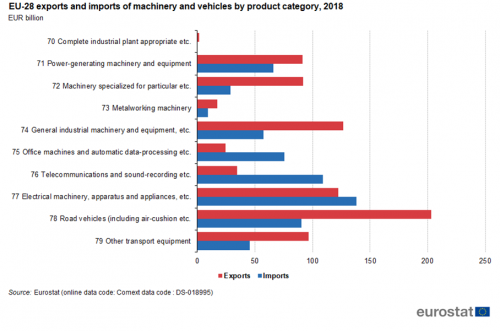
In 2018 in exports, the main product group in the sector is road vehicles with EUR 203 billion, followed at a distance by general industrial machinery with EUR 127 billion and electrical machinery with EUR 122 billion (Figure 6). In imports, the values for the top three product groups are closer to each other. They are electrical machinery (EUR 138 billion), telecommunications equipment (EUR 109 billion) and road vehicles (EUR 90 billion). The product group with the largest trade surplus was road vehicles with EUR 113 billion. The largest trade deficit was recorded in telecommunications equipment (EUR 75 billion)
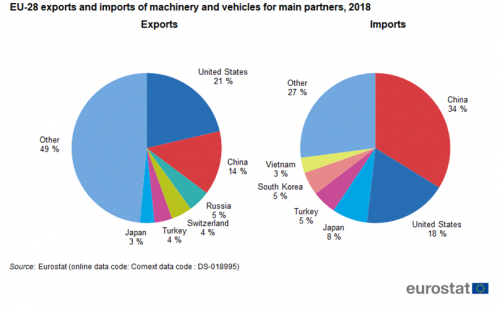
The United States was the biggest destination country for EU exports of 'Machinery and vehicles' in 2018 with 21 % (Figure 7). China (14 %) was the only other export destination with a share of more than 10 %. The top six export destinations covered slightly more than half of all exports in this sector. China (34 %) and the United States (18 %) were also the top two countries for imports. The top six in imports covered almost three quarters of all imports in this sector.
China accounts for almost a third of imports of other manufactured goods
‘Other manufactured goods’ (SITC Sections 6 and 8) is a heterogeneous sector consisting of manufactured goods which range from basic semi-manufactured goods, such as leather, rubber, wood, paper, textiles, metals, building fixtures and fittings, to more labour-intensive products, like clothes, shoes and accessories, scientific instruments, clocks, watches and cameras.
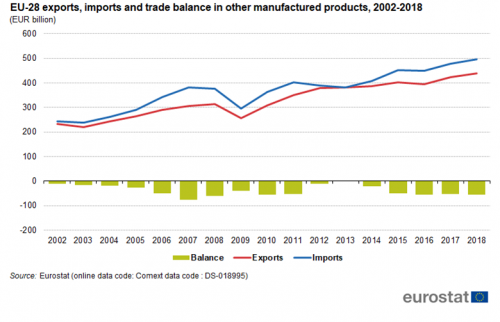
The second largest sector in the international trade of manufactured products is ‘Other manufactured goods’. The EU exported EUR 439 billion (22 % of total EU exports) and imported almost EUR 495 billion (25 % of total EU imports) in this sector in 2018 (Figure 8). With the exception of 2013, when there was a trade surplus of EUR 1 billion, the EU always had a trade deficit, which peaked at EUR 76 billion in 2007. It fluctuated somewhat in the following years, reaching EUR 55 billion in 2018.
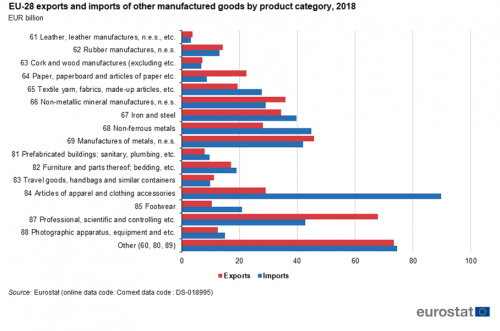
The relative size of exports and imports in product groups differs to some extent. The EU has a large trade deficit in clothing, non-ferrous metals and footwear and a sizeable trade surplus in professional, scientific and controlling equipment and paper and related products (Figure 9).
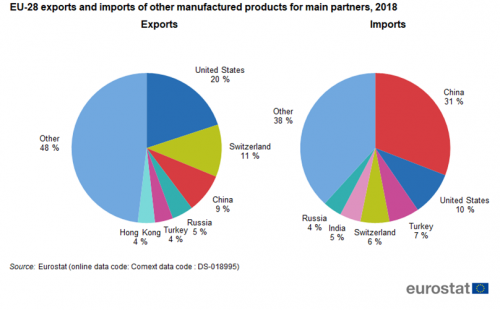
In 'Other manufactured products' the main destinations for exports were the United States (20 %), Switzerland (11 %) and China (9 %) (Figure 10). These three countries were also among the four main import partners but here China (31 %) led before the United States (10 %), Turkey (7 %) and Switzerland (6 %). The top six export partners covered 52 % of the exports while the top six import partners covered 62 % of the imports in this sector in 2018.
Chemicals fastest growing sector in manufactured goods
The chemicals sector (SITC Section 5) contains various chemical goods such as organic chemicals, inorganic chemicals, plastics and pharmaceutical products. It is the smallest of the three sectors in manufactured goods.
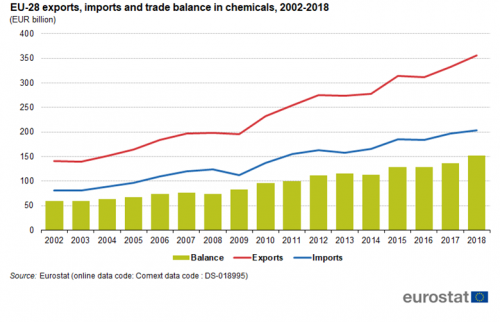
Between 2002 and 2018, this sector's exports and imports had the highest growth rate of the three sectors discussed. Both exports and imports were around 2.5 times as high in 2018 as they were in 2002, while in the other two sectors exports and imports were between 1.8 and 2.1 times as high in 2018 as they were in 2002. Exports in this sector reached EUR 356 billion in 2018 while imports were EUR 204 billion. The trade surplus for chemicals increased from EUR 60 billion in 2002 to EUR 152 billion in 2018.
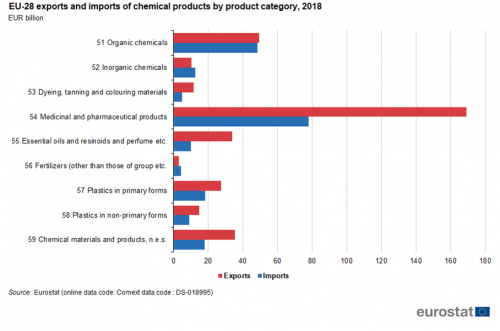
The various categories that make up 'Chemicals' can be found in Figure 12. The largest category in exports, imports and trade balance is 'medicinal and pharmaceutical products' covering 48 % of exports and 38 % of imports of chemicals. It contributed EUR 91 billion to the trade surplus. In seven of the nine categories the EU has a trade surplus with the exceptions being small deficits in inorganic chemicals and fertilizers.
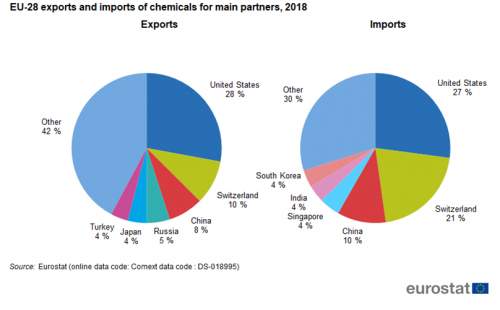
The United States (28 %), Switzerland (10 %) and China (8 %) were the EU's main export destinations for 'Chemicals' (Figure 13). In the same order, the United States (27 %), Switzerland (21 %) and China (10 %) were also the top three import partners for 'Chemicals'. The top six export partners covered 58 % of the exports while the top six import partners covered 70 % of the imports in this sector in 2018.
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
EU data come from Eurostat’s COMEXT database. COMEXT is the Eurostat reference database for international trade. It provides access not only to both recent and historical data from the EU Member States but also to statistics of a significant number of third countries. International trade aggregated and detailed statistics disseminated from Eurostat website are compiled from COMEXT data according to a monthly process. Because COMEXT is updated on a daily basis, data published on the website may differ from data stored in COMEXT in case of recent revisions.
EU data are compiled according to community guidelines and may, therefore, differ from national data published by Member States. Statistics on extra-EU trade are calculated as the sum of trade of each of the 28 Member States with countries outside the EU. In other words, the EU is considered as a single trading entity and trade flows are measured into and out of the area, but not among Member States within the EU.
Unit of measure
Trade values are expressed in billions (109) of euros. They correspond to the statistical value, i.e. to the amount which would be invoiced in case of sale or purchase at the national border of the reporting country. It is called a FOB value (free on board) for exports and a CIF value (cost, insurance, freight) for imports.
Context
The EU is the world's biggest exporter of manufactured goods, and is a global market leader for high-quality products. Thanks to some of its key assets such as chemicals, pharmacy products, motor vehicles and non-electrical machinery, the European Union has a substantial trade surplus for manufactured products.
Direct access to
- International trade data (t_ext)
- International trade long-term indicators (t_ext_lti)
- International trade short-term indicators (t_ext_sti)
- International trade data (ext)
- International trade long-term indicators (ext_lti)
- International trade short-term indicators (ext_sti)
- International trade detailed data (detail)
- International trade in goods statistics - background
- International trade in goods (ESMS metadata file — ext_go_agg_esms)
- User guide on European statistics on international trade in goods
- Regulation (EC) No 471/2009 of 6 May 2009 on Community statistics relating to external trade with non-member countries
- Regulation (EU) No 92/2010 of 2 February 2010 implementing Regulation (EC) No 471/2009, as regards data exchange between customs authorities and national statistical authorities, compilation of statistics and quality assessment
- Regulation (EU) No 113/2010 of 9 February 2010 implementing Regulation (EC) No 471/2009 , as regards trade coverage, definition of the data, compilation of statistics on trade by business characteristics and by invoicing currency, and specific goods or movements.