Government expenditure on defence
Data extracted on 29 February 2024
Planned article update: February 2025
Highlights
General government expenditure in the EU on defence amounted to 1.3 % of GDP in 2022.
This article analyses data on general government expenditure on 'defence' (according to the Classification of the Functions of Government - COFOG). It is part of a set of statistical articles based on general government expenditure by function.
Eurostat collects data on general government expenditure by economic function according to the international Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) in the framework of the European System of National Accounts (ESA 2010).
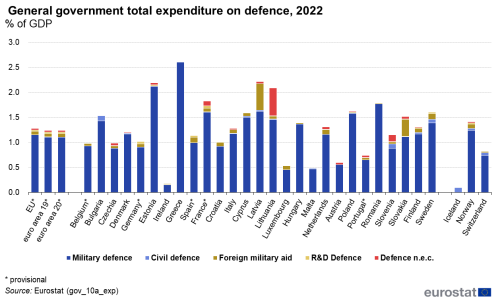
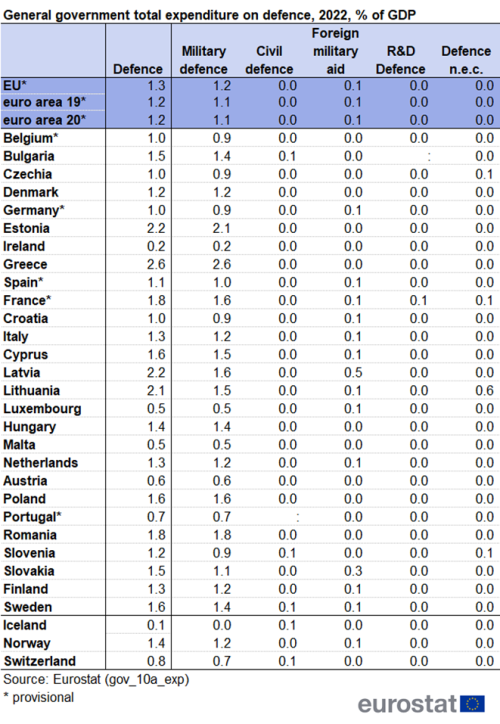
In 2022, 'defence' expenditure amounted to 1.3 % of GDP for the EU and 1.2 % of GDP the euro area.
Full article
Expenditure on 'defence'
In 2022, defence expenditure amounted to 1.3 % of GDP for the EU and 1.2 % of GDP for the euro area, with expenditure in both areas being relatively stable as a percentage of GDP in the period 2013-2022 (fluctuating between 1.2 and 1.3 % of GDP), but decreasing as a ratio to GDP compared with 1995 and 1996 (1.6 % of GDP).
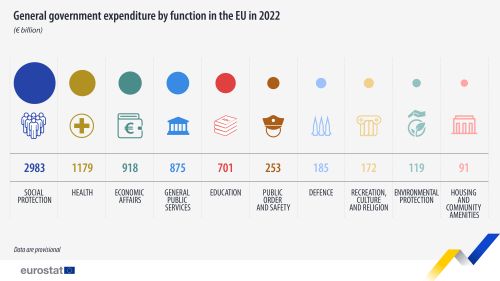
As a share of total expenditure, defence expenditure amounted to 2.6 % in 2022 in the EU and 2.5 % in the euro area.
In 2022, the highest levels of total expenditure on defence in the EU countries were observed in Greece (2.6 % of GDP), Latvia and Estonia (both 2.2 % of GDP), Lithuania (2.1 % of GDP), France and Romania (both 1.8 % of GDP), Cyprus and Sweden (both 1.6nbsp;% of GDP) as well as Bulgaria and Slovakia (both 1.5nbsp;% of GDP). By contrast, Ireland (0.2 % of GDP), Malta and Luxembourg (both 0.5 % of GDP) as well as Austria (both 0.6 % of GDP) had comparatively low expenditure on defence in the EU. Among EU and EFTA countries, Iceland reported the lowest level of expenditure on defence, as it does not have a standing army (0.1 % of GDP).
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp), see country codes
At the level of the EU, the major part of 'defence' expenditure is concentrated in the COFOG group 'military defence' (1.2 % of GDP in 2022). 'civil defence', 'R&D defence' and 'defence expenditure not elsewhere classified' together amounted to less than 0.1 % of GDP at the level of the EU, while 'foreign military aid' accounted for 0.1 % of GDP in 2022.
Research and development on defence made up a negligible part of government expenditure in all countries except France (0.1 % of GDP).
'Foreign military aid' amounted to 0.1 % of GDP for the EU, with notable amounts in Latvia (0.5 % of GDP), Slovakia (0.3 % of GDP) as well as Spain, Sweden, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Finland, Croatia, Italy, France, Cyprus, Germany and Lithuania (all at 0.1 % of GDP). It should be noted that the reporting of military aid in response to Russia's war of agression against Ukraine is not yet fully harmonised, so that donations of equipment in kind are not yet fully reflected in total expenditure in 'foreign military aid' - see also metadata notes. Such omissions do not effect the level of total expenditure.
Expenditure on 'defence' by type of transaction
At the level of the EU, a bit less than half (45 %) of total expenditure on defence in 2022 was devoted to 'compensation of employees', that is wages and salaries as well as employers' actual or imputed social contributions. 29 % was devoted to 'intermediate consumption', consisting of government purchases of goods and services, except where these are regarded as capital formation. Capital investments amounted to 22 % of defence expenditure in 2022, such as the purchase of new equipment and infrastructure. (Other) Current and capital transfers, for example for military aid, made up 2.6 % of total expenditure at the level of the EU according to the data reported.
Evolution of 'defence' expenditure over 1995-2022
At the level of the EU, decreases in 'defence' expenditure as a percentage of GDP were noted over 1995-2022 (from 1.6 % of GDP in 1995 to 1.3 % of GDP in 2022), with the share in total expenditure dropping from 3.1 % in 1995 to 2.6 % in 2022.
Compared with 2021, the level of defence expenditure in the EU remained stable expressed as a percentage of GDP and as a share of total expenditure. However, in 2022, in absolute terms, EU defence expenditure increased to €204 billion, up from €184 billion in 2021. This 11 % increase represents the second-strongest relative increase among the broad expenditure functions.
Source data for tables and graphs
The detailed tables ![]() are available here.
are available here.
Data sources and availability
Reporting of data to Eurostat
Annual government finance statistics (GFS) data are collected by Eurostat on the basis of the European System of Accounts (ESA 2010) transmission programme. Member States are requested to transmit, among other tables, table 1100, 'Expenditure of general government by function' twelve months after the end of the reference period. Table 1100 provides information about expenditure of the general government sector divided into main COFOG functions and ESA 2010 categories. The transmission of the COFOG I level breakdown (divisions) is compulsory for the years 1995 onwards, whereas information on the COFOG II level (COFOG groups) at general government level is provided on a compulsory basis for the reference years 2001 onwards. The main reference year used in this publication is 2022 as the latest year available at EU level.
Data was extracted on 29 February 2024.
Provisional data
While a significant effort was undertaken to harmonise the recording of government measures to alleviate the impact of increasing energy prices, a full harmonisation of data for the reference year 2022 was not yet achieved.
Data for the EU and euro area aggregates (2022), Belgium (2022), Germany (2020-2022), Spain (2022), France (2021-2022) and Portugal (2022) is provisional.
Definition of general government and its subsectors
The data relate to the general government sector of the economy, as defined in ESA 2010, paragraph 2.111: 'The general government sector (S.13) consists of institutional units which are non-market producers whose output is intended for individual and collective consumption, and are financed by compulsory payments made by units belonging to other sectors, and institutional units principally engaged in the redistribution of national income and wealth'.
Classification of functional expenditure of government
The Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) classifies government expenditure into ten main categories (divisions known as the 'COFOG I level' breakdown): general public services; defence; public order and safety; economic affairs; environmental protection; housing and community affairs; health; recreation, culture and religion; education; social protection. These divisions are further broken down into 'groups' (COFOG II level).
For 'defence', the groups are
- 'military defence',
- 'civil defence',
- 'foreign military aid',
- 'R&D defence',
- 'defence n.e.c.'.
Further information is available in the Eurostat Manual on sources and methods for the compilation of COFOG Statistics.
Satellite accounts
Administrative expenditure data is additionally collected in so-called satellite accounts. In general, the amount of expenditure recorded in satellite accounts is expected to exceed the expenditure recorded under the respective COFOG division. More details on the comparability of COFOG data with satellite accounts data can be found in the COFOG manual.
In particular, as regards defence expenditure, COFOG division 'defence' cannot be easily compared with NATO measures of defence expenditure. The main reasons are: COFOG is a classification by main purpose implying that some expenditure within COFOG 'public order and safety' might be counted under NATO methodology; the treatment of pensions in COFOG is within division 'social protection' and the COFOG treatment of employers' social contributions follows ESA 2010 and the time of recording may be different.
Definition of general government total expenditure
Government total expenditure is defined in ESA 2010, paragraph 8.100 by using as reference a list of ESA 2010 categories. More detail is provided in the overview article on Government expenditure by function – COFOG.
Gross Domestic Product
Throughout this publication, the nominal GDP, i.e. GDP at current prices is used. The latest GDP available at time of publication is used.
Time of recording & symbols used
In the ESA 2010 system, recording is on an accrual basis, that is, when 'economic value is created, transformed or extinguished, or when claims and obligations arise, are transformed or are cancelled.'
":" not available
"pp" percentage points
More data and information
For more country-specific notes, e.g. on missing data, please refer to the metadata published on Eurobase. The authors can be contacted at ESTAT-GFS@ec.europa.eu
Context
In the framework of the European System of National Accounts (ESA 2010), Eurostat collects data on general government expenditure by economic function according to the international Classification of the Functions of Government (COFOG) – see methodological note.
Direct access to
- Government expenditure by function - online publication
- Government expenditure by function – COFOG - overview article
- Government statistics (t_gov)
- Annual government finance statistics (t_gov_10a)
- Government statistics (gov)
- Government finance statistics (EDP and ESA2010) (gov_gfs10)
- Annual government finance statistics (gov_10a)
- Government revenue, expenditure and main aggregates (gov_10a_main)
- General government expenditure by function (COFOG) (gov_10a_exp)
- Main national accounts tax aggregates (gov_10a_tax_ag)
- Annual government finance statistics (gov_10a)
- Government finance statistics (EDP and ESA2010) (gov_gfs10)
- Government revenue, expenditure and main aggregates (ESMS metadata file — gov_10a_main_esms)
- General government expenditure by function (COFOG) (ESMS metadata file — gov_10a_exp_esms)
- Manual on sources and methods for the compilation of COFOG statistics - Classifications of the Functions of Government - 2019 edition
- Manual on government deficit and debt — implementation of ESA 2010 — 2022 edition