Packaging waste statistics
Data extracted on 10 October 2024.
Planned article update: October 2025.
Highlights
In 2022, the EU generated an estimated 186.5 kg of packaging waste per inhabitant (varying from 78.8 kg per inhabitant in Bulgaria to 233.8 kg per inhabitant in Ireland).
From 2011 to 2022, 'paper and cardboard' was the main packaging waste material in the EU (34.0 million tonnes in 2022), followed by plastic (16.1 million tonnes) and glass packaging waste (15.7 million tonnes).
Packaging waste, EU, 2011-2022
This article shows recent statistics on packaging waste in the 27 European Union (EU) Member States and some countries outside the EU. In particular, it summarises the developments during the period 2011–2022, for which official reporting on packaging waste for all EU Member States is available. The data is only partly comparable, due to a change in calculation methods for reference year 2020 onwards. The change mainly affects the calculation of recycled amounts of packaging waste. Information and data are based on the Directive 94/62/EC (consolidated text), which lays down the recycling and recovery targets. The Directive aims at providing a high level of environmental protection and harmonising national measures concerning the management of packaging and packaging waste.
Full article
Waste generation by packaging material
In 2022, the EU generated an estimated 186.5 kg of packaging waste per inhabitant. This quantity varied between 78.8 kg per inhabitant in Bulgaria and 233.8 kg per inhabitant in Ireland. Figure 1 shows that in 2022, paper and cardboard (40.8%), plastic (19.4%), glass (18.8%), wood (16.0%) and metal (4.9%) are the most common materials of packaging waste in the EU. Other materials represented only 0.2% of the total volume of packaging waste generated in 2022.
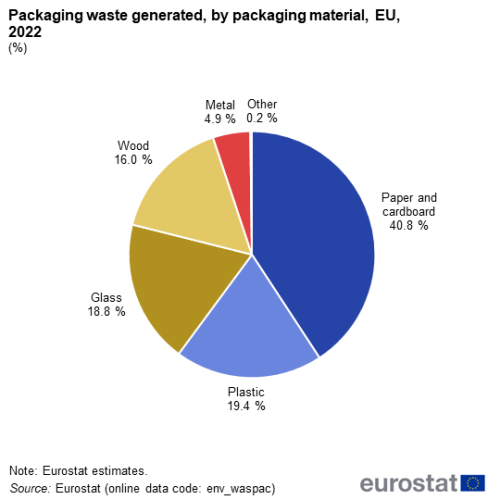
(%)
Source: Eurostat (env_waspac)
Time series of packaging waste
Figure 2 shows the development of packaging waste generated in the EU from 2011 to 2022. The total quantity of generated packaging materials rose by 14.3 million tonnes over this period (+20.6%).
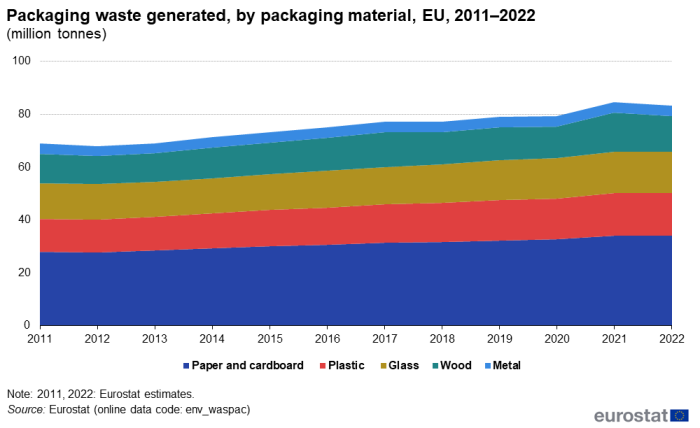
(million tonnes)
Source: Eurostat (env_waspac)
In 2022, the EU generated an estimated total volume of 83.4 million tonnes of packaging waste – a decrease of 1.6% (or 1.4 million tonnes) compared with 2021, with declines for all main packaging material categories. Overall, the decline in total packaging waste was mainly due to a decrease of 1.3 million tonnes (-8.6%) in waste from packaging made of wood. For the other main categories, the relative decreases in waste material were low, for packaging made of metal (down 83 000 tonnes; -2.0%), of plastic (down 60 000 tonnes; -0.4%), of glass (down 23 000 tonnes; -0.1%) and of paper and cardboard (down 18 000 tonnes; -0.1%).
Over the whole 11 year period from 2011 to 2022, paper and cardboard was the main packaging waste material, contributing 34.0 million tonnes to the total packaging waste generated in 2022; since 2011, this waste stream increased by 21.3%. Plastic packaging reached a total of 16.1 million tonnes as the second most important packaging material (+29.4% compared with 2011). Glass packaging waste had a volume of 15.7 million tonnes (+16.3%), wood 13.3 million tonnes (+19.9%) and metal packaging 4.1 million tonnes in 2022 (+7.3%).
Figure 3 depicts the development in the quantity of waste generated per inhabitant, by main waste materials. Compared with the total volume of generated packaging waste per inhabitant in 2011, which was 157.2 kg, the total volume increased by 29.3 kg to reach 186.5 kg per inhabitant in 2022.
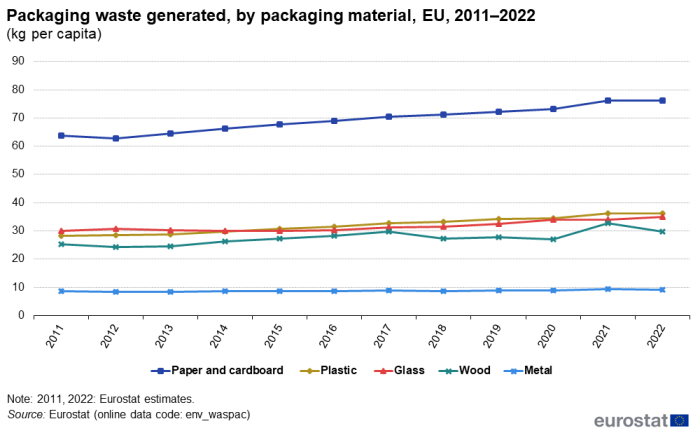
(kg per capita)
Source: Eurostat (env_waspac)
Figure 4 shows the evolution of the volume of total packaging waste generated, recovered and recycled per inhabitant. In comparison to the previous year, the amount of packaging waste generated per inhabitant in 2022 decreased by 1.9%. Recovered packaging waste also decreased, by 1.4%, but recycled packaging waste increased slightly, by 0.3%. Between 2011 and 2022, the amount of packaging waste generated per inhabitant increased substantially, by 18.7%. The recovered and recycled volumes of packaging waste grew even stronger, by 20.1% and 20.7%, respectively.
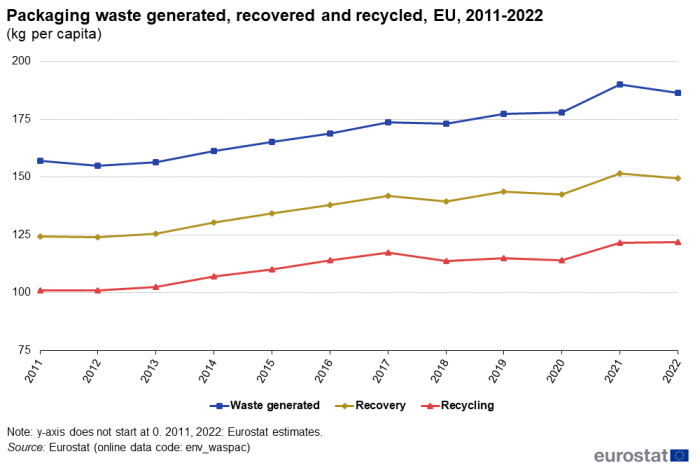
(kg per capita)
Source: Eurostat (env_waspac)
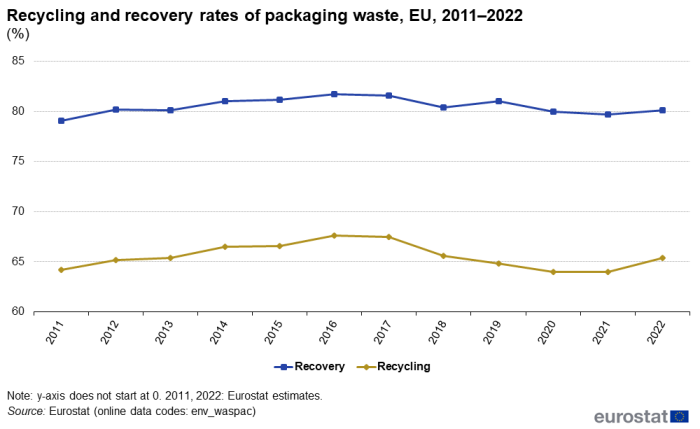
Figure 5 shows the evolution in the corresponding EU recycling and recovery rates of packaging waste over the period 2011–2022. In 2022, the recycling rate of packaging waste stood at 65.4%, up from 64.0% the previous year. By contrast, in 2011 the recycling rate stood at 64.2%. The recycling rate exceeded 65% each year from 2012 to 2018, with a peak at 67.6% in 2016. It thereafter fell to 64.0% in both 2020 and 2021, before rebounding in 2022.
From 2011 to 2018, the recovery rate followed roughly the same trend as the recycling rate. The recovery rate, including incineration at waste incineration plants with energy recovery, rose from 79.1% in 2011 to its highest value within the period, at 81.7 %, in 2016. In 2022, the recovery rate stood at 80.1%, marginally higher than in 2021 (+0.4 percentage points).
(%)
Source: Eurostat (env_waspac) and (env_waspacr)
Generation and recycling per inhabitant
The total volumes of packaging waste generated and recycled comprise all packaging materials: paper and cardboard, plastic, glass, wood, metal and others. Figure 6 gives an overview of the data reported on generation and recycling of packaging per inhabitant by the EU countries and the EEA/EFTA countries in 2022. There were 150 kg or more packaging waste generated per inhabitant in 17 of the EU countries. The amounts ranged from 233.8 kg per inhabitant in Ireland and 232.4 kg in Italy to 78.8 kg per inhabitant in Bulgaria. The highest volumes of recycled packaging waste per inhabitant were reported by Italy with 159.8 kg and Germany with 155.4 kg, while the lowest was recorded in Croatia with 43.1 kg.
Recycling and recovery targets and rates
Article 6 of the Packaging Waste Directive sets out the recovery and recycling targets. The targets had to be met in 2008 for the first time for all countries.
The Packaging Waste Directive sets the following targets: a minimum of 60% recovery rate (including waste incineration), and; between 55% and 80% of packaging waste to be recycled, with minimum rates of: 60% for glass; 60% for paper and cardboard; 50% for metals; 22.5% for plastics, and; 15% for wood.
These targets are calculated according to weight, by dividing the amount of packaging waste recycled by the total amount of packaging waste generated. The recycling rate of plastic packaging waste counts exclusively material that is recycled back into plastic.
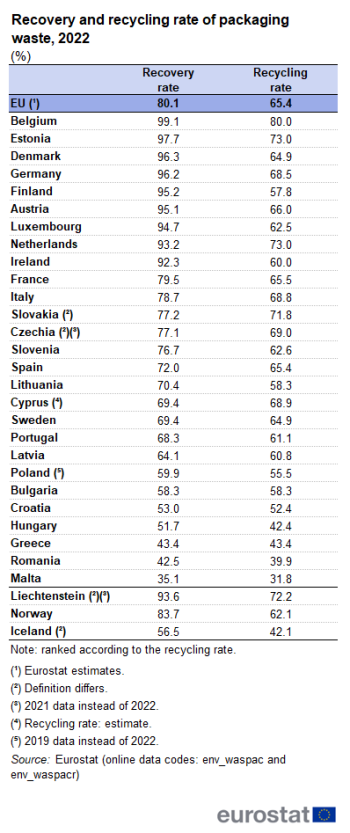
The recovery and recycling rates of all packaging waste of the EU countries and the EEA/EFTA countries in 2022 are shown in Table 1. According to these data, Belgium had the highest recovery rate among the EU countries, at 99.1%, as well as the highest recycling rate, at 80.0%.
(%)
Source: Eurostat (env_waspac) and (env_waspacr)
Figure 7 shows the share of the different recovery options for all packaging waste in 2022. The main form of recovery is recycling in all the reporting countries. In some countries, energy recovery from packaging waste contributed significantly to the overall recovery rate. It should be noted that due to methodological/technical issues, the sum of recycling, energy recovery and other recovery in Figure 7 may be different from the total recovery rates in Table 1 and may exceed 100%.
Among the EU countries, the highest energy recovery from packaging waste was recorded in Finland (37.3%). In Greece and Bulgaria, there was no energy recovery from packaging waste. Other forms of recovery contributed only a minor share, with a share of 0.1% or less % in all but 4 EU countries (the highest at 3.9% in Estonia).
Figure 8 shows the recycling rate of all packaging waste for the EU countries and the EEA/EFTA countries in 2022. 'Recycling' covers material recycling and other forms of recycling (e.g. organic recycling). In 2022, the target of 55% recycled packaging waste was met by all EU countries except Croatia (52.4%), Hungary (44.6%; 2020 data), Greece (43.4%), Romania (39.9%) and Malta (31.8%). From 2025, the recycling target is increased to 65%. Of the EU countries, 13 already met this future target in 2022, with another 6 countries closing on this target with recycling rates above 60%.
Figure 9 shows the recycling rate of plastic packaging waste for the EU countries and the EEA/EFTA countries in 2022. The recycling rate includes only material recycling and no other forms of recycling, i.e. exclusively material that is recycled back into plastics.
The target of 22.5% recycled plastic packaging waste was met by all EU countries except Malta (16.4%) in 2022.
Figure 10 shows the recovery rate of all packaging waste in 2022. Recovery includes energy recovery from packaging waste, other forms of recovery and total recycling. All EU countries and EEA/EFTA countries should have achieved the target of 60%. However, in 2022 the recovery rates were below 60 % in Poland (59.9%; 2019 data), Bulgaria (58.3%), Croatia (53.0%), Hungary (51.7%), Greece (43.4%), Romania (42.5%) and Malta (35.1%).
Conclusions
- The amount of packaging waste generated in the EU increased overall during the period 2011-2022. In 2022, the amount of packaging waste generated fell slightly, breaking with the overall upward trend observed since 2012 with only a slight exception in 2018.
- Over the period 2011–2022, the generation of all types of packaging waste material increased, although to a different extent. The highest relative increases were observed for plastic packaging waste, followed by paper and cardboard and wood. In absolute amounts, paper and cardboard packaging waste increased the most.
- The recycling rate for packaging waste rose continuously from 2011 to 2016, fell back to slightly below the 2011 level in 2020 and 2021, but recovered in 2022.
Source data for tables and figures on this page (MS Excel)
Data sources
The packaging waste data are reported by the EU countries as laid down in Commission Decision 2005/270/EC. The reported data are usually available in the Eurostat database on waste approximately 20 months after the end of the reference year.
Context
As a first legal basis, Council Directive 85/339/EEC of June 1985 required the establishment of national programs for the reduction in the volume of beverage containers disposed as waste in order to raise consumer awareness of the advantage of using refillable containers. The directive was repealed by the introduction of the European Parliament and Council Directive 94/62/EC of 20 December 1994 on packaging and packaging waste (Packaging Waste Directive). This directive aims at harmonising national measures concerning the management of packaging and packaging waste and lays down measures aimed, as a first priority, at preventing the production of packaging waste and, as additional fundamental principles, at:
- reusing packaging;
- recycling; and
- implementing other forms of recovering packaging waste hence reducing the final disposal of such waste.
It also limits the level of heavy metals in packaging.
Latest legal acts: Directive (EU) 2018/852 amending Directive 94/62/EC on packaging and packaging waste (Packaging Waste Directive).
- Commission Implementing Decision 2019/665 amending Commission Decision 2005/270/EC applies from reference year 2018.
Definitions
Packaging is defined as any material that is used to contain, protect, handle, deliver or present goods. Packaging waste can arise from a wide range of sources including supermarkets, retail outlets, manufacturing industries, households, hotels, hospitals, restaurants and transport companies. Items like glass bottles, plastic containers, aluminium cans, food wrappers, timber pallets and drums are all classified as packaging.
Article 3 and Annex I of the Packaging Waste Directive specify 'packaging' in further detail.
The main packaging materials are glass, paper and cardboard, plastics, metals (aluminium and steel) and wood.
Composite materials are made of paper, plastic and metal which could not be separated by hand. Composites are reported under their predominant material by weight. Other packaging materials are counted as 'others'.
Recovery includes recycling, energy recovery and other forms of recovery. Annex II of the Waste Framework Directive 2008/98/EC (consolidated version) defines energy recovery and other forms of recovery.
The weight of recovered or recycled packaging waste shall be the input of packaging waste to an effective recovery or recycling process. If the output of a sorting plant is sent to effective recycling or recovery processes without significant losses, it is acceptable to consider this output to be the weight of recovered or recycled packaging waste. The weight should exclude non-packaging materials as far as practical.
Reusable packaging is only counted once in its lifetime and not after every refilling and purchase trip.
The recovery rates are the total quantity of recovered materials divided by the total quantity of generated packaging waste.
The recycling rates are usually the total quantity of recycled materials divided by the total quantity of generated packaging waste, except in some cases. The data set 'Recycling rates of packaging waste for monitoring compliance with policy targets, by type of packaging (env_waspacr)' includes, for two types of waste material (plastic and wood), 'Adjusted recycling rate'. That means the recycling rates adjusted for monitoring compliance with policy targets in accordance with Article 6 of Directive 94/62/EC and Article 6b(1) of Decision 2005/270. The relevant rates for those materials are:
- Recycling rate of plastic packaging waste counts exclusively material that is recycled back into plastic (material recycling / generation).
- Recycling rate of wooden packaging waste is calculated including repair (recycling + repair of wooden packaging waste / generation + repair of wooden packaging waste).
Direct access to
See also
- Waste statistics
- Consumption of plastic carrier bags - estimates
- End-of-life vehicle statistics
- Food waste and food waste prevention - estimates
- Municipal waste statistics
- Recycling – secondary material price indicator
- Waste management indicators
- Waste shipment statistics
- Waste statistics - electrical and electronic equipment
- Waste statistics - recycling of batteries and accumulators
Publications
- All publications on waste issued by Eurostat.
Database
- Waste, see:
Dedicated section
Methodology
- Packaging waste (ESMS metadata file — env_waspac_esms)
- Guidance on packaging and packaging waste
Legislation
- Directive 94/62/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 1994 on packaging and packaging waste (consolidated version)
- Commission Decision 2005/270/EC of 22 March 2005 establishing the formats relating to the database system pursuant to Directive 94/62/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 December 1994 on packaging and packaging waste
- Directive (EU) 2018/852 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 on packaging and packaging waste
- Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2019/665 of 17 April 2019 amending Decision 2005/270/EC establishing the formats relating to the database system pursuant to European Parliament and Council Directive 94/62/EC on packaging and packaging waste (notified under document C(2019) 2805) (Text with EEA relevance.)




