Archive:Extra-EU trade in manufactured goods
Data from April 2022
Planned update: April 2023
Highlights
In 2021, manufactured goods made up 82% of all EU exports and 70% of EU imports.
China and the United States were the main EU trading partners for manufactured goods in 2021.
EU trade in manufactured products, 2002 - 2021
This article focuses on the structure and evolution of the European Union (EU) international trade in manufactured goods: imports and exports at EU level.
This article is part of an online publication providing recent statistics on international trade in goods, covering information on the EU's main partners, main products traded, specific characteristics of trade as well as background information.
Full article
The Standard international trade classification (SITC) distinguishes four main groups (sections) of manufactured goods:
- chemicals (SITC 5);
- manufactured goods classified chiefly by material (SITC 6);
- machinery and vehicles (SITC 7);
- miscellaneous manufactured articles (SITC 8).
Categories 6 and 8 are often grouped together as 'other manufactured goods'. This grouping is also used in this article.
Manufactured goods dominate international trade
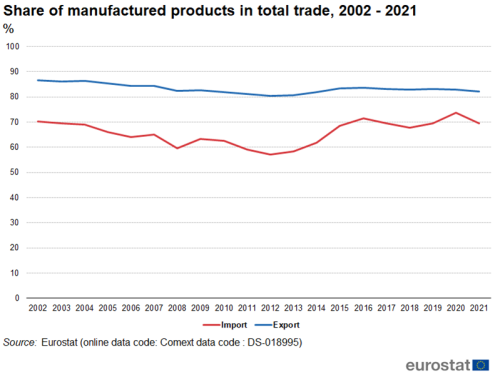
The share of manufactured goods in total exports of goods was 87 % in 2002 (Figure 1). It had its lowest value in 2012 at 80 % then gradually recovered, standing at 82 % in 2021. There was more fluctuation in the share of manufactured goods in total imports of goods. It was 70 % in 2002. It had its lowest value in 2012 at 57 %, peaked in 2020 at 74 % and in 2021 dropped to 70 %. These fluctuations in the share of imports are closely correlated to price developments of energy products.
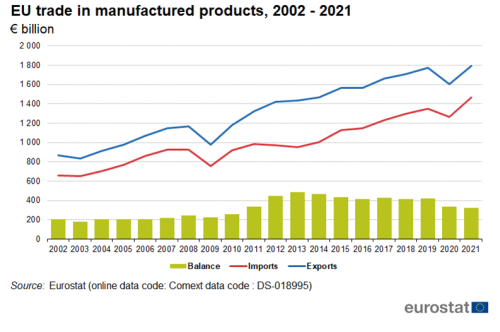
Between 2002 and 2019, exports of manufactured goods increased from €865 billion to €1 773 billion (Figure 2). Due to the COVID-19 pandemic exports fell to €1 603 billion in 2020 but recovered to €1 794 billion in 2021. Imports of manufactured goods increased from €662 billion in 2002 to €1 350 in 2019, then fell to €1 266 billion in 2020 but more than recovered in 2021, reaching €1 470 billion. In this period, the trade balance increased from €204 billion in 2002 to €324 billion in 2021. It had its lowest value of €182 billion in 2003 and peaked in 2013 at €483 billion.
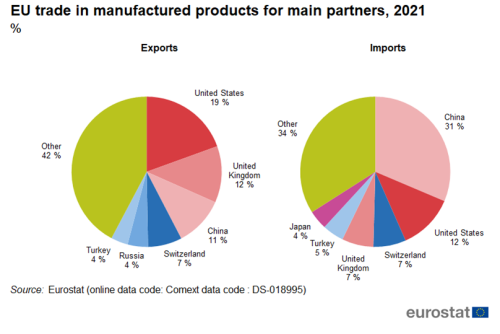
The United States was the largest export partner for manufactured goods in 2021 with a share of 19 %, followed by the United Kingdom (12 %) and China (11 %). The top six partners accounted for 58 % of total exports of manufactured goods. China was the largest import partner for manufactured goods in 2021 with a share of 31 %, followed by the United States (12 %), Switzerland and the United Kingdom (both 7 %). The top six partners accounted for 66 % of total imports of manufactured goods.
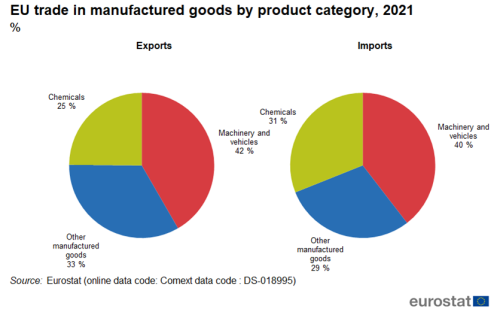
Within manufactured goods, machinery and vehicles was the largest group, both in exports (42 %) and imports (40 %). In exports other manufactured goods (33 %) was the second largest group followed by chemicals (25 %). In imports, chemicals (31 %) was the second largest group followed by other manufactured goods (29 %) .
In the next three paragraphs these three groups are discussed in more detail.
Road vehicles largest category in exports of machinery and vehicles
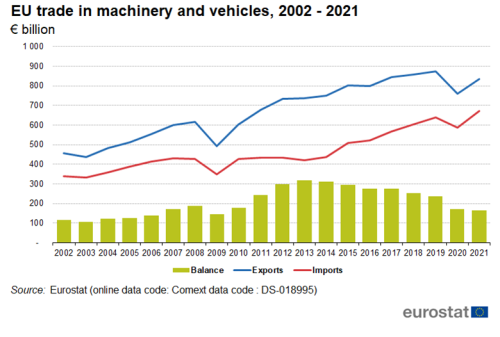
Between 2002 and 2021, exports of machinery and vehicles increased from €455 billion to €836 billion (Figure 5); imports increased from €338 billion to €671 billion. There was a trade surplus throughout the whole period. It had its lowest value of €106 billion in 2003 and peaked in 2013 at €317 billion. It decreased to €164 billion in 2021.
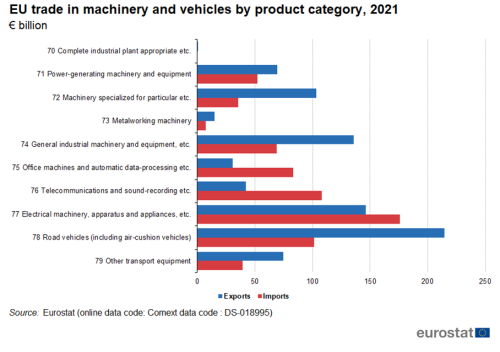
The largest category in exports of machinery and vehicles was road vehicles with 26 % (Figure 6). It was followed by electrical machinery and parts thereof (18 %) and general industrial machinery and equipment and (16 %). The largest category in imports of machinery and vehicles was electrical machinery and parts thereof with 26 %. It was followed by telecommunications and sound-recording with (16 %) and road vehicles (15 %).
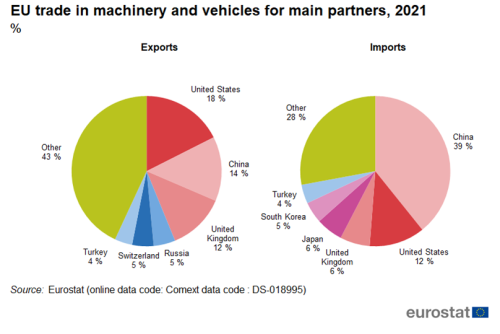
The United States was the largest export partner for machinery and vehicles in 2021 with a share of 18 % (Figure 7), followed by China (14 %) and the United Kingdom (12 %). The top six partners accounted for 57 % of total exports of machinery and vehicles. China was the largest partner for imports of machinery and vehicles in 2021 with a share of 39 %, followed by the United States (12 %). The top six partners accounted for 72 % of total imports of machinery and vehicles.
China accounts for almost a third of the imports of other manufactured goods
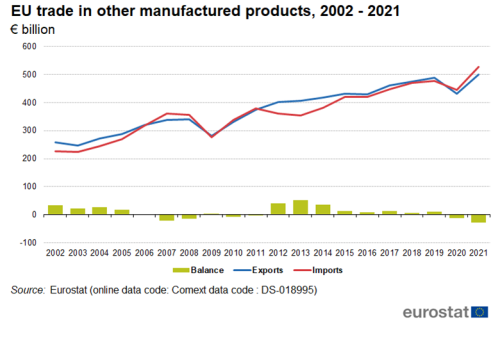
Between 2002 and 2021, exports of other manufactured goods increased from €259 billion to €499 billion (Figure 8). In this period, imports of other manufactured goods increased from €226 billion to €527 billion. The trade balance was €33 billion in 2002, it dropped to €-21 billion in 2007 and peaked in 2013 at €52 billion. From 2019 to 2021 it went from a surplus of €12 billion to a deficit of €28 billion, its lowest value during the whole period.
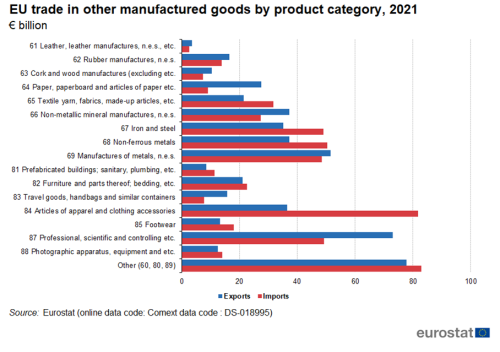
The largest categories in exports of other manufactured goods were miscellaneous manufactured articles (16 %), followed closely by professional, scientific and controlling equipment with 15 % (Figure 9). The largest categories in imports of other manufactured goods were articles of apparel and clothing accessories and miscellaneous manufactured articles (both 16 %).
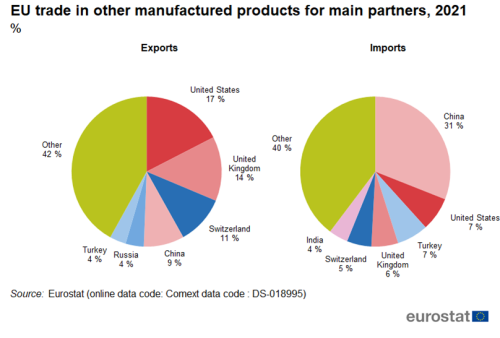
The United States (17 %) and the United Kingdom (14 %) and Switzerland (11 %) were the largest export partners for other manufactured goods in 2021 (Figure 10). The top six partners accounted for 58 % of total exports of other manufactured goods. China was the largest import partner for other manufactured goods in 2021 with a share of 31 %. The top six partners accounted for 60 % of total imports of other manufactured goods.
Exports of chemicals tripled since 2002
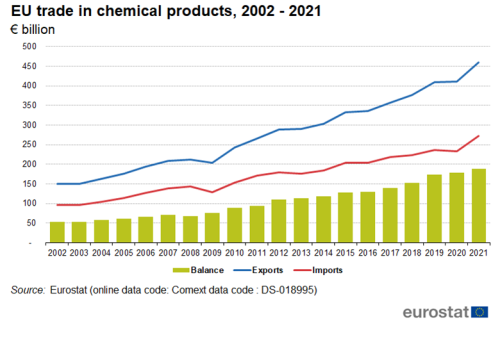
Between 2002 and 2021, exports of chemicals increased from €151 billion to €459 billion (Figure 15) while imports of chemicals increased from €97 billion to €271 billion. Between 2002 and 2021, the trade balance increased from €54 billion to a peak of €188 billion in 2021.
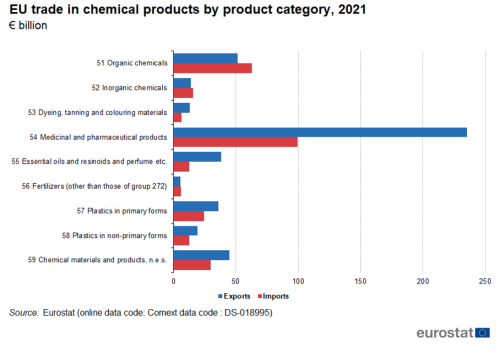
The largest category in exports of chemicals was medicinal and pharmaceutical products with 51 % (Figure 12). It was followed by organic chemicals with 11 %. The largest category in imports of chemicals was also medicinal and pharmaceutical products with 37 %, again followed by organic chemicals with 23 %.
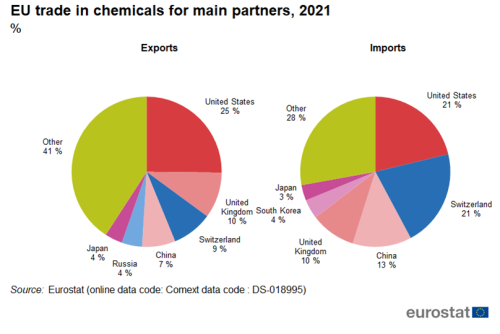
The United States was the largest export partner for chemicals in 2021 with a share of 25 %, followed by the United Kingdom with 10 % (Figure 13). The top six partners accounted for 59 % of total exports of chemicals. Switzerland and the United States were the largest import partners for chemicals in 2021, each with a share of 21 %. The top six partners accounted for 72 % of total imports of chemicals.
Product categories
Some of the labels in Figures 7, 11, 12 and 16 have been shortened for graphical reasons. The complete label for each category is shown in the table below.
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
EU data come from Eurostat’s COMEXT database. COMEXT is the Eurostat reference database for international trade. It provides access not only to both recent and historical data from the EU Member States but also to statistics of a significant number of third countries. International trade aggregated and detailed statistics disseminated from Eurostat website are compiled from COMEXT data according to a monthly process. Because COMEXT is updated on a daily basis, data published on the website may differ from data stored in COMEXT in case of recent revisions.
EU data are compiled according to community guidelines and may, therefore, differ from national data published by Member States. Statistics on extra-EU trade are calculated as the sum of trade of each of the 27 Member States with countries outside the EU. In other words, the EU is considered as a single trading entity and trade flows are measured into and out of the area, but not among Member States within the EU.
The United Kingdom is considered as an extra-EU partner country for the EU for the whole period covered by this article. However, the United Kingdom was still part of the internal market until the end of the transitory period (31 December 2020), meaning that data on trade with the United Kingdom are still based on statistical concepts applicable to trade between the EU Member States. Consequently, while imports from any other extra-EU trade partner are grouped by country of origin, the United Kingdom data reflect the country of consignment. In practice this means that the goods imported by the EU from the United Kingdom were physically transported from the United Kingdom but part of these goods could have been of other origin than the United Kingdom. For this reason, data on trade with the United Kingdom are not fully comparable with data on trade with other extra-EU trade partners.
Unit of measure
Trade values are expressed in billions (1 000 millions) of euros. They correspond to the statistical value, i.e. to the amount which would be invoiced in case of sale or purchase at the national border of the reporting country. It is called a FOB value (free on board) for exports and a CIF value (cost, insurance, freight) for imports.
Context
The EU is the world's biggest exporter of manufactured goods, and is a global market leader for high-quality products. Thanks to some of its key assets such as chemicals, pharmacy products, motor vehicles and non-electrical machinery, the European Union has a substantial trade surplus for manufactured products.
Direct access to
- International trade data (t_ext)
- International trade long-term indicators (t_ext_lti)
- International trade short-term indicators (t_ext_sti)
- International trade data (ext)
- International trade long-term indicators (ext_lti)
- International trade short-term indicators (ext_sti)
- International trade detailed data (detail)
- International trade in goods statistics - background
- International trade in goods (ESMS metadata file — ext_go_agg_esms)
- User guide on European statistics on international trade in goods
- Regulation (EC) No 471/2009 of 6 May 2009 on Community statistics relating to external trade with non-member countries
- Summaries of EU Legislation: Extrastat: statistics relating to trade with non-EU countries
- Regulation (EU) No 92/2010 of 2 February 2010 implementing Regulation (EC) No 471/2009, as regards data exchange between customs authorities and national statistical authorities, compilation of statistics and quality assessment
- Regulation (EU) No 113/2010 of 9 February 2010 implementing Regulation (EC) No 471/2009 , as regards trade coverage, definition of the data, compilation of statistics on trade by business characteristics and by invoicing currency, and specific goods or movements.