Quarterly sector accounts - households
Data extracted on 25 January 2024.
Planned article update: 26 April 2024.
Highlights
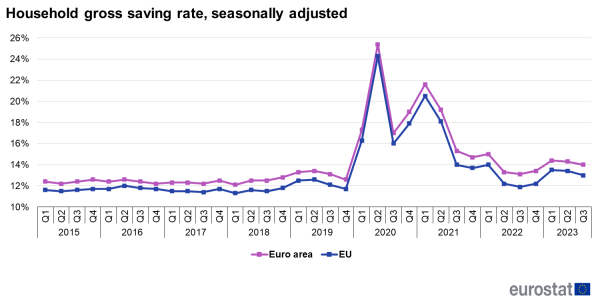
In the third quarter of 2023, the household saving rate went down to 14 % in the euro area and down to 13 % in the EU.
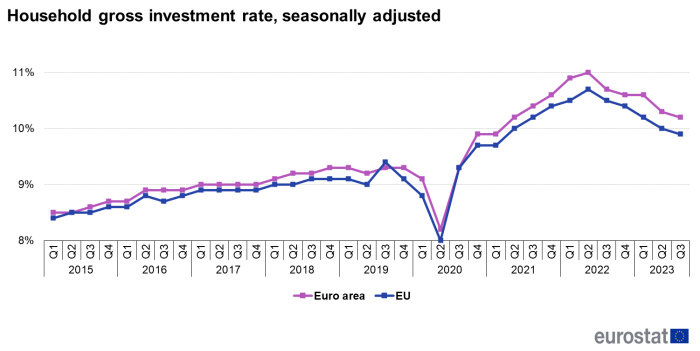
In the third quarter of 2023, the household investment rate was nearly stable at 9.7 % in the euro area and at 9.4 % in the EU.
This article focuses on a selection of indicators on quarterly sector accounts for households in the European Union (EU) and the euro area. Covered are, among others, the household saving rate and the household investment rate. A similar article focuses on quarterly sector accounts for non-financial corporations, covering, among others, the business investment rate and the profit share of non-financial corporations.
Full article
The household saving rate decreased in the euro area and the EU
The household saving rate in the euro area (EA-20) was 14 % in the third quarter of 2023, showing a decline from 14.3 % in the previous quarter. Similarly, in the EU, the household saving rate was 13 % in the third quarter of 2023, compared to 13.4 % in the second quarter of 2023.
These data come from a detailed set of seasonally adjusted[1] quarterly European sector accounts released by Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union and the European Central Bank (ECB).
Nearly stable household investments in the euro area and the EU
In the third quarter of 2023, in the EU, the household investment rate slightly decreased to 9,4 % in the third quarter of 2023, compared with 9,5 % in the second quarter of 2023. Similarly, in the euro area, the household investment rate slightly decreased to 9,7 % in the third quarter of 2023, compared with 9,8 % in the previous quarter.
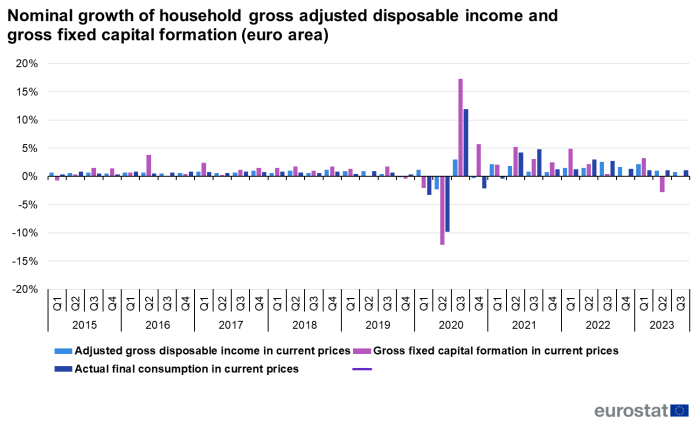
During the third quarter of 2023, the euro area witnessed a 0.8 % increase in household income in nominal terms, slower than the growth rate of consumption (+1.1%)[2]. This resulted in decrease in saving rate, as indicated earlier. Furthermore, there was a decrease of 0.1 % in investment (gross fixed capital formation), consisting primarily of dwellings.
Data sources
The compilation of the European sector accounts follows the European System of Accounts 2010 (ESA 2010) and covers the period from the first quarter of 1999 onwards.
Institutional sectors bring together economic units with broadly similar characteristics and behaviour, namely: households (including non-profit institutions serving households), non-financial corporations, financial corporations, government and the rest of the world. In the latter, to measure the external transactions of the euro area / EU, it is necessary to remove cross-border flows within the area concerned.
The ECB and Eurostat publish integrated non-financial and financial accounts, including financial balance sheets, for the euro area. Eurostat also publishes the non-financial accounts of the European Union.
Eurostat's website includes detailed sequence of accounts and derived key indicators, which also include the indicators that combine non-financial and financial accounts such as debt-to-income ratios.
The full set of quarterly sector accounts is published for euro area / EU aggregates. Quarterly sector accounts data are also available for most of the European Economic Area (EEA) Member States in the Eurostat database, and a subset of quarterly key indicators is published around 102 days after each quarter at quarterly data and annual data. The EEA members whose GDP is below 1 % of the EU total do not have to transmit the quarterly accounts of households to Eurostat.
- The European Union (EU) consists of 27 Member States: Belgium, Bulgaria, Czechia, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Croatia, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Hungary, Malta, the Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland and Sweden plus the EU institutions.
- The euro area (EA-20) consists of 20 Member States: Belgium, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Croatia, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Austria, Portugal, Slovenia, Slovakia and Finland, plus the European Central Bank, the European Stability Mechanism and the European Financial Stability Facility. From 1 January 2023 the euro area (EA20) also includes Croatia. The aggregate data series presented in this article refer to EA20.
Source data for tables and graphs
The detailed tables ![]() are available here.
are available here.
Direct access to
Notes
- ↑ Seasonal adjustment has been performed using the Tramo-Seats method. The seasonally adjusted series are built up indirectly as the sum of seasonally adjusted components.
- ↑ In this article, household income/consumption refers to the adjusted gross disposable income / actual final consumption of households including the value of goods and services (e.g. in education and health) financed by the government. The goods and services funded by the government are recorded under 'social transfers in kind'.