Archive:Agricultural census in Cyprus
This article has been archived.
This article is part of a series of country-specific essays on the results of the European Union (EU) Farm structure survey (FSS) 2010.The FSS collects information on the structural characteristics of agricultural holdings (land use, livestock and labour force) and is carried out by all European Union Member States every 10 years as an Agricultural census, with two or three additional, intermediate sample surveys carried out in-between. The present analysis of the Cypriot farm structure includes a comparison with the Agricultural census 2003, the first one to be conducted in the country in compliance with EU regulations.

Source: Eurostat (ef_kvaareg) (ef_ov_kvaa) (demo_pjan) and FSS 2003 and 2010

Source: Eurostat (ef_kvaareg) (ef_ov_kvaa)
Source: Eurostat (ef_lu_ovcropaa) (ef_oluaareg)

Source: Eurostat (ef_lu_ovcropaa) (ef_oluaareg)
Source: Source: Eurostat (ef_pmhouscatlaa)
Main statistical findings
Key indicators
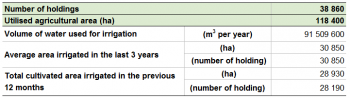
As presented in Table 1, there were 38 860 agricultural holdings in Cyprus in 2010; among the other European Member States, Denmark (42 100) and Slovakia (24 460) recorded comparable values. In Cyprus, 6 340 farms ceased their activities (-14%) over the inter-census period as there were 45 200 farms recorded in 2003.
The utilised agricultural area (UAA) also decreased (-24%) between the two reference years and stood at 118 400 hectares in 2010. This equated to 13% of the entire country's area, which was one of the lowest proportions in the EU-28.
In 2010, Cyprus was among the EU Member States with the smallest average area per farm, with only Malta having a lower value. As the decrease in the agricultural area (-24%) was sharper than the fall in the number of farms (-14%), the average size of the holdings actually decreased in Cyprus (-12%): from 3.5 hectares per farm in 2003 to 3.0 hectares in 2010.
As seen in the vast majority of the EU-28 countries, the Cypriot agricultural labour force also decreased over the period of analysis, from 86 240 workers in 2003 to 82 040 in 2010 (-4.9%). However, the agricultural labour force still represented 19% of the active population [1] in 2010, one of the highest proportions within the EU-28.
The Cypriot livestock, expressed in livestock units (LSU), decreased by about 56 000 LSU over the 2003-2010 timeframe (-22%) to 200 750 LSU in 2010. Among the other EU Member States, Estonia (306 280 LSU) and Luxembourg (167 660 LSU) were the Member States above and below Cyprus in terms of livestock units.
Agricultural holdings
As shown in Figure 1, 90% of Cypriot agricultural holdings (34 820) had less than 5 hectares of agricultural land in 2010. Despite the fact that they represented the vast majority of the country’s population of farms, those holdings covered only a small portion (31%) of Cyprus’ UAA. Among the nine different size classes, the majority of holdings (74%) had 0.1 ha to 1.9 hectares of agricultural land with 28 710 farms falling into this category. As expected, the very largest farms (those with at least 100 hectares of UAA) covered the biggest area (19 770 hectares, 17% of total UAA) even though there were only 120 of them.
See detailed data at NUTS 2 level for 2003 and 2010
Economic size of the farm
Between 2007 and 2010 the totalstandard output (SO) of agricultural holdings in Cyprus, which is calculated by adding all the SO values per hectare of crop and per head of livestock of the farms, decreased by about a quarter (- EUR 145 million) to EUR 459 million in 2010. Among the other EU Member States, Estonia (EUR 594 million) and Luxembourg (EUR 268 million) had the closest values of SO.
Although they registered the biggest decrease (-41%) compared to 2007, holdings with at least EUR 500 000 (see Table 2) represented 27% of the country’s Standard Output in 2010 (EUR 125 million), the largest proportion of all the size classes. At the other end of the scale, farms with an SO of less than EUR 2 000 were the only size class that saw an increase (+3.3%).
Agricultural holdings by main type of farming
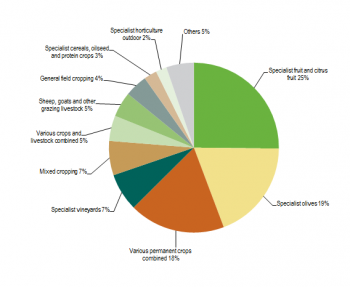
In terms of the number of holdings, three main types of production characterised the structure of agriculture in Cyprus: the production of fruits and citrus fruits, which accounted for a quarter of the entire population of holdings, the production of olives (19%) and the production of various permanent crops (18%). As shown in Figure 2, holdings specialised in any other type of agricultural production made up proportions lower than 10%.
If the economic size is taken into account, the ranking looks different as dairy farms accounted for the largest proportion (16%). Farms dedicated to sheep, goats and other grazing livestock made up a slightly lower proportion (15%), followed by specialist pig farms (13%) and those specialised in fruits and citrus fruits (12%).
See detailed data at NUTS 2 level for 2010
Land use
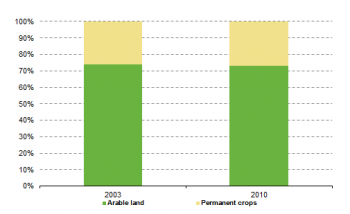
The Utilised Agricultural Area (UAA) is the total area used by a farm, regardless of the type of tenure or whether it is used as a part of common land. It includes four major components: arable land, permanent grassland and meadow, permanent crops and kitchen gardens.
In Cyprus, the agricultural area was mainly made up of arable land (115 140 hectares, 72% of UAA) and permanent crops (40 780 hectares, 26% of UAA). Both components decreased in area between the two reference years, the arable land by 26% and permanent crops by 23%.
See detailed data at NUTS 2 level for 2003 and 2010
Arable land
As presented in Table 3, the three main components of Cypriot arable land in 2010 were cereals (33 280 ha), fodder crops (32 860 ha) and fallow land (9 470 ha), accounting for 28%, 28% and 8% of arable land respectively. The area of cereals more than halved between 2003 and 2010, whereas that of fodder crops increased by 38%. Fallow land saw a large 75% increase in area between the two reference years.
See detailed data at NUTS 2 level for 2003 and 2010
Permanent crops
The land dedicated to permanent crops covered about a quarter of the country’s UAA with 31 340 hectares in 2010. Among the different types of permanent crops, olive plantations accounted for the largest proportion (9.8%) of the total agricultural area with 11 640 hectares. Vineyards (7 620 ha) and fruits and berry plantations (6 970 ha) had similar areas and accounted for 6.4% and 5.9% respectively of the country’s UAA.
See detailed data at NUTS 2 level for 2010 and 2003
Livestock
Statistics on livestock use two different units of measurement, the number of head (number of animals) and the livestock unit (LSU), with the latter allowing comparison between different types.
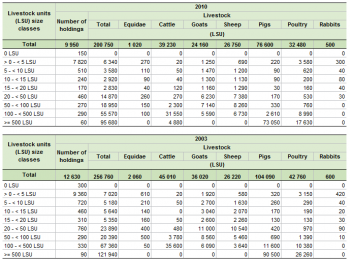
In 2010, 9 950 holdings farmed 200 750 LSU in Cyprus. Similar decreases were observed for both the number of farms with livestock (-21%) and the population of farm animals (-22%) between 2003 and 2010. As a result, the average number of livestock per farm remained stable at about 20 LSU per farm in both reference years. Although the decrease in the number of farms with livestock was common to all size classes of farms, holdings with 10 to 14 LSU had the biggest drop (-48%), while holdings with 50 to 99 LSU had the smallest (-7%).
Labour force
As shown in Table 5, 82 040 people were regularly working on farms in Cyprus in 2010, a 4.9% decrease compared with 2003. In absolute terms, 4 200 people left the agricultural sector over the timeframe under analysis. The proportional decrease in the agricultural labour force is much larger (-42%) if the annual work unit (AWU) is taken into account as figures dropped from 28 730 AWU in 2003 to 16 720 AWU in 2010.
Management practices
Type of tenure
In 2010, the majority of Cypriot agricultural land (52%) was farmed by tenants (see Table 6). A further 46% was farmed by the land owners and the remaining 2.3% was farmed in partnership by the landlord and the sharecropper under a written or oral share-farming contract (or under other type of tenure).
Irrigation
In 2010, the total irrigable area stood at 40 310 hectares. About a quarter (24%) of the Cypriot agricultural area was irrigated at least once a year, equating to 28 930 hectares. However it should be noted that the extent of the irrigated area varies over the years according to the weather conditions.
As presented in Figure 7, the largest area irrigated was olive plantations, which accounted for 24% of the total irrigated area, followed by fruits and berry plantations (20%), other crops on arable land (14%), potatoes (13%) and citrus plantations (13%).
In Cyprus, about 91 million cubic metres of water were used to irrigate 28 930 hectares of agricultural area in 2010. This equates to 3 246 cubic metres of water per hectare of irrigated land. Information on the amount of irrigation water was estimated using a multiple regression model which took into account the type of crop, the irrigated area and its location.
Animal housing
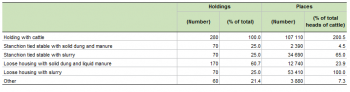
Within the whole EU-28, Cyprus had the lowest number of farms with cattle (280); these holdings farmed 53 410 head of cattle in 2010.
The most common types of cattle housing were those where the animals are allowed to move freely (loose housing). Going by the number of holdings, loose housing where the manure is typically removed mechanically from the building as solid dung was the most common with 170 farms having this type of housing system. However going by the total cattle capacity (number of places), loose housing where the animal waste drops below the floor into a pit to form slurry was the most common (53 410 places). In Cyprus, the capacity of cattle housing was twice as high as the number of heads of cattle, which explains why the related ratio is 200%.
Other gainful activities
In 2010 there were 390 holdings with activities other than farm work directly related to the holding and having an economic impact on it, the second smallest number across the EU Member States, ahead of Malta (270). Farms with extra sources of income represented only a marginal proportional of Cypriot holdings (1.0%) and were only engaged in the processing of farm products.
Organic farming
Organic agriculture is an ecological production management system that promotes and enhances biodiversity, biological cycles, and soil biological activity. It is based on the minimal use of off-farm inputs and on management practices that restore, maintain or enhance ecological harmony.
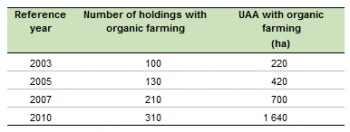
Although the number of holdings practising organic farming has trebled in Cyprus between 2003 and 2010, there were still only 310 organic farms in 2010. As a result the area under organic farming covered only 1.4% (1 640 ha) of the country’s UAA.
See detailed data at Nuts 2 level for 2010, 2007, 2005, 2003 and 2000
Data sources and availability
Methodological notes Cyprus – Agricultural census 2010
In Cyprus, the first Farm Structure Survey conducted in compliance with EU regulations was carried out as an exhaustive survey in 2003. The Agricultural census 2010 was the first to be conducted in Cyprus after the country’s accession to the EU in 2004; the responsible body was the Statistical Service of Cyprus (CYSTAT).
Survey on agricultural production methods (SAPM)
In 2010 a unique survey was carried out together with the Agricultural census, the Survey on agricultural productions methods (SAPM). This survey collected data at regional level needed to establish agri-environmental indicators as indicated in COM final 508/2006 and to evaluate the greening of the Common agricultural policy.
Data were collected according to the specifications listed in Annex V of the above mentioned regulation, namely data on tillage methods, soil conservation, landscape features, animal grazing, animal housing, manure application, manure storage and treatment facilities and irrigation.
In Cyprus, the SAPM was conducted as a sample survey; a stratified sampling method was employed to select about 7 200 holdings from a population of 38 860.
Reference period
Information on the structure of Cypriot agriculture refers to the 1 October 2009 – 30 September 2010 timeframe. However, data on livestock were collected with reference to 1 November 2010, and information on rural development measures refer to the calendar years 2007, 2008 and 2009.
Thresholds for agricultural holdings
In Cyprus the vast majority of holdings are small in size, therefore all farms with at least 0.1 hectares of agricultural area or 0.05 hectares of glasshouse crops were surveyed in 2010. Moreover, holdings falling below this threshold but complying with a set of different physical thresholds (related to head of livestock) were also included in the target population.
Common land
Common land is land that does not directly belong to any agricultural holding but on which common rights apply. It can consist of pasture, horticultural or other land. The treatment of the common land used by an agricultural holding might differ from country to country.
In Cyprus, information on common land was recorded under the category “other types of tenure”, using the same methodology already employed in the previous waves of the FSS.
Geo-reference of the holding
In Cyprus, information on the location of the farms was obtained through the geo code of the community where the holdings are located.
Economic size
From FSS 2007 onwards, the Standard output (SO), a new classification of the economic size of the holding, is used. The SO has replaced the Standard gross margin (SGM) used before. Nonetheless, for comparability reasons, in FSS 2007 both classifications are available.
Volume of irrigation water
In Cyprus, the volume of water used for irrigation was estimated using a multiple regression model, which took into account the irrigated area, the type of cultivation and the community where the irrigated area was located. The model included all types of crops, with the exception of those cultivated in greenhouses and kitchen gardens.
Context
European Commission Rural development policy aims to improve competitiveness in agriculture and forestry, the environment and the countryside, as well as to improve the quality of life in rural areas, and to encourage the diversification of rural economies.
As agriculture has modernised and the importance of industry and services within the economy has increased, so agriculture has become much less important as a source of jobs. Consequently, increasing emphasis is placed on the role farmers can play in rural development, including forestry, biodiversity and the diversification of the rural economy, in order to create alternative jobs and provide environmental protection in rural areas.
The FSS continues to adapt in order to provide timely and relevant data to help analyse and follow these developments.
See also
- Agricultural census 2010
- All articles on Cyprus
- All farm structure articles by country
- Farm structure statistics
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Agriculture, fishery and forestry statistics — Main results – 2010-11 - 2012 edition
- Farm Structure in Cyprus - 2005 - Issue number 21/2007
- Farm Structure Survey in Cyprus - 2007 - Issue number 82/2009
- Structure of Agricultural Holdings - Cyprus 2003 - Statistics in focus 34/2005
Main tables
- Agriculture, see:
- Farm structure: historical data (1990-2007) (t_ef)
Database
- Agriculture, see:
- Farm structure (ef)
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Farm structure (ESMS metadata file — ef_esms)
- Methodological Report - FSS 2007 Cyprus
- Methodological Report - FSS 2010 Cyprus
Source data for tables and figures (MS Excel)
Other information
- Regulation 1166/2008 of 19 November 2008 on farm structure surveys and the survey on agricultural production methods and repealing Council Regulation 571/88
- Regulation 1200/2009 of 30 November 2009 implementing Regulation 1166/2008 on farm structure surveys and the survey on agricultural production methods, as regards livestock unit coefficients and definitions of the characteristics
External links
Notes
- ↑ A value calculated over the active population in the 4th quarter 2010 of the EU Labour force survey (LFS) Population, activity and inactivity - quarterly data