Archive:Norway-EU - international trade in goods statistics
Data extracted in March 2019.
Planned article update March 2020.
Highlights
This article provides a picture of the international trade in goods between the European Union (EU) and Norway. It analyses the type of goods exchanged between the two economies and the shares of each EU Member State in those exchanges.
This article is part of an online publication providing recent statistics on international trade in goods, covering information on the EU's main partners, main products traded, specific characteristics of trade as well as background information.
Full article
EU and Norway in world trade in goods
Figure 1a shows the position of Norway among the largest traders in the world. The four largest exporters were China (EUR 2 004 billion, 16 %), the EU (EUR 1 879 billion, 15 %), the United States (EUR 1 368 billion, 11 %) and Japan (EUR 618 billion, 5 %). The four largest importers were the United States (EUR 2 131 billion, 17 %), the EU (EUR 1 857 billion, 15 %), China (EUR 1 632 billion, 13 %) and Japan (EUR 594 billion, 5 %). Figure 1b has some more details. It shows that Norway (EUR 90 billion, 1 %) was the 24th largest exporter in the world between Iran (EUR 94 billion, 1 %) and South Africa (EUR 78 billion, 1 %). It was the 25th largest importer in the world (EUR 76 billion, 1 %) preceded by the Philippines (EUR 90 billion, 1 %).

Source: Eurostat (ext_lt_introle)
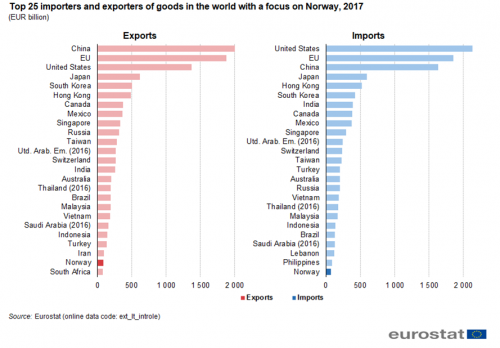
Source: Eurostat (ext_lt_introle)
Figure 2 shows the imports and exports of the EU and Norway indexed at 100 in 2007 for the period to 2017. It also shows the cover ratio (exports / imports) for this period. Exports from the EU were lowest in 2009 (89) and highest in 2017 (152). Imports to the EU were lowest in 2009 (85) and highest in 2017 (128). The cover ratio for the EU was lowest in 2008 (83 %) and highest in 2015 (104 %) and was 101 % in 2017. Exports from Norway were lowest in 2016 (81) and highest in 2012 (126) and was 91 in 2017. Imports to Norway were lowest in 2009 (84) and highest in 2017 (129). The cover ratio for Norway was lowest in 2017 (119 %) and highest in 2012 (184 %).

Source: Eurostat (ext_lt_introle)
Growing exports to but falling imports from Norway
Figure 3a shows the position of Norway among the largest trade partners of the EU. The four largest export partners of the EU were the United States (21 %), China (11 %), Switzerland (8 %) and Russia (4 %). The four largest import partners of the EU were China (20 %), the United States (13 %), Russia (8 %) and Switzerland (6 %). Figure 3b has some more details. It shows that Norway (EUR 54 billion, 2.8 %) was the seventh largest export partner of the EU, between Japan (EUR 65 billion, 3.3 %) and South Korea (EUR 49 billion, 2.5 %). In imports Norway (EUR 84 billion, 4.2 %) was the fifth largest partner of the EU, between Switzerland (EUR 109 billion, 5.5 %) and Turkey (EUR 76 billion, 3.8 %).

Source: Eurostat (ext_lt_maineu)

Source: Eurostat (ext_lt_maineu)
Figure 4 shows exports, imports and trade balance between the EU and Norway. In 2008 the EU had a trade deficit with Norway of EUR 52 billion. This remained a deficit throughout the whole period, reaching EUR 30 billion in 2018. EU exports to Norway were highest in 2018 (EUR 54 billion) and lowest in 2009 (EUR 37 billion). EU imports from Norway were highest in 2012 (EUR 100 billion) and lowest in 2016 (EUR 63 billion).
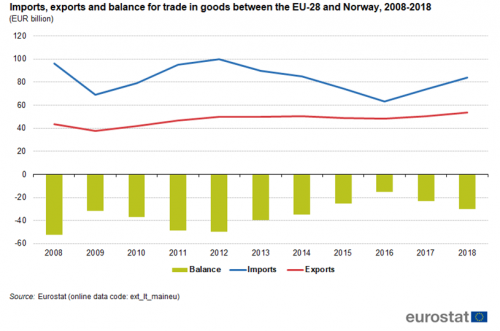
Source: Eurostat (ext_lt_maineu)
EU-Norway trade by type of goods
Figure 5 shows the breakdown of EU trade with Norway by SITC groups. The red colours denote the primary products: food & drink, raw materials and energy, while the blue colours show the manufactured goods: chemicals, machinery & vehicles and other manufactured goods. Finally, other goods are shown in green. In 2018, EU exports of manufactured goods (81 %) had a higher share than primary goods (17 %). The most exported manufactured goods were machinery & vehicles (42 %), followed by other manufactured products (28 %) and chemicals (10 %). In 2018, EU imports of primary goods (66 %) had a higher share than manufactured goods (19 %). The most imported primary goods were energy (55 %), followed by food & drink (9 %) and raw materials (2 %).
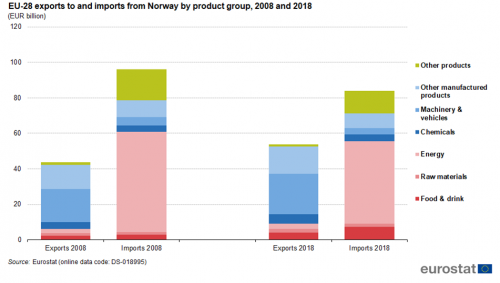
Source: Eurostat DS-018995
Figure 6 shows the evolution of EU imports and exports by SITC group since 2008. In 2018, the EU had trade surpluses in machinery & vehicles (EUR 19.1 billion), other manufactured products (EUR 6.9 billion), chemicals (EUR 1.6 billion) and raw materials (EUR 0.1 billion). The EU had trade deficits in food & drink (EUR 3.1 billion), other products (EUR 11.2 billion) and energy (EUR 43.5 billion).

Source: Eurostat DS-018995
EU-Norway most traded goods
Another interesting way to look at the data is to investigate the cover ratio (exports / imports) of traded goods, showing the direction of the trade flows between the two economies. These ratios can be found in the right-hand margin of Figure 7. Twelve products have ratios above 200, indicating EU exports to Norway are at least twice as large as EU imports from Norway. Six products have ratios below 50, indicating EU imports from Norway are at least twice a large as EU exports to Norway. Two products have ratios between 50 and 200, showing more balanced trade.

Source: Eurostat DS-018995
Trade with Norway by Member State
Figure 8a shows the EU imports from Norway by Member State. The three largest importers from Norway in the EU were the United Kingdom (EUR 21 873 million), the Netherlands (EUR 16 715 million) and Germany (EUR 11 945 million). Sweden (27 %) held the highest share for Norway in its total extra-EU imports.
Figure 8b shows the EU exports to Norway by Member State. The three largest exporters to Norway in the EU were Sweden (EUR 14 770 million), Germany (EUR 9 076 million) and Denmark (EUR 5 655 million). Sweden (26 %) held the highest share for Norway in its total extra-EU exports.
Figure 8c shows the trade balance between the EU Member States and Norway. Nineteen Member States had a trade surplus with Norway. The largest was held by Sweden (EUR 2 876 million), followed by Poland (EUR 1 047 million) and Czechia (EUR 682 million). Nine Member States had a trade deficit with Norway. The largest was held by the United Kingdom (EUR 18 046 million), followed by the Netherlands (EUR 11 904 million) and Belgium (EUR 3 823 million).

Source: Eurostat DS-018995
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
EU data is taken from Eurostat's COMEXT database. COMEXT is the reference database for international trade in goods. It provides access not only to both recent and historical data from the EU Member States but also to statistics of a significant number of third countries. International trade aggregated and detailed statistics disseminated via the Eurostat website are compiled from COMEXT data according to a monthly process.
Data are collected by the competent national authorities of the Member States and compiled according to a harmonised methodology established by EU regulations before transmission to Eurostat. For extra-EU trade, the statistical information is mainly provided by the traders on the basis of customs declarations.
EU data are compiled according to Community guidelines and may, therefore, differ from national data published by the Member States. Statistics on extra-EU trade are calculated as the sum of trade of each of the 28 EU Member States with countries outside the EU. In other words, the EU is considered as a single trading entity and trade flows are measured into and out of the area, but not within it.
Data for the other major traders are taken from the Comtrade database of the United Nations. Data availability differs among countries, therefore Figure 1 shows the latest common available year for all the main traders. For the calculation of shares world trade is defined as the sum of EU trade with non-EU countries (source: Eurostat) plus the international trade of non-EU countries (source: IMF Dots database).
Methodology
According to EU concepts and definitions, extra-EU trade statistics (trade between EU Member States and non-EU countries) do not record exchanges involving goods in transit, placed in a customs warehouse or given temporary admission (for trade fairs, temporary exhibitions, tests, etc.). This is known as 'special trade'. The partner is the country of final destination of the goods for exports and the country of origin for imports.
Product classification
Information on commodities exported and imported is presented according to the Standard international trade classification (SITC). A full description is available from Eurostat's classification server RAMON.
Unit of measure
Trade values are expressed in millions or billions (109) of euros. They correspond to the statistical value, i.e. to the amount which would be invoiced in the event of sale or purchase at the national border of the reporting country. It is called a FOB value (free on board) for exports and a CIF value (cost, insurance, freight) for imports.
Context
Trade is an important indicator of Europe's prosperity and place in the world. The bloc is deeply integrated into global markets both for the products it sources and the exports it sells. The EU trade policy is an important element of the external dimension of the 'Europe 2020 strategy for smart, sustainable and inclusive growth' and is one of the main pillars of the EU's relations with the rest of the world.
Because the 28 EU Member States share a single market and a single external border, they also have a single trade policy. EU Member States speak and negotiate collectively, both in the World Trade Organization, where the rules of international trade are agreed and enforced, and with individual trading partners. This common policy enables them to speak with one voice in trade negotiations, maximising their impact in such negotiations. This is even more important in a globalised world in which economies tend to cluster together in regional groups.
The openness of the EU's trade regime has meant that the EU is the biggest player on the global trading scene and remains a good region to do business with. Thanks to the ease of modern transport and communications, it is now easier to produce, buy and sell goods around the world which gives European companies of every size the potential to trade outside Europe.
Direct access to
- International trade in goods (t_ext_go), see:
- International trade in goods - long-term indicators (t_ext_go_lti)
- International trade in goods - short-term indicators (t_ext_go_sti)
- International trade in goods (ext_go), see:
- International trade in goods - aggregated data (ext_go_agg)
- International trade in goods - long-term indicators (ext_go_lti)
- International trade in goods - short-term indicators (ext_go_sti)
- International trade in goods - detailed data (detail)
- EU trade since 1988 by SITC (DS-018995)
- International trade in goods statistics - background
- International trade in goods (ESMS metadata file — ext_go_esms)
- User guide on European statistics on international trade in goods
- European Commission

