Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - Greece
- Data from June 2017. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables. Planned article update: July 2018.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles on Europe 2020 strategy, focusing on the situation in Greece.
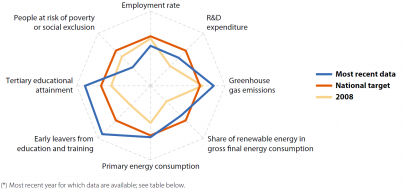
Source: Eurostat (see dedicated web section: Europe 2020 headline indicators)
Explanations on this radar chart are available here.
Main statistical findings
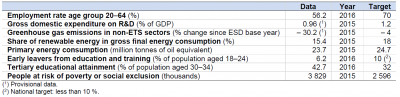
Source: Eurostat (see dedicated web section: Europe 2020 headline indicators)
Partly as a result of the economic slowdown, by 2015 Greece had reduced its GHG emissions in non-ETS sectors by 30.2 % compared to 1990 levels, significantly exceeding its national target for a 4 % reduction by 2020. Greece had already met its target on primary energy consumption in 2013 and has stabilised its energy efficiency at almost the same level since then. In 2016, the country also surpassed its national targets on tertiary education and early leavers from education and training, by 10.7 and 3.8 percentage points, respectively. Between 2008 and 2015, Greece almost doubled its share of renewable energy in gross final energy consumption and increased its expenditure on R&D as a share of GDP, thus narrowing the distance to the respective national targets. In contrast, in 2016 it was the EU country with the lowest employment rate and the greatest distance to its employment target. Moreover, the number of people living at risk of poverty or social exclusion increased by about 783 000 between 2008 and 2015, increasing the distance to the national target to more than 1.2 million people.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Main tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Europe 2020 is the EU’s agenda for jobs and growth for the current decade. It emphasises smart, sustainable and inclusive growth as a way to strengthen the EU economy and prepare its structure for the challenges of the next decade. As a main objective, the strategy strives to deliver high levels of employment, productivity and social cohesion in the Member States, while reducing the impact on the natural environment.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council COM(2011) 211 final.
Other information
- Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics