Archive:European Neighbourhood Policy - East - education statistics
- Data extracted in August 2016. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database. Planned article update: August 2017.
This article is part of an online publication; it presents information on a range of education statistics for the European Union (EU) and six countries that together form the European Neighbourhood Policy-East (ENP-East) region, namely, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine. Note that data shown in this article for Georgia excludes the regions of Abkhazia and Tskhinvali region/South Ossetia over which the government of Georgia does not exercise effective control, and data for Moldova excludes areas over which the government of the Republic of Moldova does not exercise effective control. The latest data for Ukraine generally exclude the territories which are not under effective control of Ukrainian government and the illegally annexed Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the City of Sevastopol (see specific footnotes for precise coverage).
The article includes information relating to expenditure on education, numbers of pupils and students, educational attainment among those aged 20–24, and a special focus on tertiary education.
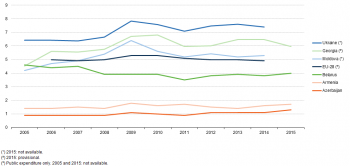
(% of GDP)
Source: Eurostat (gov_10a_exp) and (enpr_pseduc)
(thousand)
Source: Eurostat (educ_ilev) and (enpr_pseduc)
(% of 20–24 year olds)
Source: Eurostat (edat_lfse_03) and (enpr_siinr)
(% per annum)
Source: Eurostat (educ_ilev) and (enpr_pseduc)
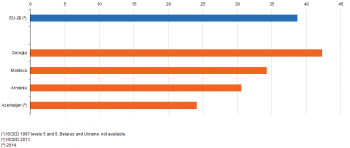
(%)
Source: Eurostat (edat_lfse_03) and (enpr_pseduc)
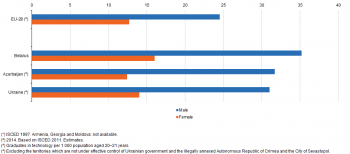
(per 1 000 male / female inhabitants aged 20–29)
Source: Eurostat (educ_uoe_grad02), (demo_pjangroup) and (enpr_pseduc)
Main statistical findings
Expenditure on education
Expenditure on education (relative to GDP) was lowest in Armenia and Azerbaijan
Figure 1 shows the importance of expenditure on education relative to GDP over the period 2005–15. For the EU-28, the ratio presented concerns only public expenditure and this fluctuated close to 5 % during those years for which data are available (2006–14). The modest increase observed in 2009 should be interpreted in its context, as the global financial and economic crisis resulted in GDP falling in 2009, while public educational expenditure continued to rise slightly; it was not until 2011 that the effects of austerity measures resulted in the level of educational expenditure stagnating across the EU-28 (as spending was unchanged compared with the year before).
Many of the ENP-East countries had similar developments, insofar as they saw the relative importance of educational expenditure rising between 2008 and 2009, followed by a subsequent contraction in the relative size of education spending through to 2011. More recent data for the ENP-East countries shows a general increase in the relative importance of educational expenditure. Looking at the most recent data available in Figure 1, spending on education represented 4 % or more of GDP in Ukraine, Georgia, Moldova and Belarus, while it was below 1 % and 2 % in Armenia and Azerbaijan.
Numbers of pupils and students
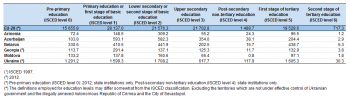
There were almost 109 million pupils and students attending pre-primary and educational establishments across the EU-28 in 2012, while the corresponding total for the six ENP-East countries was 12.8 million pupils and students in 2015. Table 1 presents the latest data available showing the distribution of these pupils and students across the various educational levels (classified according to the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED 1997)).
More than a fifth of the total number of pupils and students in Moldova attended a pre-primary educational establishment
An analysis of these data shows that 14.4 % of all pupils and students in the EU-28 attended pre-primary education (ISCED 1997 level 0) in 2012. The relative importance of pre-primary education varied considerably among the ENP-East countries in 2015, from around one twentieth (5.5 %) of the total number of pupils and students in Azerbaijan to more than one fifth (22.3 %) of the total number of pupils and students in Moldova.
Approximately a quarter (25.9 %) of all pupils and students in the EU-28 attended a primary education establishment in 2012. Shares for four of the ENP-East countries were slightly lower than this in 2015 — within the range of 21.06 % to 23.1 % — while primary education accounted for a higher share of the total number of pupils and students in Georgia (35.7 %; including 2012 data for pre-primary education in the denominator for the total number of pupils and students) and Azerbaijan (31.6 %).
Post-graduate students accounted for a higher share of the total number of pupils and students in the EU than in any of the ENP-East countries
At the other end of the educational system, 17.9 % of all pupils and students in the EU-28 attended the first stage of tertiary education in 2012, with a further 0.7 % following second stage tertiary (post-graduate) studies. Compared with the EU-28, a higher proportion of all pupils and students attended a first stage of tertiary education in Belarus (23.8 %) and Ukraine (23.0 %) in 2015, while the shares of first stage tertiary students in Georgia and Moldova were only slightly below that in the EU-28.
The relative share of post-graduate students in the EU-28 was higher than in any of the ENP-East countries; note that this group of students are particularly mobile and it is relatively common for post-graduate students to study abroad.
Educational attainment among those aged 20–24 years
Education and training are increasingly seen as a basis for international competitiveness and a drive towards creating high-value, high-skill economies. Indeed, the EU’s goal of becoming a smart, sustainable and inclusive economy is, in part, founded upon the premise of developing its knowledge-based economy.
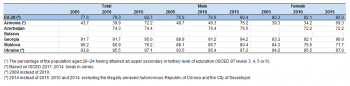
Almost the entire youth population in Ukraine and Georgia completed at least an upper secondary level of education
The share of the population aged 20–24 that reached at least an upper secondary educational level — otherwise referred to as the youth education attainment level — was 82.7 % in the EU-28 in 2015; note that from the 2014 reference year education statistics for the EU are based on the 2011 version rather than the 1997 version of ISCED. The latest data for 2015 marked an increase of 5.1 percentage points when compared with the corresponding share recorded in 2005 (see Table 2). Within the EU-28 there were differences in the youth education attainment level between the sexes, as the female youth education attainment level was, at 85.0 %, some 4.6 percentage points higher than the male level.
Among the ENP-East countries there were considerable differences in youth education attainment levels. In 2015, almost the whole of the youth population (aged 20–24) had completed at least an upper secondary level of education in Ukraine (97.1 %, 2014 data) and Georgia (95.0 %), while the same ratio was 74.4 % in Azerbaijan and 72.2 % in Armenia. Differences between the sexes were quite varied across the ENP-East countries in 2015: for example, in Moldova the male youth education attainment level was 8.7 percentage points higher than the female level and in Armenia and Azerbaijan the rates for men were 5.9 and 4.3 percentage points higher. By contrast, female youth education attainment levels were moderately higher in Georgia, while in Ukraine (2014 data) the male and female rates were almost balanced.
Focus on tertiary education
The last couple of decades have seen policymakers increase their focus on human capital. Attempts have been made to raise the proportion of the workforce with a post-secondary education and to improve access to lifelong learning opportunities, leading to higher participation rates in tertiary education (ISECD 1997 levels 5 and 6). The global financial and economic crisis may also have resulted in more young people remaining in further education and/or training, as employment opportunities — especially among the youth population — were limited.
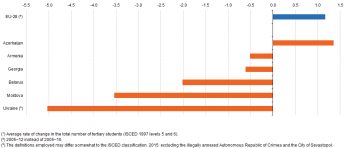
Azerbaijan was the only ENP-East country to record an expansion in its number of tertiary students that was at a faster pace than growth witnessed in the EU
Within the EU-28 the number of tertiary students grew, on average, by 1.2 % per annum during the period 2005–12. There were just over 20 million tertiary students in the EU-28 in 2012, equivalent to almost one in five (18.6 %) of the total population of pupils and students.
Somewhat fresher data is available for the ENP-East countries (covering the period 2005–15). Azerbaijan was the only ENP-East country to report an expansion in its number of tertiary students. Its average rate of change was — at 1.6 % per annum — higher than that recorded for the EU-28 (see Figure 2). In the five remaining ENP-East countries, Armenia and Georgia reported relatively modest reductions in their respective number of tertiary students between 2005 and 2015, while there were stronger falls in student numbers in Ukraine. Note that overall population numbers have been falling in some ENP-East countries for several years and that these reductions in the number of inhabitants may impact upon the absolute number of students in tertiary education, while the relative share of the population attaining higher levels of education continues to rise (see below for more details).
More than 40 % of the population aged 30–34 in Georgia had completed a tertiary level of education
Figure 3 shows the proportion of 30–34 year olds who had completed a tertiary level of education. Within the EU-28, this ratio rose at a rapid pace: from over a quarter (28.1 %) of those aged 30–34 in 2005 to more than one third (38.7 %) of this subpopulation a decade later in 2015. Georgia was the only ENP-East country (for which data are available) to report a higher proportion (42.3 % in 2015) of persons aged 30–34 having completed a tertiary level of education than the corresponding share for the EU-28. Among the three other ENP-East countries for which data are availble, this ratio ranged from 24.1 % (Azerbaijan; 2014 data) to 34.3 % (Moldova).
The proportion of women graduating from science and technology disciplines in the ENP-East countries was considerably lower than for men, as it was in the EU-28
There has been considerable focus on differences between subjects that are studied by men and women at tertiary level. Figure 4 shows that the ratio of men graduating with a science or technology degree to the male population aged 20–29 (24.5 per 1 000 male inhabitants) in the EU-28 in 2014 was approximately twice as high as the corresponding ratio for women (12.7 per 1 000 female inhabitants).
The ratio of men having graduated from a science or technology discipline to the male population aged 20–29 in Belarus, Azerbaijan and Ukraine was higher than in the EU-28, peaking in Belarus at 35.2 per 1 000 in 2015. The equivalent ratio for women was also higher in Belarus and Ukraine for these disciplines than it was across the EU-28, while in Azerbaijan the ratio for women was in line with that for the EU-28. The gender gap for this ratio was higher in all three of the ENP-East countries shown in Figure 4 than in the EU-28, most notably in Azerbaijan.
Data sources and availability
The data for ENP-East countries are supplied by and under the responsibility of the national statistical authorities of each country on a voluntary basis. The data result from an annual data collection cycle that has been established by Eurostat. These statistics are available free-of-charge on Eurostat’s website, together with a range of additional indicators for ENP-East countries covering most socio-economic topics.
Education statistics cover a range of subjects, including: expenditure, personnel, participation and attainment. The standards for international statistics on education are set by three organisations:
- the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO) institute for statistics (UIS);
- the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD);
- Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union.
The main source of data for the EU-28 aggregate is a joint UNESCO/OECD/Eurostat (UOE) questionnaire on education systems and this is the basis for the core components of the Eurostat database on education statistics; Eurostat also collects data on regional enrolments and foreign language learning. EU-28 data on educational attainment are mainly provided through household surveys, in particular the EU labour force survey (LFS).
Note that the collection of data on education is currently undergoing a considerable change as a result of the introduction of a new version of ISCED, namely ISCED 2011, replacing ISCED 1997. Longer time series are generally available on the basis of ISCED 1997, while data for the EU-28 and its Member States are often available on the basis of ISCED 2011 from the 2014 reference period.
Tables in this article use the following notation:
| Value in italics | data value is forecasted, provisional or estimated and is therefore likely to change; |
| : | not available, confidential or unreliable value. |
| – | not applicable. |
Context
Each EU Member State is responsible for its own education and training systems. As such, EU policy in this area is designed to support national action and address common challenges, by providing a forum for exchanging best practices. Through the strategic framework for European cooperation in education and training (known as ET 2020), which was adopted by the Council in May 2009, EU Member States identified four common objectives for 2020: making lifelong learning and mobility a reality; improving the quality and efficiency of education and training; promoting equity, social cohesion, and active citizenship; and enhancing creativity and innovation, including entrepreneurship, at all levels of education and training. The strategy sets a number of benchmarks in relation to education that are to be achieved by 2020, including:
- at least 95 % of children between the age of four and the age for starting compulsory primary education should participate in early childhood education;
- the share of early leavers from education and training should be less than 10 %;
- the share of low-achieving 15-year olds in reading, mathematics and science should be less than 15 %;
- the share of 30–34 year olds with tertiary educational attainment should be at least 40 %.
In 2014, recent progress was assessed and priorities reviewed: as a result, in November 2015 the Council adopted a set of six new priorities for the period 2016–20 based on a joint report(2015/C 417/04) from the European Commission and the EU Member States.
On 18 November 2015, the High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy and the European Commission jointly presented a review of the European Neighbourhood Policy (SWD(2015) 500 final) which underlined a new approach for the EU in relation to its eastern and southern neighbours, based on stabilising the region in political, economic, and security-related terms.
In cooperation with its ENP partners, Eurostat has the responsibility ‘to promote and implement the use of European and internationally recognised standards and methodology for the production of statistics, necessary for developing and monitoring policy achievements in all policy areas’. Eurostat undertakes the task of coordinating EU efforts to increase the statistical capacity of the ENP countries. Additional information on the policy context of the ENP is provided here.
See also
- All articles on non-EU countries
- European Neighbourhood Policy countries — statistical overview — online publication
- Statistical cooperation — online publication
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Basic figures on the European Neighbourhood Policy — East countries — 2014 edition
- European Neighbourhood Policy — East countries — Key economic statistics — 2014 edition
- European Neighbourhood Policy — East countries — Labour market statistics — 2014 edition
- European Neighbourhood Policy — East countries — Youth statistics — 2014 edition
Database
- Population and social conditions (enpr_ps)
- ENP countries: education (enpr_pseduc)
- Science and technology (enpr_sc)
- ENP countries: science and technology (enpr_scienc)
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Eastern European Neighbourhood Policy countries (ENP-East) (ESMS metadata file — enpr_esms)
Source data for tables and figures (MS Excel)
External links
- Directorate-General for Education and Training
- Erasmus+
- European External Action Service — European Neighbourhood Policy
- Strategic framework for education and training
- Vocational education and training