Archive:Household consumption expenditure - national accounts
This article analyses Household_consumption_expenditure in the European Union (EU), the concepts and nomenclatures used, data sources and the individual components ofwhich vary widely among Member States of the due to cultural, economic and some other factors affecting spending and saving habits.
The final consumption expenditure of households encompasses all domestic costs (by residents and non-residents) for individual needs. Among other things, it includes expenditure on goods and services, the consumption of garden produce and rent for owner-occupied dwellings.
Information on consumption expenditure, according to the Classification of individual consumption by purpose, combines three sources from Eurostat’s database the Household budget survey (HBS), national accounts and the harmonised index of consumer prices.,
Main statistical findings
Data sources and availability
Information on consumption expenditure, according to the Classification of individual consumption by purpose, comes from three sources in the database section of Eurostat’s website:
- the Household budget survey (HBS) - see living conditions and social protection;
- National accounts (including GDP) - see annual national accounts (nama);
The first two sources provide information both on amounts and on the structure, whilst the last only provides a structure of expenditure. In fact, the HBS shows amounts per household and per adult equivalent in PPS, whilst the NA shows data in current prices and volumes, as well as price indices. Obviously, the three sources are related, but they do show some differences, due to the way the data are collected, differing definitions and the publishing timeliness.
As its name implies, the HBS is a survey which is run on a sample of households in the participating countries and collected, aggregated and published by Eurostat on an informal basis. In all the countries, sharing common accommodation and expenditures is a prerequisite for a group of persons to be considered a household. In addition, many countries include the share of a common budget in their definition of household. Big institutions, such as hospitals, hotels, institutes and prisons are excluded from this survey.
National accounts data are compiled through a variety of statistical sources; such as HBS, business surveys, foreign trade statistics and value-added tax statistics. NA also uses slightly different definitions. Final consumption expenditure of households on detailed COICOP levels is estimated according to the 'domestic' concept. It consists of expenditure on goods and services incurred by resident and non-resident households on the economic territory. On an aggregated level, national accounts also publish final consumption expenditure of households according to the 'national' concept, meaning it includes expenditure by resident households both on the economic territory and abroad (and excludes expenditure by non-resident households on the economic territory). The national concept of final consumption is used in the GDP expenditure approach.
Finally, in order to arrive at the structure of consumption expenditure, which is then used to compile the weights used for the estimation of the consumer price index, in many cases the harmonised index of consumer prices uses the information coming from the HBS which is adjusted by using other sources, such as the NA. It should be noted here that in the HICP, imputed rent is not accounted for while in the other two sources it is.
Another important difference comes from the timeliness in publication of the results. National accounts publish quarterly data on aggregate level and annual data for detailed COICOP levels, the HICP updates its weights annually, and although in many countries the HBS is run on an annual basis, in some, it is run on a five-year basis so Eurostat only collects, aggregates and publishes this information on a five year cycle, normally with a two-year time lag.
Now what are the pros and cons one has to consider in using each source? The HBS deals strictly with households and all the information is gathered directly from them. Besides information on consumption expenditure, there is also information on income, place of residence, and some characteristics of the reference person. There are some doubts on the accuracy, or at least the completeness, in reporting on what is considered as “sin consumption”, such as prostitution, illicit drugs, alcohol, and tobacco. This does not have an effect on the amounts reported for the other divisions of the COICOP. However, it does affect the structure of expenditure. Besides this, another handicap for this source is the frequency that it is collected and the timeliness with which it is published. Finally, since this survey is conducted based on a 'gentlemen’s agreement', no one is in a position to dictate stringent standards. Having said that, participating countries have taken huge steps to harmonise their methodology, resulting in high-quality results.
National accounts rely on several sources to estimate consumption expenditure, both from the demand and supply sides. Member States are legally obliged to transmit the data to Eurostat. Moreover, this information is published much more frequently and is more recent then the HBS. The major issue with this source is that, since it covers expenditure from a macro level, expenditure cannot be correlated with characteristics pertaining to different households.
Finally, the HICP tries to take into account and make good for the weaknesses in the previous two sources by using adjustment techniques to calculate the weights to be used in the estimation of the index. Moreover, it produces figures on an annual basis. The contentious issues related to this source may be that it produces only the structure and that it does not include imputed rent.
Table 5, which represents the structure of expenditure according to the different sources, highlights the similarities and the differences between them. Actually, in the national accounts, no structure is formally published but it can be easily compiled by taking the expenditure per COICOP division, divided by the total expenditure.
Context
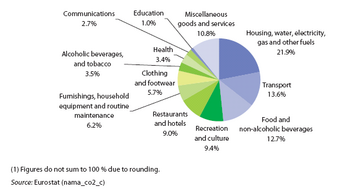
Consumption is a key indicator of citizens’ wellbeing, with housing, energy, transport and food accounting for about half of total household expenditure. This article uses data on the development and structure of expenditure to identify trends over the past decade. For instance, the impact of the economic and financial crisis on actual individual consumption of households was relatively moderate, as rising government consumption counterbalanced at least partly a more significant contraction in household consumption.
While the Baltic economies suffered most in 2009, household spending continued to decline in Greece due to the deepening recession and the fall was sharpest in 2011. Despite some general trends in EU-27 data, detailed consumption patterns vary significantly between Member States and the impact of the crisis on specific expenditure categories was also quite varied.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
Main tables
- Mean consumption expenditure of private households (hbs_exp)
- Structure of mean consumption expenditure (hbs_struc)
- Annual national accounts (t_nama)
- National accounts detailed breakdowns (by industry, by product, by consumption purpose) (t_nama_brk)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose (COICOP) (t_nama_co)
- Household expenditure per inhabitant, by category (tsdpc520)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose (COICOP) (t_nama_co)
- National accounts detailed breakdowns (by industry, by product, by consumption purpose) (t_nama_brk)
- Prices (prc), see
- Harmonised indices of consumer prices (HICP) (prc_hicp)
- HICP - Item weights (prc_hicp_inw)
Database
- Mean consumption expenditure of private households (hbs_exp)
- Structure of mean consumption expenditure (hbs_struc)
- National accounts (na), see:
- Annual national accounts (nama),
- National Accounts detailed breakdowns (by industry, by product, by consumption purpose) (nama_brk)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose (COICOP) (nama_co)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose - COICOP 2 digit - aggregates at current prices (nama_co2_c)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose - COICOP 2 digit - volumes (nama_co2_k)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose - COICOP 2 digit - price indices (nama_co2_p)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose - COICOP 3 digit - aggregates at current prices (nama_co3_c)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose - COICOP 3 digit - volumes (nama_co3_k)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose - COICOP 3 digit - price indices (nama_co3_p)
- Final consumption expenditure of households by consumption purpose (COICOP) (nama_co)
- National Accounts detailed breakdowns (by industry, by product, by consumption purpose) (nama_brk)
- Prices (prc), see:
- Harmonised indices of consumer prices (HICP) (prc_hicp)
- HICP - Item weights (prc_hicp_inw)
Methodology / Metadata
- Annual national accounts (ESMS metadata file - nama_esms)
- Consumption expenditure of private households (ESMS metadata file - hbs_esms)
- Harmonised indices of consumer prices (HICP) (ESMS metadata file - prc_hicp_esms)
Other information
- Inflation dashboard (visualisation tool)