Glossary:Cereal
This is the stable Version.
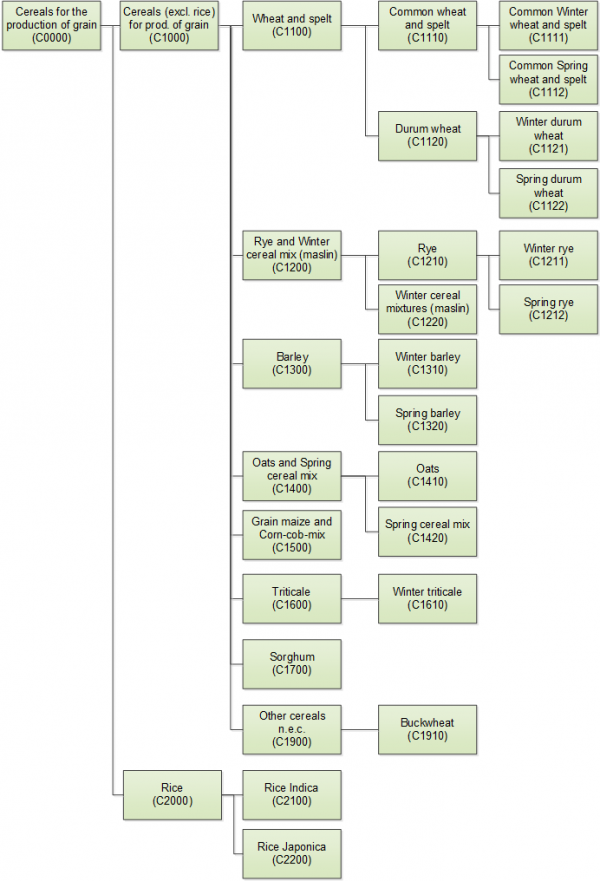
Cereals are annual plants, generally of the graminaceous family, yielding grains used for food, feed, seed and industrial purposes such as production of ethanol.
Includes
- Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Mill.)
- Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)
- Canary seed (Phalaris canariensis L.)
- Common wheat ('Triticum aestivum L. emend. Fiori et Paol.)
- Durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.)
- Einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum L.)
- Emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccum Schrank ex Schübl.)
- Grain maize (Zea mays L.)
- Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.)
- Oats (Avena sativa L.)
- Perennial sorghum (Sorghum x sudanense (Piper) Stapf.)
- Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Wild.)
- Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Rye (Secale cereale L.)
- Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Conrad Moench)
- Spelt (Triticum spelta L.)
- Triticale (x Triticosecale Wittmack)
- Cereals seeds
- Cereal grains harvested just before maturity
- Cereals used for renewable energy production
- Rye and winter cereal mixtures (maslin)
- Spring cereal mixtures (mixed grain, other than maslin)
Excludes
- Maize harvested green (G3000)
- Cereals (excluding maize) harvested green or yellow as whole plant for fodder, or renewable energy (G9100)
- Sweet corn cobs for human consumption (V0000_S0000; V3900 in ACS)