Archive:Travel agency and tour operator statistics - NACE Rev. 2
- Data from April 2012. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
This article presents an overview of statistics for the travel agency and tour operator reservation and related service activities sector in the European Union (EU), as covered by NACE Rev. 2 Division 79, hereafter referred to as travel agency and related services.
(% share of sectoral total) - Source: Eurostat (sbs_na_1a_se_r2)
Main statistical findings
Structural profile
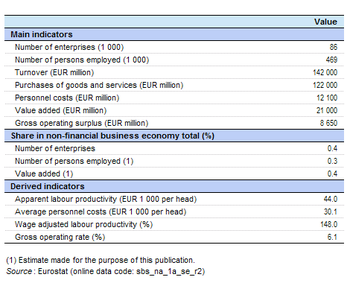
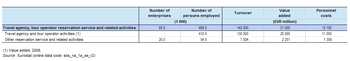
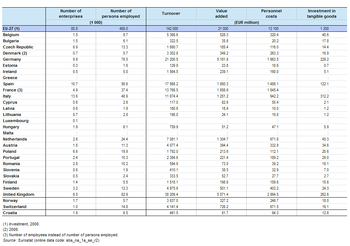
There were 86 thousand enterprises operating within the travel agency and related services (Division 79) subsector in the EU-27 in 2009. Together they employed 469 thousand persons, equivalent to 0.3 % of the total workforce in the non-financial business economy (Sections B to J and L to N and Division 95) and 3.9 % of persons in administrative and support services (Section N). Travel agency and related services generated EUR 21 000 million of value added which was 0.4 % of the non-financial business economy total or 6.0 % of the added value for administrative and support services. As such, in both employment and value added terms, travel agency and related services were the smallest of the six NACE divisions that make-up administrative and support services. Given the nature of travel agency and related services it is not surprising to find that they had relatively high turnover, some EUR 142 000 million across the EU-27 in 2009, which was equivalent to 0.6 % of the non-financial business economy total.
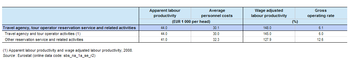
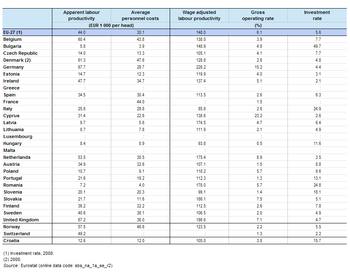
The somewhat higher share of non-financial business economy value added compared with employment for the travel agency and related services sector meant that the apparent labour productivity of EUR 44 thousand per person employed in this sector in 2009 was slightly above the non-financial business economy average of EUR 41.6 thousand and also much higher than the administrative and support services average of EUR 29 thousand. Average personnel costs within the EU-27’s travel agency and related services sector were just EUR 100 per employee higher than the non-financial business economy average, as they stood at EUR 30.1 thousand per employee in 2009, considerably above the average for administrative and support services (EUR 20.9 thousand per employee). The wage-adjusted labour productivity ratio for EU-27 travel agency and related services in 2009 was 148.0 %, somewhat higher than the non-financial business economy average (138.8 %) or the administrative and support services average (139.1 %).
The gross operating rate (the relation between the gross operating surplus and turnover) is one measure of operating profitability; it stood at 6.1 % for the EU-27’s travel agency and related services sector in 2009, which was less than two thirds of the non-financial business economy average (9.7 %) and considerably lower than the administrative and support services average (15.2 %). Indeed, the gross operating rate for travel agency and related services was the lowest among the six NACE divisions within administrative and support services.
Sectoral analysis
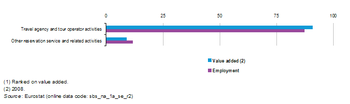
The travel agency and related services sector can be divided into two subsectors, the largest of which in the EU-27 – by far – was the travel agency and tour operator activities subsector (Group 79.1). It accounted for 90.9 % of sectoral value added in 2008 and for 87.4 % of sectoral employment in 2009; the residual shares being attributed to other reservation services and related activities (Group 79.9).
Given the relative weight of the travel agency and tour operator activities subsector there was little difference between it and the whole of the travel agency and related services sector for a range of productivity and profitability measures.
For apparent labour productivity, the latest information available shows that both subsectors recorded productivity levels that were close to the EU-27 non-financial business economy average, with persons employed in the travel agency and tour operator activities subsector generating on average EUR 44 thousand of added value in 2008, while for other reservation services and related activities the corresponding ratio stood at EUR 41 thousand in 2009. EU-27 average personnel costs for the travel agency and tour operator activities subsector were, at EUR 30.0 thousand per employee in 2009, identical to the average for the whole of the non-financial business economy, while those for other reservation services and related activities subsector were some EUR 2.3 thousand per employee higher. Wage-adjusted labour productivity ratios – which are constructed through dividing apparent labour productivity by average personnel costs – were also close to the non-financial business economy average. This was particularly true for the travel agency and tour operator activities subsector (145.0 % in 2008), while the ratio was somewhat lower for other reservation services and related activities (127.9 % in 2009).
The relatively low gross operating rate (6.0 %) for the EU-27’s travel agency and tour operator activities subsector in 2009 reflects, to some degree, the trading nature of these activities and the high volume of buying and reselling travel and tourism services. The gross operating rate for other reservation services and related activities (12.6 %) was above the non-financial business economy average of 9.7 %.
Country analysis
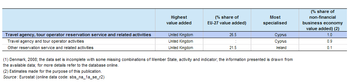
More than half of the EU-27’s value added within the travel agency and related services sector in 2009 was generated in either the United Kingdom (26.5 %) or Germany (24.7 %); these figures reflect the high tourism demand in these two countries. The data also suggest that these two countries have relatively large enterprises in this sector, as there were less enterprises operating in Germany or the United Kingdom than in either Spain or Italy which in turn accounted for 9.3 % and 6.0 % of EU-27 value added.
The relative importance of travel agency and related services in terms of their contribution to non-financial business economy value added was highest in Cyprus, attaining a 1.0 % share in 2009. This was much higher than in any of the other Member States for which data are available, as the second most specialised Member State was the United Kingdom, where 0.6 % of non-financial business economy value added was generated in the travel agency and related services sector. At the other end of the range, there were three Member States where less than 0.2 % of non-financial business economy value added was generated within the travel agency and related services sector – these were Romania, Poland and Hungary.
In employment terms, the travel agency and related services sector’s workforce was less concentrated than for value added. There were as many as 82.9 thousand persons employed within travel agency and related services in the United Kingdom in 2009 (a 17.7 % share of the EU-27 total). Germany had the second largest workforce (16.3 % of the EU -27 total), while Spain (12.1 %) and Italy (10.4 %) also recorded double-digit shares; note that the information for France is based on the number of employees and not persons employed.
Most Member States reported wage-adjusted labour productivity ratios for travel agency and related services in 2009 that were below their national averages for the whole of the non-financial business economy. However, there were four countries –the two largest in terms of value added, the United Kingdom and Germany, as well as the Netherlands and Slovakia – that did not follow this pattern; all four of these recorded wage-adjusted labour productivity ratios that were over 170 % as did Romania and Latvia. The highest wage-adjusted labour productivity ratio was recorded for Germany (228.2 %). At the other end of the range, the lowest ratios – falling below 100 % – were recorded in Slovenia, Hungary and Italy, showing that, on average, the added value generated per person employed did not cover average personnel costs per employee.
Gross operating rates for travel agency and related services were generally relatively low across the Member States – and were situated below non-financial business economy averages in 2009 for all of the Member States except for Cyprus and Germany. These were the only two countries where this measure of operating profitability rose into double-digits, reaching 23.2 % and 15.2 % respectively. In contrast, the gross operating rate for travel agency and related services fell below 2 % in France, Austria, Slovenia, Portugal and Hungary (where the lowest rate was recorded, 0.5 %).
Data sources and availability
The analysis presented in this article is based on the main dataset for structural business statistics (SBS) which are disseminated annually. The series provides information for each Member State as well as a number of non-member countries at a detailed level according to the activity classification NACE. Data are available for a wide range of variables.
Context
This article presents an overview of statistics for the travel agency and tour operator reservation and related service activities sector in the EU-27, as covered by NACE Rev. 2 Division 79. This division includes the activity of agencies, primarily engaged in selling travel, tour, transportation and accommodation services and the activity of arranging and assembling tours; other travel-related services are also included. Travel agencies activities are primarily engaged in selling travel, tour, transportation and accommodation services on a wholesale or retail basis to the general public and commercial clients. Tour operators arrange and assemble tours that are sold through travel agencies or directly by tour operators. The tours may include any or all of the following: transportation, accommodation, food, and visits to museums, historical or cultural sites, theatrical, musical or sporting events. Other reservation services and related activities include: marketing and promoting of services for conventions and visitors by providing information and assistance to organisations to locate accommodation, convention centres and entertainment venues; tourist guide services; condominium time-share exchange services; travel-related reservation services; ticket sales for theatrical, sports and all other amusement and entertainment events.
This NACE division is composed of two groups:
- travel agency and tour operator activities (Group 79.1);
- other reservation service and related activities (Group 79.9).
Note that the information presented in this article does not cover accommodation and food service activities, such as the running of hotels, campsites, restaurants, bars or cafés, but is rather restricted to selling, organising and reserving services that are sourced from these (and other) providers.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
Main tables
Database
- SBS – services (sbs_serv)
- Annual detailed enterprise statistics - services (sbs_na_serv)
- Annual detailed enterprise statistics for services (NACE Rev.2 H-N and S95) (sbs_na_1a_se_r2)
- Preliminary results on services, main indicators (NACE Rev.2) (sbs_sc_r2preli)
- SMEs - Annual enterprise statistics broken down by size classes - services (sbs_sc_sc)
- Services broken down by employment size classes (NACE Rev.2 H-N and S95) (sbs_sc_1b_se_r2)
- Annual detailed enterprise statistics - services (sbs_na_serv)
- SBS - regional data - all activities (sbs_r)
- SBS data by NUTS 2 regions and NACE Rev.2, from 2008 onwards (sbs_r_nuts06_r2)
Dedicated section
Source data for tables, figures and maps (MS Excel)
Other information
- Decision 1578/2007/EC of 11 December 2007 on the Community Statistical Programme 2008 to 2012
- Regulation 295/2008 of 11 March 2008 concerning structural business statistics