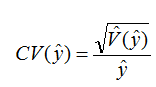|
|
 |
| For any question on data and metadata, please contact: Eurostat user support |
|
|||
| 1.1. Contact organisation | Statistics Poland (GUS) |
||
| 1.2. Contact organisation unit | Regional Statistical Office in Szczecin, Centre for Science Technology Innovation and Information Society Statistics ul. Jana Matejki 22 70-530 Szczecin |
||
| 1.5. Contact mail address | ul. Jana Matejki 22, 70-530 Szczecin |
||
|
|||
| 2.1. Metadata last certified | 28/02/2024 | ||
| 2.2. Metadata last posted | 28/02/2024 | ||
| 2.3. Metadata last update | 28/02/2024 | ||
|
|||
| 3.1. Data description | |||
Data on the Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) usage and e-commerce in enterprises are survey data. They are collected by the National Statistical Institutes or Ministries and are in principle based on Eurostat's annual model questionnaires on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises. Large part of the data collected is used to measure the progress in the implementation of one of the main political priorities of the European Commission for 2019 to 2024 – A Europe fit for the digital age. Part of this is the "European strategy for data", envisioning a single market for data to ensure the EU's global competitiveness and data sovereignty, in which context a comprehensive set of new rules for all digital services was proposed: the Digital Services Act and the Digital Markets Act, which are centrepieces of the EU digital strategy. Furthermore, the Commission and the High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy presented a new “EU cybersecurity strategy”, which is intended to bolster the EU's collective resilience against cyber threats, safeguard a global and open internet and protect EU values and the fundamental rights of its people. Furthermore, data will allow monitoring the progress towards A Europe fit for the digital age, one of the six priorities for the period 2019-2024 of the von der Leyen European Commission. The aim of the European survey on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises is to collect and disseminate harmonised and comparable information at European level.
|
|||
| 3.2. Classification system | |||
| 3.3. Coverage - sector | |||
All economic activities in the scope of Annex I of the Commission Regulation are intended to be included in the general survey, covering enterprises with 10 or more employees and self-employed persons. These activities are: NACE Rev. 2 sections C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, L, M and N, division 95.1. For micro-enterprises see the sub-concepts below. |
|||
| 3.3.1. Coverage-sector economic activity for micro-enterprises - All NACE Rev. 2 categories are covered | |||
| 3.3.2. Coverage sector economic activity for micro-enterprises - If not all activities were covered, which ones were covered? | |||
Micro-enterprises are not included in the survey. |
|||
| 3.4. Statistical concepts and definitions | |||
The model questionnaire on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises provides a large variety of variables covering among others the following areas: - Access to and use of the Internet - E-commerce and e-business - Use of cloud computing services - Artificial Intelligence - Other topics: Data utilisation, sharing, analytics and trading, Invoicing. The annual model questionnaires and the European businesses statistics compliers’ manual for ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises comprise definitions and explanations regarding the topics of the survey. |
|||
| 3.5. Statistical unit | |||
Statistical unit is legal unit. |
|||
| 3.6. Statistical population | |||
Target Population As required by Annex of the Commission Implementing Regulation, enterprises with 10 or more employees and self-employed persons shall be covered by the survey. For micro-enterprises see the sub-concepts below. |
|||
| 3.6.1. Coverage of micro-enterprises | |||
| No | |||
| 3.6.2. Breakdown between size classes [0 to 1] and [2 to 9] | |||
| No | |||
| 3.6.3. If for micro-enterprises different size delimitation was used, please indicate it. | |||
Not applicable. |
|||
| 3.7. Reference area | |||
All territory of country is covered. |
|||
| 3.8. Coverage - Time | |||
Years 2022 and 2023. |
|||
| 3.9. Base period | |||
Not applicable |
|||
|
|||
Percentages of enterprises, Percentages of turnover, Percentages of employees and self-employed persons, Million Euro. |
|||
|
|||
Reference period in national questionnaire is the same as in Model Questionnaire. |
|||
|
|||
| 6.1. Institutional Mandate - legal acts and other agreements | |||
Complementary national legislation constituting the legal basis for the survey on the use of ICT in enterprises: Act of 29 June 1995 on Official Statistics and the annual regulations of the Council of Ministers concerning the programme of statistical surveys of official statistics.
|
|||
| 6.2. Institutional Mandate - data sharing | |||
Not applicable. |
|||
|
|||
| 7.1. Confidentiality - policy | |||
Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 on European statistics (recital 24 and Article 20(4)) of 11 March 2009 (OJ L 87, p. 164), stipulates the need to establish common principles and guidelines ensuring the confidentiality of data used for the production of European statistics and the access to those confidential data with due account for technical developments and the requirements of users in a democratic society. At national level : In case of variables which unit_measure is ' Million National Currency', breakdown is marked as confidential where share of value of one enterprise in breakdown is at least 75% of total. If the risk of identification of enterprise exist e.g because of addition, subtraction of values, additional breakdowns are hidden. In case variables concerning e-sales if total number of enterprises in breakdown is 0,1 or 2 then it is marked as confidential. |
|||
| 7.2. Confidentiality - data treatment | |||
Data are transmitted via eDamis (encrypted) and delivered to a secure environment where they are treated. Flags are added for confidentiality in case results must not be disclosed. At national level : Confidentiality of data is ensured. Indcators are not pubblished if there is a risk of breach of confidentiality. |
|||
|
|||
| 8.1. Release calendar | |||
Editorial Title-Plan of the Statistics Poland is created for every year. It is publicly accessible. |
|||
| 8.2. Release calendar access | |||
Editorial Title-Plan of the Statistics Poland and Regional Statistical Offices 2023 |
|||
| 8.3. Release policy - user access | |||
First, a press release containing the most important indicators is published.Then the main publication is published and the databases are fed. |
|||
|
|||
Annual |
|||
|
|||
| 10.1. Dissemination format - News release | |||
News release was published in October 2023. |
|||
| 10.2. Dissemination format - Publications | |||
Publication will be released in December 2023. Below .there is a link for last year publication. |
|||
| 10.3. Dissemination format - online database | |||
See detailed section 10.3.1. |
|||
| 10.3.1. Data tables - consultations | |||
Results for selected variables collected in the framework of this survey are available for all participating countries on Digital economy and society of Eurostat website. At national level : Not available. |
|||
| 10.4. Dissemination format - microdata access | |||
Microdata are not publicly available. Access may be granted upon request |
|||
| 10.5. Dissemination format - other | |||
Not requested |
|||
| 10.5.1. Metadata - consultations | |||
Not requested |
|||
| 10.6. Documentation on methodology | |||
Methodological report is available. |
|||
| 10.6.1. Metadata completeness - rate | |||
Not requested |
|||
| 10.7. Quality management - documentation | |||
All procedures apllied for quality management are consistent with Methodological Manual and Eurostat's recommendations. |
|||
|
|||
| 11.1. Quality assurance | |||
The European businesses statistics compliers’ manual for ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises provides guidelines and standards for the implementation of the surveys. It is updated every year according to the changed contents of the model questionnaires. At national level : The Methodological Manual provides guidelines and standards for the implementation of the surveys in the Member States. It is updated every year according to the changed contents of the model questionnaires. Survey is based on Methodological Manual.
|
|||
| 11.2. Quality management - assessment | |||
European level : At European level, the recommended use of the annual Eurostat model questionnaire aims at improving comparability of the results among the countries that conduct the survey on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises. Moreover, the Methodological Manual provides guidelines and clarifications for the implementation of the surveys. National level : European methodology for quality assessment is applied. Any national methodology is not applied.
|
|||
|
|||
| 12.1. Relevance - User Needs | |||
European level : At European level, European Commission users (e.g. DG CNECT, DG GROW, DG JUST, DG REGIO, DG JRC) are the principal users of the data on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises and contribute in identifying/defining the topics to be covered. Hence, main users are consulted regularly (at hearings, task forces, ad hoc meetings) for their needs and are involved in the process of the development of the model questionnaires at a very early stage. User needs are considered throughout the whole discussion process of the model questionnaires aiming at providing relevant statistical data for monitoring and benchmarking of European policies. National level : At national level the survey is included in annual regulation of the Council of Ministers concerning the programme of statistical surveys of official statistics. A draft regulation is consulted with main groups of users (local and central entities of public administration i.e. Ministry of Digitalization, Ministry of Economic Development Labour and Technology, Ministry of Development Funds and Regional Policy). Users are allowed to make proposals of topics which should be covered in survey. All proposals are discussed with Regoional Statistical Office in Szczecin. Accepted proposals (after examination of respondent's burden and substantive recognition of the proposal) are included in questionnaire as national level questions. Every year there are some requests for more detailed regional statistics which are not fulfilled due to costs (sample adjustment). Big interest for ICT survey idicators is showed by institutions of private sector, educational institutions (e.g universities) and individuals (e.g. students) Big interest is also noted for ICT sector data (e.g. for NUTS 2: employment,R&D expunditures). |
|||
| 12.2. Relevance - User Satisfaction | |||
European level : At European level, contacts within the Commission, the OECD and other stakeholders give a clear picture about the key users' satisfaction as to the following data quality aspects: accuracy and reliability of results, timeliness, satisfactory accessibility, clarity and comparability over time and between countries, completeness and relevance. Overall users have evaluated positively (good, very good) the data quality on the ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises. National level : At national level data users can express satisfaction or dissatisfaction during the consultation of annual regulation of the Council of Ministers concerning the programme of statistical surveys of official statistics. Any dedicated satisfaction surveys are not performed. |
|||
| 12.3. Completeness | |||
Detailed information is available in “ Annex I _ Completeness “ excel file - related to questionnaire, coverage, additional questions. |
|||
| 12.3.1. Data completeness - rate | |||
Not requested. |
|||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.1. Accuracy - overall | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Comments on reliability and representativeness of results and completeness of dataset These comments reflect overall standard errors reported for the indicators and breakdowns in section 13.2.1 (Sampling error - indicators) and the rest of the breakdowns for national and European aggregates, as well as other accuracy measurements. The estimated standard error should not exceed 2pp for the overall proportions and should not exceed 5pp for the proportions related to the different subgroups of the population (for those NACE aggregates for the calculation and dissemination of national aggregates). If problems were found, these could have implications for future surveys (e.g. need to improve sampling design, to increase sample sizes, to increase the response rates). More detailed information is available in “ Annex II. _ Accuracy “ excel file - related to European aggregates, comments on reliability and use of flag. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2. Sampling error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For calculation of the standard error see 13.2.1.1. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2.1. Sampling error - indicators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Standard error (for selected indicators and breakdowns) Precision measures related to variability due to sampling, unit non-response (the size of the subset of respondents is smaller than the size of the original sample) and other (imputation for item non-response, calibration etc.) are not (yet) required from the Member states for all indicators. Eurostat will make basic assumptions to compute these measures for all indicators produced (e.g. stratified random sampling assuming as strata the crossing of the variables “Number of employees and self-employed persons” and “Economic Activity” as it was defined in the 3 tables of section 18.1). More detailed information is available in“ Sample and standard error tables 2023 “ excel file – worksheets starting with “Standard error". |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.2.1.1. Sampling error indicator calculation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Calculation of the standard error Various methods can be used for the calculation of the standard error for an estimated proportion. The aim is to incorporate into the standard error the sampling variability but also variability due to unit non-response, item non-response (imputation), calibration etc. In case of census / take-all strata, the aim is to calculate the standard errors comprising the variability due to unit non-response and item non-response.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3. Non-sampling error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See detailed sections below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1. Coverage error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See concept 18.1.1. A) Description of frame population. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1.1. Over-coverage - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.165% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.1.2. Common units - proportion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.2. Measurement error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Measurement error does not exist. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3. Non response error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See detailed sections below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1. Unit non-response - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See detailed sub-concepts below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1.1. Unit response | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following table contains the number of units (i.e. enterprises), by type of response to the survey and by the percentage of these values in relation to the gross sample size.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1.2. Methods used for minimizing unit non-response | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In order to reduce unit non-response rate following activities are made:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1.3. Methods used for unit non-response treatment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.1.4. Assessment of unit non-response bias | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.2. Item non-response - rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.7% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.2.1. Methods used for item non-response treatment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.3.2.2. Questions or items with item response rates below 90% and other comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comments relating to the item non-response
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.4. Processing error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Processing error does note exist. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13.3.5. Model assumption error | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Not requested |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||
| 14.1. Timeliness | |||
See detailed section below. |
|||
| 14.1.1. Time lag - first result | |||
Not applicable |
|||
| 14.1.2. Time lag - final result | |||
European level : Data are to be delivered to Eurostat in the fourth quarter of the reference year (due date for the finalised dataset is 5th October). European results are released before the end of the survey year or in the beginning of the year following the survey year (T=reference year, T+0 for indicators referring to the current year, T+12 months for other indicators referring to the previous year e.g. e-commerce). At national level : National results are released before the end of the survey year too. |
|||
| 14.2. Punctuality | |||
See detailed section below. |
|||
| 14.2.1. Punctuality - delivery and publication | |||
There is no time lag. Data was delivered to Eurostat on 27 September 2023. |
|||
|
|||
| 15.1. Comparability - geographical | |||
The model questionnaire is generally used by the countries that conduct the survey on ICT usage and e-commerce in enterprises. Due to (small) differences in translation, in the used survey vehicle, in non-response treatment or different routing through the questionnaire, some results for some countries may be of reduced comparability. In these cases, notes are added in the data. Detailed information on differences in the wording of the questions in the national questionnaires is available in “ Annex I _ Completeness “ excel file - related to questionnaire, coverage, additional questions. |
|||
| 15.1.1. Asymmetry for mirror flow statistics - coefficient | |||
Not applicable |
|||
| 15.2. Comparability - over time | |||
See section below. |
|||
| 15.2.1. Length of comparable time series | |||
The length of comparable time series depends on the module and the variable considered within each survey module. Additional information is available in annexes attached to the European metadata.
|
|||
| 15.3. Coherence - cross domain | |||
Not applicable |
|||
| 15.3.1. Coherence - sub annual and annual statistics | |||
Not applicable |
|||
| 15.3.2. Coherence - National Accounts | |||
Not applicable |
|||
| 15.4. Coherence - internal | |||
Not applicable |
|||
|
|||
| Restricted from publication | |||
|
|||
| 17.1. Data revision - policy | |||
Data revision policy is applied in some other domains than ICT statistics. |
|||
| 17.2. Data revision - practice | |||
Data revision is not applied for ICT statistics. |
|||
| 17.2.1. Data revision - average size | |||
Not requested |
|||
|
||||||||||
| 18.1. Source data | ||||||||||
A) Frame population description and distribution For more information see concept 18.1.1.
B) Sampling design - Sampling method Description of the sampling method used (e.g. stratified random sample, quota sampling, cluster sampling; one-stage or two-stage sampling) and information which variables were used to stratify, the categories of those variables, in particular for the NACE Rev. 2 categories related to the "possible calculation of European aggregates", and the final number of strata: The sample size fluctuates around 18.4% of the population of N units, which, based on the results from previous years, ensured adequate precision of the results in the assumed breakdowns. The variables used for stratification are: the economy activity (NACE rev2, 25 categories, RD variable) and size of enterprise (as number of persons employed, 3 categories, WLK variable). All large enterprises (with more than 249 employees) and all entities from WLK * RD stratas, whose N is less than 200, are included in the sample. The rest of the sample is allocated in WON * NTS1 * WLK * RD stratas (WON and NTS1 are territory codes to ensure that enterprises from all country will be choosen) by solving the following formula : nh = 0.6 * (allocation proportional to the size of the strata) + 0.4 * (allocation to square root of the number of elements in given strata). The use of such a method of sample allocation gives a slight over-representation of the smallest stratas at the expense of the larger ones - it has been used to improve precision - especially in small breakdowns.
C) Gross sample distribution More detailed information is available in “ Sample and standard error tables 2023 “ excel file (Worksheet: GROSS SAMPLE)
D) Net sample distribution More detailed information is available in “ Sample and standard error tables 2023 “ excel file (Worksheet: NET SAMPLE) |
||||||||||
| 18.1.1. Population frame | ||||||||||
A) Description of frame population
B) Frame population distribution More detailed information is available in “ Sample and standard error tables 2023 “ excel file (Worksheet: FRAME POPULATION) |
||||||||||
| 18.2. Frequency of data collection | ||||||||||
Annual |
||||||||||
| 18.3. Data collection | ||||||||||
See detailed sections below. |
||||||||||
| 18.3.1. Survey period | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| 18.3.2. Survey vehicle – general survey | ||||||||||
| General survey - Stand-alone survey | ||||||||||
| 18.3.3. Survey vehicle – micro-enterprises | ||||||||||
| The collection of micro-enterprises was integrated with the general survey | ||||||||||
| 18.3.4. Survey type | ||||||||||
It is a the self-reporting method - web survey accessible via the Statistical Reporting Portal. Enterprises which don't have online access get possibility to submit paper form. Respondents who have difficulties to answer questions, can make a telephone interview with Statistican. |
||||||||||
| 18.3.5. Survey participation | ||||||||||
| Mandatory | ||||||||||
| 18.4. Data validation | ||||||||||
Before transmitting the dataset, its final validation will be made using the tool prepared by Eurostat. Moreover electronic form and Survey IT System (where paper form are registered) is equipped with a many of restrictive validation rules aimed at reducing the number of errors and data quality checks. There will be two types of validation rules:
After closing the Statistical Reporting Portal, the submitted forms will be transferred to Survey IT System too. Access to the full dataset, so it will allow the survey coordinators to analyze the response rate and errors. (generating reports, filtering, searching, etc.). These functionalities will improve work of Statisticans, particularly activities related to locating “suspected” enterprises which have:
|
||||||||||
| 18.5. Data compilation | ||||||||||
Grossing-up procedures
Grossing-up is used to all variables in the survey. There are used standard formulas, for estimators of the parameters, in stratified random sampling. The base weight(primary) of a sampled unit is the reciprocal of its probability of selection into the sample. However, due to unit non-response, primary weights must be corrected. The correction takes into account the phenomenon of non-response and information about the reasons for not obtaining data from some sampled units. Taking into account the information for the entire sample included in the RA symbols (symbols for participation in the survey), on the level of stratas according to the variables of WLK (3 size classes) and RD (types of activity according to PKD) correction factor is calculated.
Correction factor is calculated according to the following formula
The correction factor estimates the proportion of units which should be surveyed in relation to the responded units.
Adjusted weights equal design weights multiplied by the corresponding correction factors.
|
||||||||||
| 18.5.1. Imputation - rate | ||||||||||
Imputation rate for turnover variable is 0,1% |
||||||||||
| 18.6. Adjustment | ||||||||||
Not applicable |
||||||||||
| 18.6.1. Seasonal adjustment | ||||||||||
Not applicable |
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
Problems encountered and lessons to be learnt: |
||||||||||
| 19.1. Documents | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|||
|
|||
| National questionnaire for 2023 Annex 2 Annex 3 Annex 4 |
|||