Glossary:Cereal
Cereals are annual plants, generally of the graminaceous family, yielding grains used for food, feed, seed and industrial purposes such as production of ethanol.
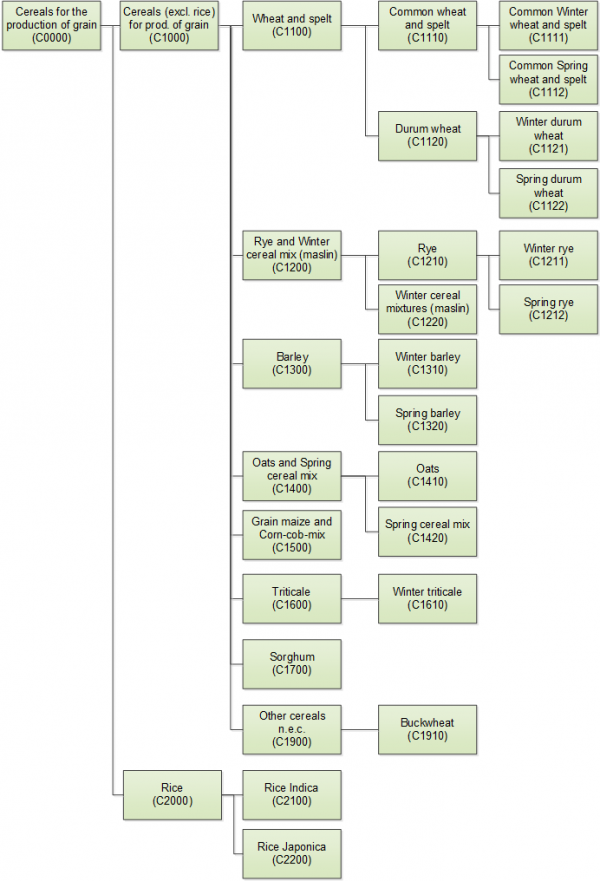
Includes
- Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Mill.)
- Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)
- Canary seed (Phalaris canariensis L.)
- Common wheat ('Triticum aestivum L. emend. Fiori et Paol.)
- Durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.)
- Einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum L.)
- Emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccum Schrank ex Schübl.)
- Grain maize (Zea mays L.)
- Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.)
- Oats (Avena sativa L.)
- Perennial sorghum (Sorghum x sudanense (Piper) Stapf.)
- Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Wild.)
- Rice (Oryza sativa L.)
- Rye (Secale cereale L.)
- Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Conrad Moench)
- Spelt (Triticum spelta L.)
- Triticale (x Triticosecale Wittmack)
- Cereals seeds
- Cereal grains harvested just before maturity
- Cereals used for renewable energy production
- Rye and winter cereal mixtures (maslin)
- Spring cereal mixtures (mixed grain, other than maslin)
Excludes
- Maize harvested green (G3000)
- Cereals (excluding maize) harvested green or yellow as whole plant for fodder, or renewable energy (G9100)
- Sweet corn cobs for human consumption (V0000_S0000; V3900 in ACS)