Education at a Glance 2021 from OECD

date: 03/11/2021
On 16 September, OECD published its annual Education at a Glance. For the 2021 edition, OECD focused on the output of educational institutions and the impact of learning; access to education, participation and progress; financial resources invested in education; and teachers, the learning environment and the organisation of schools.
Concerning public spending on education, total public spending on primary to tertiary education as a percentage of total government expenditure averages 11% across OECD countries. This percentage was the highest in Chile with 17.4%, followed by South Africa (15.3%) and Costa Rica (14.3%); and the lowest in Greece with 6.8%, followed by Hungary (7.4%) and Luxembourg (7.6%). The EU country with the highest share is Ireland with 12.6%, ranking 12 among the countries analysed, and behind countries like Switzerland, Norway, South Korea or Israel.
Between 2012 and 2018, the proportion of government expenditure devoted to education slightly decreased on average across OECD countries (1%). However, this share increased over the same period in half of OECD and partner countries and most notably in the Czech Republic and Greece, where it rose by more than 12%. Nevertheless, in many countries, increases in educational expenditure did not keep pace with the growth in government expenditure overall.

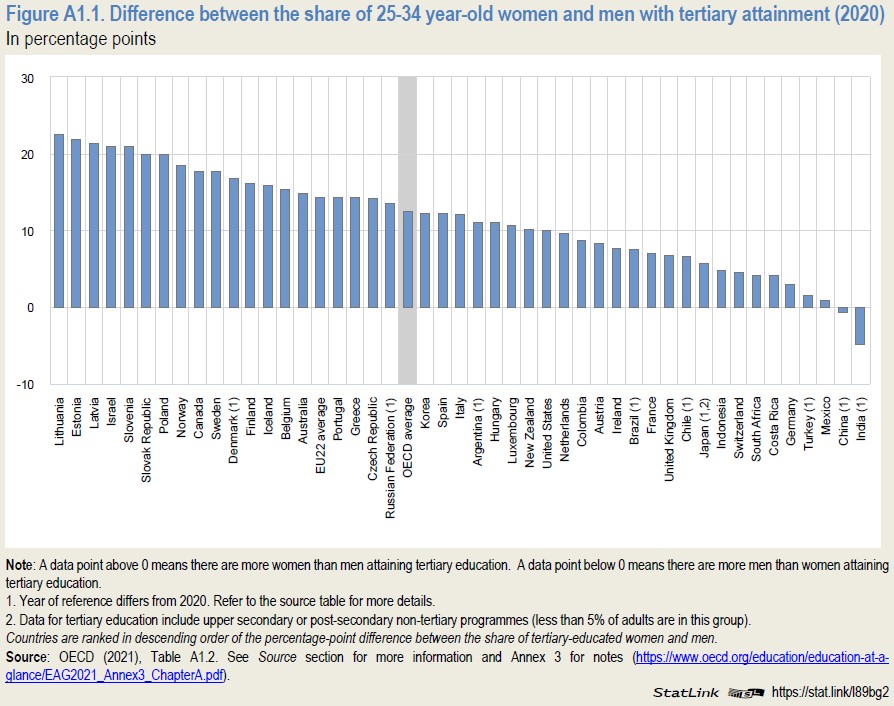
In terms of tertiary attainment, the results show that in all OECD countries, the expansion of tertiary education has been higher for women than for men. As shown in the graph below, the difference between the share of women and men aged 25-34 years with tertiary attainment in 2020 is positive for all countries except China and India (which are not OECD countries). The difference is the highest in the three Baltic countries, Lithuania, Estonia and Latvia with more 20 percentage points difference; and the lowest in Mexico, Turkey and Germany. In India and China, the difference is negative, i.e. the share of men aged 25-34 years with tertiary attainment is higher than that of women.
More information.
However, the share of women within the larger age group 25-64 tends to decrease with the level of tertiary education. On average, women account for 56% of adults with a bachelor’s or equivalent degree, 54% among adults with a master’s or equivalent degree, and 45% of those with a doctoral or equivalent degree.
