Joining forces against climate change

date: 19/04/2021
On 21 April, the Council and the European Parliament negotiators reached a provisional political agreement on the European Climate Law that enshrines the EU’s objective of becoming climate-neutral by 2050 into a legislation. It also sets the EU’s 2030 greenhouse gas emissions reduction goal at a net 55% cut (compared to 1990) up from the current 40% target. Once formally adopted, these goals will become legally binding for the EU.
The agreement came just before the Leaders’ Summit on Climate hosted by US President Joe Biden. At the summit, the President of the European Council, Charles Michel emphasised the EU’s leadership in fighting climate change. He also stressed the need for a global approach to carbon pricing, saying that ‘if we want to be at peace with nature, we need to chase carbon from our business model’. He also urged all developed countries to scale up their contributions to climate finance.
The EU was represented by European Council President Charles Michel and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen. The leaders of EU member states Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Poland and Spain also attended the event. EU leaders sought to persuade their international partners to commit to similarly ambitious targets.
The virtual summit, organised on 22 April - Earth Day - was intended to highlight the fact that stronger climate action is not only urgently needed for the planet but is also beneficial for economies. It was a milestone on the road to the UN climate change conference (COP26) this November in Glasgow, United Kingdom.
Why is fighting climate change a global issue?
Collective action and the commitment of other global players are indispensable for fighting climate change. Why? Have a look at some selected data.
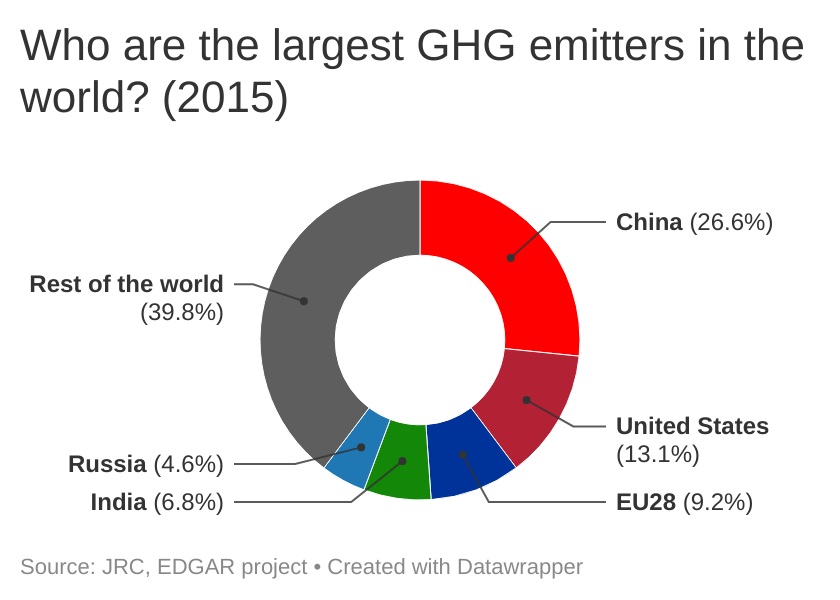
The EU is the third greenhouse gas (GHG) emitter in the world, after China and the US. The five largest emitters are responsible for over 60% of global emissions.
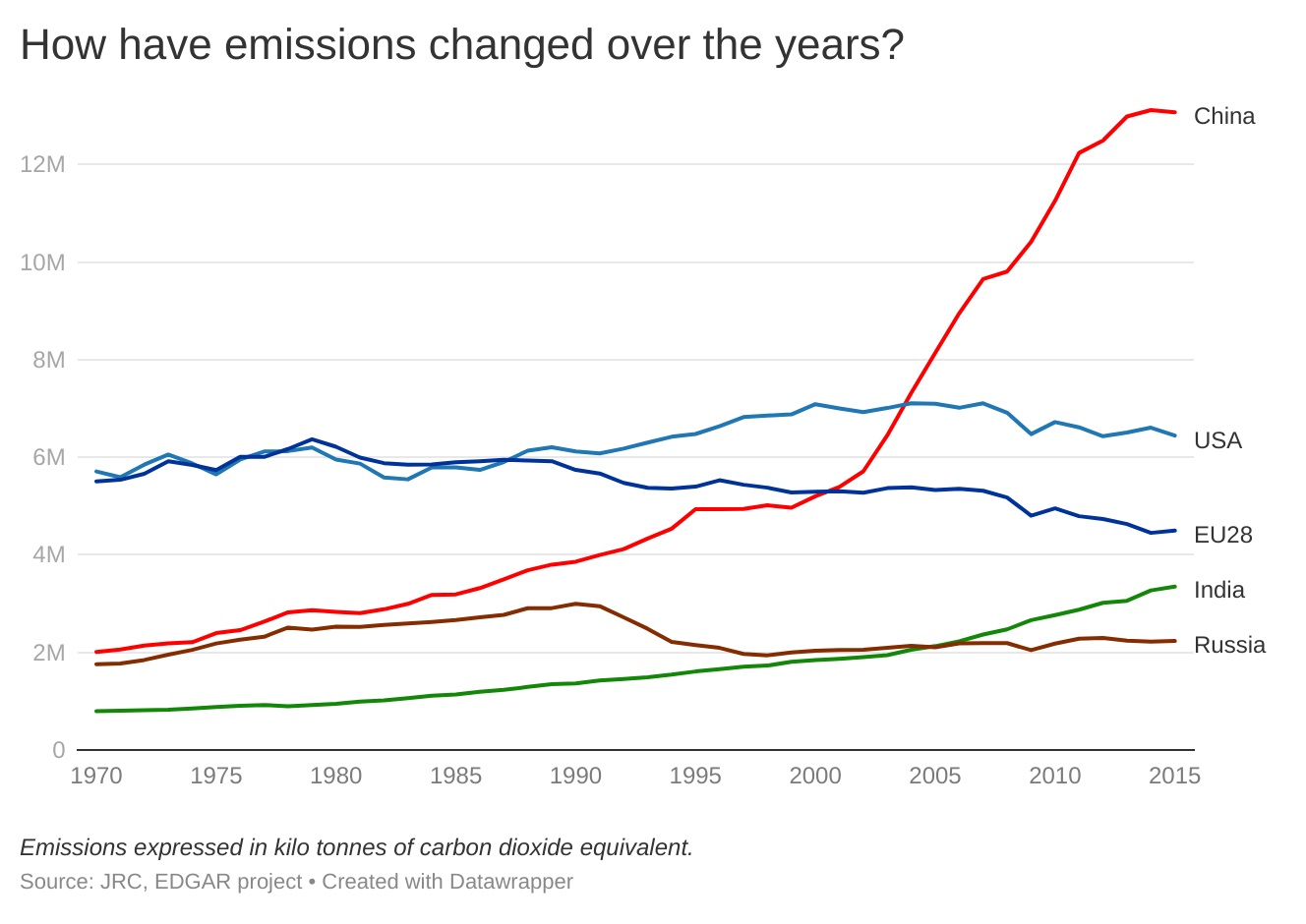
Between 1990 and 2015, global GHG emissions grew by 50%. At the same time, the EU reduced emissions by 22% while China more than tripled its emissions.
Since 2015, the EU reduced its emissions even further (by 27% between 1990 and 2019) but 2015 is the last year with comparable data for all key global players.
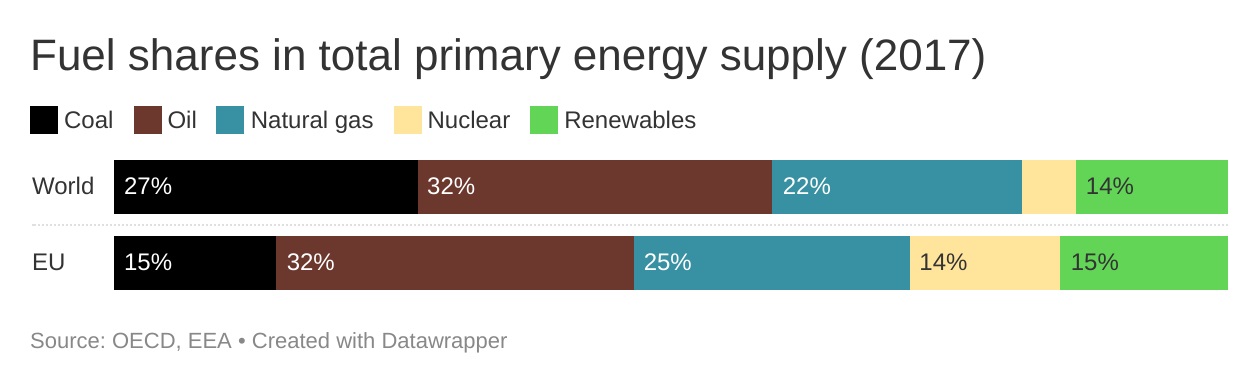
Globally, fossil fuels are still used to produce over 80% of energy. In the EU, the share of fossil fuels is 70% - mainly due to a slightly higher share of renewables in the EU and a significantly higher share of nuclear energy.
If you want to know more about the EU’s actions to involve others more in fighting climate change, visit our website.
