Archive:Pesticide sales statistics
This article has been archived. For more information about, see the online publication Agri-environmental indicators.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat online publication "Agriculture, forestry and fishery statistics". It focuses on data covering the sale of pesticides from national industries in EU Member States and aims to give an overview of the latest available information in the European Union (EU).
The use of pesticides in agriculture has helped to improve yields and to prevent crop losses. Pesticides include active ingredients that in spite of the beneficial actions on agricultural production could have other less positive impacts on the environment and habitats where they are used. Data on the sale of pesticides are used in the agri-environmental indicator on consumption of pesticides.
Regulation (EC) No 1185/2009 is the legal basis for the data on pesticide sales and it outlines the definitions and list of active substances. The data collected is the active substance contained in the pesticides and is categorised into six major groups according to the action of the pesticide.
(tonnes)
Source: Eurostat (aei_fm_salpest09)

(kilograms per hectare)
Source: Eurostat (aei_fm_salpest09); (apro_cpp_luse)
Main statistical findings
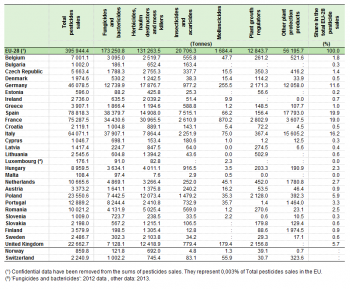
In 2014, the total quantity of pesticide sales in the EU-28 amounted to close to 400 000 tonnes. Spain (19.9 %), France (19.0 %), Italy (16.2 %), Germany (11.6 %) and Poland (5.9 %) were the Member States in which the highest quantities of pesticides were sold, and together they made up 72.7 % of the EU-28’s pesticide sales (see Table 1 and Figure 1).
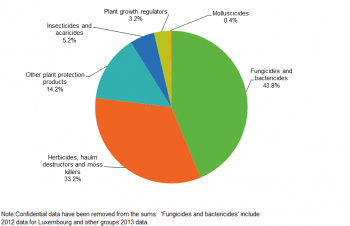
‘Fungicides and bactericides’ were the most sold group of pesticides with a 44 % share, followed by ‘herbicides, haulm destructors and moss killers’ with 33 % of the total. Together with the group ‘other plant protection products’ (14 %), the three groups added up to 91 % of the pesticides sold in the EU-28 in 2014. Of the other three groups of pesticides, ‘insecticides and acaricides’ had a 5 % share of the total, plant growth regulators 3 % and ‘molluscicides’ held the smallest share of pesticides sales with less than 1 % (see Figure 2).
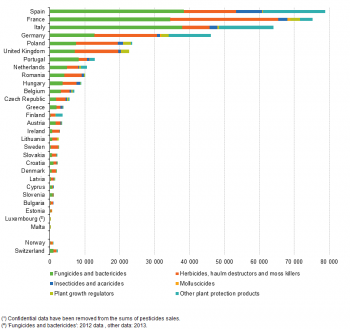
Looking at individual EU Member States, Spain, France, Italy and Germany are top ranked in the amount of sales of each group of pesticides, just like in the total amount of sold pesticides (see Figure 3).
The largest quantities of both ‘fungicides and bactericides’ (38.4 thousand tonnes) ‘insecticides and acaricides’ (7.5 thousand tonnes) and ‘other plant protection products’ (17.8 thousand tonnes) were placed on the market in Spain. France ranked top in ‘herbicides, haulm destructors and moss killers’ with 31.0 thousand tonnes and in ‘molluscicides’ with 0.9 thousand tonnes of sales. With 2.8 thousand tonnes in 2014, France also had the highest share of sold ‘plant growth regulators’.
There were exceptions to the pattern of the top four countries. In the United Kingdom for instance, 12.4 thousand tonnes of ‘herbicides, haulm destructors and moss killers’, 0.2 thousand tonnes of ‘molluscicides’ and 2.2 thousand tonnes of ‘plant growth regulators’ were sold. Poland also ranked in the top four for sales of ‘insecticides and acaricides’ (1.5 thousand tonnes) and ‘plant growth regulators’ (2.1 thousand tonnes).
The quantities of pesticides that are put on the market yearly can be associated with other statistics directly related to the use of the pesticides. In Figure 4, the quantities of sold pesticides are compared to each country's utilised agricultural area (UAA), and the Member States are ranked by the amount of pesticides (kilograms) per hectare (ha) of UAA. Bulgaria had the smallest proportion of pesticide sales per ha with 0.22 kg/ha. Ireland, Estonia, Finland , Denmark, Latvia, Romania, Greece, Sweden and Lithuania all had quantities of sold pesticides under 1 kilogram per ha of UAA.
None of the top four countries having the highest pesticides sales, ranked in the top four of pesticide sales per ha of UAA. With a value of 9.97 kg/ha, Malta recorded the highest quantity of pesticides per hectare. The most active substance sold and used in Malta is Sulphur, which covers around 65% of total sales and also around 90% of total active substances used. Cyprus had the second highest value of pesticide sales per ha of UAA, with 9.57 kg/ha.
The Netherlands, Belgium, Italy, Portugal, Spain, Germany, France and Slovenia all had amounts of pesticides sold per hectare above 2 kg/ha.
Data sources and availability
The data on sales of pesticides from national industries is available in two different series:
- Data series 1997-2008
This collection presents data on sales of plant protection products communicated by EU Member States and Norway on the basis of a ‘gentlemen’s agreement’.
- Data series from reference year 2011 onward
This collection is based on Regulation (EC) No 1185/2009 concerning statistics on pesticides which establishes a common framework for the systematic production of Community statistics on the placing on the market and use of those pesticides which are plant protection products. The current article focusses on this data series.
Context
As a result of their potential toxicity, often even at very low levels, the application of pesticides is strictly controlled by Community legislation since 1991 (by national legislation prior to 1991). Policy control measures in the EU are driven by the objectives of protecting human health and the environment (consumers, operator safety, protection of water quality and biodiversity).
The most important legislation with regard to pesticides are as follows:
- Directive 128/2009 establishing a framework for Community action to achieve the sustainable use of pesticides;
- Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market.
- Regulation (EC) No 83/1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption (Drinking Water Directive) which stipulates a maximum concentration of 0.1 μg/l (which in practice means the absence) for any single pesticide and its relevant metabolites (maximum of 0.5 μg/l for total pesticides) in potable water;
- Directive 60/2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy (Water Framework Directive) which identifies a large number of particularly toxic, persistent or bioaccumulative polluting substances in Annex VIII including organophosphate compounds.
Other relevant legislation include:
- Directive 105/2008 on environmental quality standards in the field of water policy,
- Directive 32/2002 on undesirable substances in animal feed,
- Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 on maximum residue levels of pesticides in or on food and feed of plant and animal origin.
In addition to controls on impacts such as the Drinking Water Directive, a number of EU Member States have introduced specific measures to restrict use involving the introduction of pesticide taxes (e.g. Denmark and Sweden), and/or government targets for reducing pesticide use (e.g. NL target of 50 % reduction by 2000 in terms of weight of active ingredients compared with the reference period 1984–88).
In 2002 the European Commission adopted a communication ‘Towards a thematic strategy on the sustainable use of pesticides’ (COM final 349/2002) following the mandate to develop a thematic strategy in the Sixth Environment Action Programme. The Commission Communication contained a description of the current situation regarding pesticides and related areas at EU and Member State level. A number of objectives are identified and analysed. The subsequent Thematic Strategy on the Sustainable Use of Pesticides (COM final 372/2006) was adopted in 2006.
See also
- Agri-environmental indicators (online publication)
- Agri-environmental indicator - consumption of pesticides] (Data series 1997-2008)
- Agri-environmental indicator – pesticide risk
- Agri-environmental indicator – pesticide pollution of water
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Agriculture, forestry and fishery statistics — 2016 edition
- Agriculture, forestry and fishery statistics — 2014 edition (Pocketbook)
- Environmental statistics and accounts in Europe — 2010 edition
- Figures for the future — 2010 edition
- Sustainable development in the European Union — 2011 monitoring report on the EU sustainable development strategy - Sustainable development in the European Union
Database
- Agri-environmental indicators (aei)
- Farm management (aei_fm)
- Pesticide sales (aei_fm_salpest09)
- Farm management (aei_fm)
- Agri-environmental indicators (aei)
Dedicated sections
Methodology / Metadata
- Pesticide sales (ESMS metadata file — aei_fm_salpest09)
Source data for tables and figures (MS Excel)
Other information
- Staff working document SEC (2006) 1136] - Development of agri-environmental indicators for monitoring the integration of environmental concerns into the common agricultural policy
External links