Archive:Europe 2020 indicators - country profiles
Data extracted in August 2019.
No planned update.
This Statistics Explained article is outdated and has been archived - for recent information on Europe 2020 strategy see here.
This article is part of a set of statistical articles on the Europe 2020 strategy. It introduces the country articles outlining the situation at national level in relation to the Europe 2020 headline indicators and specific national targets (see list).
Full article
Country profiles
Member States define their national targets in their National Reform Programmes (NRPs), taking into account their current situation. These programmes outline the actions and measures they plan to undertake to meet their national targets. The European Commission assesses each NRP and provides country-specific recommendations to support the programmes. The full NRPs and country-specific recommendations can be downloaded from the European Commission’s European Semester website.

Source: Eurostat (see dedicated web section: Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website
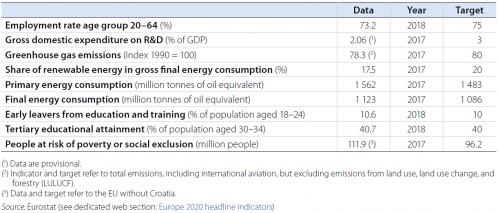
Source: Eurostat (see dedicated web section: Europe 2020 headline indicators)
This article illustrates the current situation of each Member State with the help of radar charts. The charts show how far a country is from its national targets as a percentage of the targets by comparing the national target (red line), the country’s situation in 2008 (green line) and the most recent situation (blue line). The distance between the blue line and the red line for a particular indicator shows how far a country currently is from its national target. Data points on or outside the red line mean the country has met or exceeded this target, while those inside show it still has some way to go. Comparing a country’s most recent performance with the green line reveals whether it has moved closer to or further away from its targets since 2008 [1].
National targets that are not harmonised with the overall EU targets are not presented in the diagram. For example, this is the case with the poverty and social exclusion targets adopted by some countries. Regarding the indicator on energy efficiency, Member States have set indicative national targets based on different indicators (primary or final energy consumption, primary or final energy savings, or energy intensity) in line with the Energy Efficiency Directive. These have been translated into absolute levels of primary energy consumption, expressed in million tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe).
Progress towards national greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions targets is analysed based on emissions in sectors not covered by the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) and in relation to the base year defined in the Effort Sharing Decision (ESD) [2]. For further details on the EU ETS and the ESD see the article on ‘Climate change and energy’.
The national targets (as defined in the NRPs) and the latest available national data for the headline indicators are presented in a separate table. Data on Europe 2020 headline indicators, targets and related issues are disseminated by Eurostat on a dedicated section of its website.
Articles by country
- (alphabetical order: 1st column down, then 2nd, etc. - click on country to access the article)
Direct access to
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council COM(2011) 211 final.
- Regulation (EC) No 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics
<notes>
Notes
- ↑ Please note that in a few cases, some countries have changed their national targets since 2008, therefore comparisons with earlier editions of this publication may be misleading.
- ↑ The Effort Sharing Decision (406/2009/EC) originally defined 2005 as the base year for Member States' GHG emissions reductions. However, due to recent recalculations with improved methodologies used at national level to measure the estimated emissions, 2005 values of countries are not necessarily equal to the value of the ESD base year.
