Archive:Energy, transport and environment - statistics on three closely related domains
- Data extracted in Month YYYY. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database. Planned article update: (dd) Month YYYY(, hh:00).
Energy supply and use is of fundamental importance to society. However, energy production and consumption in all sectors of the economy has environmental impacts with transport, being recognised as one of the major sectors affecting the environment. Transportation is accounting for a big share of the energy spent for carrying out and maintaining the range and scope of human activities. The use of the internal combustion engine has facilitated the efficient movement of freight and passengers and prompted the development of a world trade network. Nevertheless, there are environmental aspects linked to transportation and these include atmospheric and noise pollution, land take, resource use and the effects of waste disposal. The largest impacts come from fuel use by transport, but the effects from development and construction of infrastructure and vehicles, as well as the waste from their disposal, add to the environmental costs of transport.
This article provides one of many examples of how transport, energy and the environment are interlinked in everyday human activities. It discusses our societal needs for transport and how they relate to the economy; the demand in energy in order to cover these needs; some impacts of transport and energy demand on the environment; and the policies that the European Union has put in place in order to develop clean energy technologies and a resource-efficient transport system that will benefit the environment and our well-being.
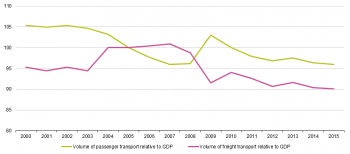
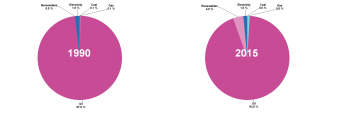
Source: Eurostat (trans_hv_pstra)
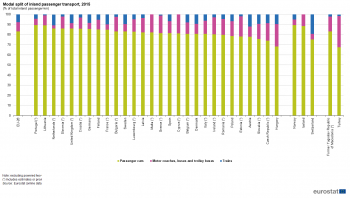
Source: Eurostat (trans_hv_psmod)
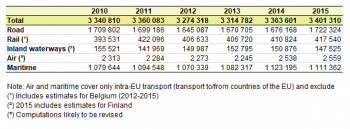
Source: Eurostat (rail_go_typeall) (rail), (iww_go_atygo) (inland waterways), (road_go_ta_tot) (national road transport) (road_go_ca_c) (road cabotage transport) and Eurostat computations (international road transport, air and maritime transport)
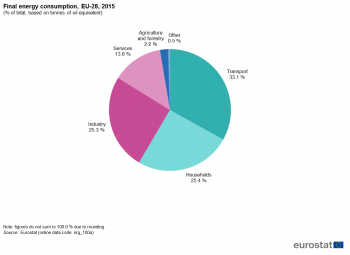
Source: Eurostat (nrg_100a)
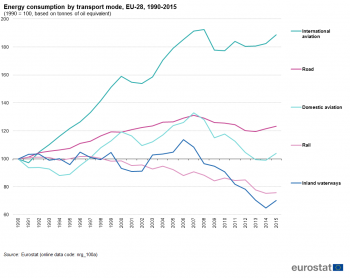
Source: Eurostat (nrg_100a)
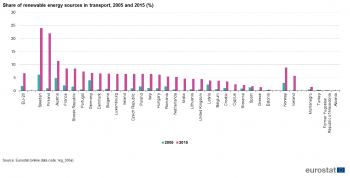
Source: Eurostat (nrg_ind_335a)
[[Image:Consumer prices of petroleum products, EU, 2005–15 (¹) (EUR per litre).png|thumb|right|350px|Figure 7: Consumer prices of petroleum products, EU, 2005–15 (¹) (EUR per litre)
Source: Oil bulletin, Directorate-General for Energy, European Commission]
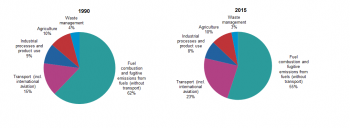
Source: Eurostat (env_air_gge), European Environment Agency
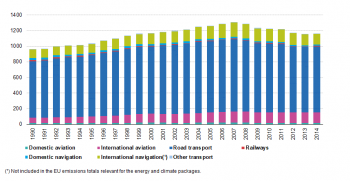
Source: EEA, republished by Eurostat (env_air_gge)
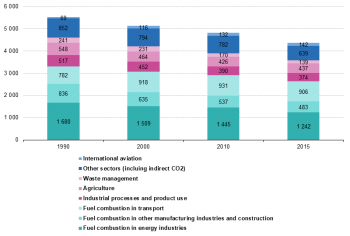
Source: European Environment Agency, Eurostat ({{{code}}})
Main statistical findings
<description and/or analysis of most important statistical data, illustrated by tables and/or figures and/or maps>
Text with Footnote [1]
Subtitle 1
Subtitle 2
Data sources and availability
<description of data sources, survey and data availability (completeness, recency) and limitations>
Context
<context of data collection and statistical results: policy background, uses of data, …>
See also
- Name of related Statistics Explained article
- Name of related online publication in Statistics Explained (online publication)
- Name of related Statistics in focus article in Statistics Explained
- Subtitle of Statistics in focus article=PDF main title - Statistics in focus x/YYYY
Further Eurostat information
Data visualisation
- Regional Statistics Illustrated - select statistical domain 'xxx' (= Agriculture, Economy, Education, Health, Information society, Labour market, Population, Science and technology, Tourism or Transport) (top right)
Publications
Publications in Statistics Explained (either online publications or Statistics in focus) should be in 'See also' above
Main tables
- Title(s) of second level folder (if any)
- Title(s) of third level folder (if any)
Database
- Title(s) of second level folder (if any)
- Title(s) of third level folder (if any)
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
<link to ESMS file, methodological publications, survey manuals, etc.>
- Crime and criminal justice (ESMS metadata file — crim_esms)
- Title of the publication
Source data for tables, figures and maps (MS Excel)
Other information
<Regulations and other legal texts, communications from the Commission, administrative notes, Policy documents, …>
- Regulation (EC) No 1737/2005 (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32005R1737:EN:NOT Regulation (EC) No 1737/2005]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
- Directive 2003/86/EC (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32003L0086:EN:NOT Directive 2003/86/EC]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
- Commission Decision 2003/86/EC (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32003D0086:EN:NOT Commission Decision 2003/86/EC]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
<For other documents such as Commission Proposals or Reports, see EUR-Lex search by natural number>
<For linking to database table, otherwise remove: {{{title}}} ({{{code}}})>
External links
Notes
- ↑ Text of the footnote.
[[Category:<Subtheme category name(s)>|Name of the statistical article]] [[Category:<Statistical article>|Name of the statistical article]]
Delete [[Category:Model|]] below (and this line as well) before saving!