Archive:Extra-EU trade in manufactured goods
- Data from February 2010, most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
This article focuses on the structure and evolution of the European Union (EU) external trade in manufactured goods: imports and exports at EU level. The EU is the world's biggest exporter of manufactured goods, and is a global market leader for high-quality products. Thanks to some of its key assets such as chemicals, pharmacy products, motor vehicles and non-electrical machinery, the European Union's trade balance for manufactured products is improving greatly, partially offsetting the rise in the energy deficit.
The Standard international trade classification (SITC) distinguishes four main categories (sections) of primary goods:
- Chemicals (SITC 5 );
- Manufactured goods classified chiefly by material (SITC 6);
- Machinery and vehicles (SITC 7);
- Miscellaneous manufactured articles (SITC 8);
Sections 6 and 8 are often grouped together as ' Other manufactured goods'.
Main statistical findings
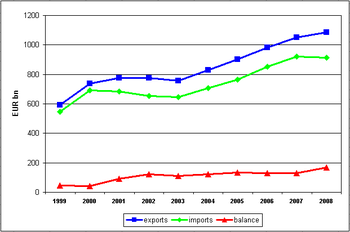
The EU exports mainly manufactured products: their share has annually been around 85 % of total EU exports. In 2008, machinery and vehicles made up almost half of total exports while other manufactured products accounted for 24 % and chemical products for 15 %. More than half of EU imports are manufactured goods, but their share is decreasing . The breakdown diverges from exports: machinery and vehicles and chemical products account for a smaller share while the share of other manufactured products is similar to that for exports. The surplus in trade of manufactured goods nearly quadrupled from 1999 to 2008.
Chemicals
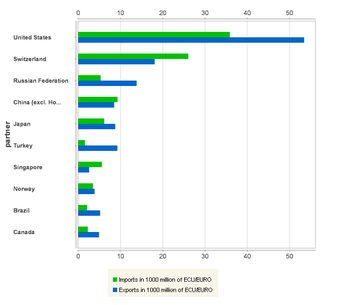
The chemicals sector (SITC Section 5) contains various chemical goods such as organic chemicals, inorganic chemicals, plastics and pharmaceutical products. Trade in chemicals has grown steadily every year since 2003 but its share of the total EU trade has remained quite stable: in 2008, chemicals accounted for 15 % of exports and 8 % of imports. Besides machinery and vehicles, the chemicals sector is the only product group where the EU posts a trade surplus. The surplus reached EUR 74.5 billion in 2008. The most important products within the group, both for exports and imports, are pharmaceutical products and organic chemicals. The majority of imports come from a small number of countries: in 2008, the eight biggest suppliers accounted for over three quarters of total EU imports. The USA was the main source, with a proportion of 29 %, followed by Switzerland with 21 %. The USA (27 % in 2007) and Switzerland (9 %) were also the main partner countries for exports.
Machinery and vehicles
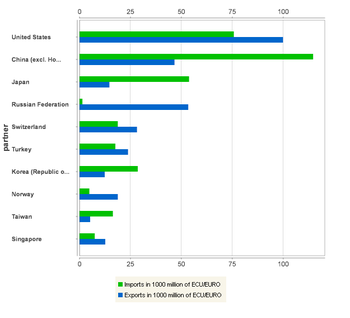
‘Machinery and vehicles’ (SITC Section 7) includes power generating and industrial machinery, computers, electric and electronic parts and equipment, road vehicles and parts, ships, airplanes and railway equipment. ‘Machinery and vehicles’ is the most important individual product group in the external trade of the EU, accounting for 44 % of total EU exports and 27 % of imports in 2008. The group records also the largest surplus in EU trade: EUR 154 billion in 2007. The main exported products within the group are road vehicles, industrial machinery and electrical machinery, while the imports are dominated by electrical machinery, IT products and telecommunications equipment. The USA is by far the biggest destination country of EU exports, although its proportion diminished from 30 % to 18 % between 1999 and 2008. Concerning the other main partner countries, exports to Russia and China increased strongly during the same period while the share of EU exports to Switzerland decreased. The USA and Japan are still two of the top three source countries in imports although their importance has decreased. In 1999, they covered 52 % of EU imports but only 31 % in 2007. During the same period China’s share increased from 6 % to 28 %.
Other manufactured goods
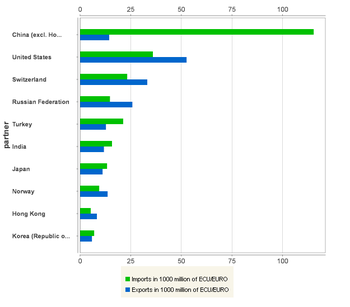
‘Other manufactured products’ (SITC Sections 6 and 8) is a heterogeneous group consisting of manufactured products which range from basic semi-manufactured products such as leather, rubber, wood, paper, textiles, metals, building fixtures and fittings to more labour-intensive products like clothes, shoes and accessories, scientific instruments, clocks, watches and cameras. The structure of exports and imports, in terms of products, differs to some extent. The EU exports more semi-manufactured products such as metals and metal products while, for imports, manufactured products are more relevant, in particular clothing. The share of both imports and exports is about one fourth of the total trade and is quite stable. The EU trade deficit has risen in the last few years, reaching the record of EUR 72 billion in 2007. After overtaking the USA in 2001, China has been the biggest supplier of the EU in this product group, reaching a share of 31 % in 2008. Other important suppliers include the USA, Switzerland and Turkey. The main destinations of exports are the USA, Switzerland and Russia.
Data sources and availability
EU data come from Eurostat’s COMEXT database. COMEXT is the Eurostat reference database for external trade. It provides access not only to both recent and historical data from the EU Member States but also to statistics of a significant number of third countries. External trade aggregated and detailed statistics disseminated from Eurostat website are compiled from COMEXT data according to a monthly process. Because COMEXT is updated on a daily basis, data published on the website may differ from data stored in COMEXT in case of recent revisions.
EU data are compiled according to community guidelines and may, therefore, differ from national data published by Member States. Statistics on extra-EU trade are calculated as the sum of trade of each of the 27 Member States with countries outside the EU (including the new Member States when they had not yet joined). In other words, the EU is considered as a single trading entity and trade flows are measured into and out of the area, but not within it.
Context
The EU is the world's biggest exporter of manufactured goods, and is a global market leader for high-quality products. Thanks to some of its key assets such as chemicals, pharmacy products, motor vehicles and non-electrical machinery, the European Union's trade balance for manufactured products is improving greatly, partially offsetting the rise in the energy deficit.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- Energy prices boosted the EU-27 trade deficit in 2008
- EU-27 imports of telecom products increased by 61% over 2000 – 2008
- EU-27 trade in chemical products in 2007
- EU-27 trade in motor cars in 2007
- Monthly bulletin on external and intra-European Union trade
Main tables
- External Trade, see:
- External trade aggregated data (t_ext)
Database
- External trade aggregated data (ext)
- External trade detailed data (detail)