- Data from July 2013. Most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables.
This article is part of a greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy set of statistical articles based on the Eurostat publication Smarter, greener, more inclusive? - Indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy. It provides recent statistics on the Europe 2020 strategy of the European Union (EU), focusing on the situation in Finland.
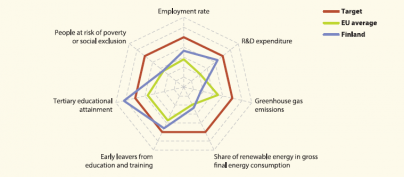
Main statistical findings
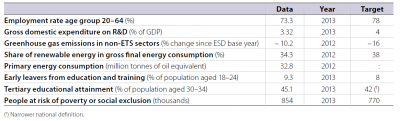
With a 45.8 % tertiary education attainment rate in 2012, Finland has already exceeded its national target of 42 %. The country was close to its targets on early school leaving and to a lesser extent social inclusion, with the deviations from the respective benchmarks being smaller than the EU average. Although the employment rate and R&D expenditure have experienced fluctuations in recent years, the two indicators were closer to their respective than the EU average in 2012 and 2011 respectively. Renewable energy sources have increased considerably in the past years; yet, in 2011, Finland remained at some distance from its target, even though it was slightly closer than the EU average. Reductions in GHG emissions larger than in most other countries are required to bring them in line with the national target of – 16 % compared with 2005 levels.
Data sources and availability
More information about the origin of the data and the calculation of indicators can be obtained via the Europe 2020 indicators dedicated website.
Under 'Tables', click on the icons next to the indicators:
- 'Explanatory texts (metadata)' for a detailed overview of the collection and compilation methods;
- 'Information on the leaf' for data availability per country.
A more general overview of quality procedures can be found in Implementation of standard reference metadata for indicators - the ESMS Indicator Profile (ESMS-IP) (PDF file).
Context
Measures implemented to meet the national targets
- Employment: Adoption of labour policy measures aimed at increasing labour force mobility, mainstreaming mobilisation of the whole labour force potential and supporting the business environment; introduction of flexible child home care allowance to facilitate the consolidation of work and family life.
- R&D expenditure: New tax incentives for promoting investment in R&D in the private sector; provision of annual funding for a new research and innovation policy action programme; revision of the current university funding model and shift towards more outcome oriented financial targeting; launch of a new research infrastructure policy.
- Climate and energy: Implementation of the National Energy and Climate Strategy including reducing the share of oil in overall energy consumption, adoption of clean energy, in particular in housing and transport sectors; preparation of a national climate act; adoption of measures for increasing energy efficiency.
- Tertiary education: Setting up the ambitious goal of becoming the most competent nation in Europe by 2020; shortening study time and lowering the graduation age; reforming the student financial aid system; implementing a student selection reform with the aim of enhancing the ability of higher education institutions to respond more flexibly to changes in working life and society.
- Early school leavers: Adoption of educational guarantee and skill programme for young adults ensuring increase in places for vocational upper secondary education and training; measures for improving the welfare of students in primary and secondary education.
- Poverty: Launch of the National Development Programme for Social Welfare and Health Care; reforms for promoting employment, improving unemployment security; initiatives aimed at improving social services for older people and people from immigrant backgrounds.
The European Commission's 2013 country-specific recommendations
- Employment: Address adverse demographic developments and ensure sustainability of the pension system by extending working lives; effective implementation of the proposed measures for tackling youth and long-term unemployment; implement measures for ensuring balance between wage growth and productivity
- Innovation: Enhancing the innovation capacity of the business sector; ensure the investment in R&D is effectively translated into new innovative products and services
- Energy: Step up diversification towards less energy intensive sectors
- Other recommendations: Ensure public finances are in line with the expected increase in health and long-term care due to population ageing; reform the municipal structure to ensure higher productivity and cost savings in the public sector; further strengthen competition in the product and service markets.
See also
Further Eurostat information
Publications
- [Smarter, greener, more inclusive - indicators to support the Europe 2020 strategy] (online publication, also downloadable as PDF file)
Main tables
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
- Towards robust quality management for European Statistics - Communication from the Commission COM(2011) 211 final
Other information
- Regulation 223/2009 of 11 March 2009 on European statistics
