Archive:Biodiversity statistics
- Data from September 2011, most recent data: Further Eurostat information, Main tables and Database.
This draft article has been updated for the 2012 edition of the ESTAT yearbook and is ready for review – please see the talk/discussion page for more detailed information.
Biodiversity – a contraction of biological diversity – encompasses the number, variety and variability of living organisms, including mankind. Preventing a loss of biodiversity is important for mankind, given that humans depend on the natural richness of the planet for the food, energy, raw materials, clean air and clean water that make life possible and drive economies and societies. As such, a reduction or loss of biodiversity may not only undermine the natural environment but also economic and social goals. The challenges associated with preserving biodiversity have made this topic an international issue. This article presents some main indicators for biodiversity, such as the number of protected areas and bird populations, and examines the development of these indicators in the European Union (EU).
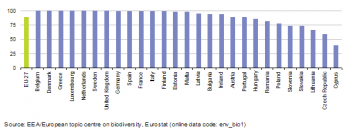
(%) - Source: Eurostat (env_bio1)
Main statistical findings
Habitats
Areas protected for the preservation of biodiversity are proposed by the Member States under the EU's Habitats Directive; they are indicated as a percentage of the total area of each country. About 14 % of the EU-27’s territory was proposed for protection under the Habitats Directive as of 2010. Additional areas were proposed for protection under the Birds Directive. Since there is some overlap between the two types of protected areas, the joint area for both Directives was estimated to amount to approximately 18 % of the EU-27's terrestrial area in 2010. Figures for the Member States show that areas protected under the Habitats Directive range between 31 % of the total area of Slovenia and 30 % of that in Bulgaria to less than 10 % of the total area of France, the Netherlands, Denmark or the United Kingdom. In general, these protected areas adequately cover the biogeographical regions present in the Member States, with an EU-27 average of 89 % of sufficiently covered species and habitats in 2010; using this measure, only Cyprus reported less than 50 % sufficiency (see Figure 1).
Birds
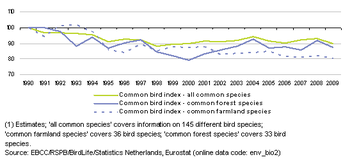
(aggregated index of population estimates of selected groups of breeding bird species, 1990=100) - Source: Eurostat (env_bio2)
Since 1990 there has been a general downward trend in the abundance of both common farmland and forest species of birds, as measured by common bird indices (see Figure 2). Part of the relatively steep decline (-20 % between 1990 and 2009) in numbers of common farmland birds may be attributed to changes in land use and agricultural practices. There was a more rapid reduction in numbers of common forest birds between 1990 and 2000 across the EU (-21 % between 1990 and 2000). However, recent years have seen a recovery in forest bird numbers, with the index rising from a relative low of 79 to reach 87 by 2009. The index of all common bird species has been relatively stable since 1995, some 10 % below its 1990 level, and stood at 90 in 2009.
Data sources and availability
Habitats
Annual data are available on areas protected under the Habitats Directive. The data are presented as the percentage of compliance with the obligation to protect habitats and species that are typical for the wider biogeographical regions of the EU. The indicator is based on the extent of the area proposed by countries for the protection of natural and semi-natural habitats, wild fauna and flora according to annexes I and II of the Habitats Directive. The index of sufficiency measures the extent to which sites of Community importance proposed by the Member States adequately cover the species and habitats listed in those annexes, in proportion to the share of the biogeographical region that falls within the territory of the country.
Birds
Birds are considered good proxies for measuring the diversity and integrity of ecosystems as they tend to be near the top of the food chain, have large ranges and the ability to move elsewhere when their environment becomes unsuitable; they are therefore responsive to changes in their habitats and ecosystems. The bird indicators presented in this article measure trends of bird populations.
The indicators are designed to capture the overall, average changes in population levels of common birds to reflect the health and functioning of the ecosystems they inhabit. The population index of common birds is an aggregated index (with base year 1990 or the first year the Member State entered the scheme) of population trend estimates for a selected group of common bird species. Indices are calculated for each species independently and are then combined to create a multi-species EU indicator by averaging the indices with an equal weight using a geometric average. Indices rather than bird abundance are averaged in order to give each species an equal weight in the resulting indicator. The EU index is based on trend data from 20 Member States (Greece, Cyprus, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Romania and Slovenia, not available), derived from annually operated national breeding bird surveys collated by the Pan-European Common Bird Monitoring Scheme (PECBMS); these data are considered as a good proxy for the whole of the EU-27.
Three different indices are presented:
- common farmland birds (36 species);
- common forest birds (33 species);
- all common birds (145 species).
For the first two categories, the bird species have a high dependence on agricultural or on forest habitats in the nesting season and for feeding. Both groups comprise both year-round residents and migratory species. The aggregated index comprises farmland and forest species together with other common species that are generalists, meaning that they occur in many different habitats or are particularly adapted to life in cities.
Context
People depend on natural resources and the variety of species found on the planet for tangible goods that make life possible and drive economic development, such as food, energy, wood, raw materials, clean air and water. Many aspects of the natural environment are public goods, in other words they have no market value or price. As such, the loss of biodiversity can often go undetected by economic systems. However, the natural environment also provides a range of intangibles, such as the aesthetic pleasure derived from viewing landscapes and wildlife, or recreational opportunities. In order to protect this legacy for future generations, the EU seeks to promote policies in a range of areas to ensure that biodiversity is protected through the sustainable development of, among others, agriculture, rural and urban landscapes, energy provision and transport.
Biodiversity strategy is based on the implementation of two landmark Directives, the Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC) of 21 May 1992 and the Birds Directive (79/409/EEC) of 2 April 1979. Implementation of these Directives has involved the establishment of a coherent European ecological network of sites under the title Natura 2000. The EU wants to expand Natura 2000, which currently counts around 26 000 sites and a land area of more than 750 000 km² (and an area of almost 930 000 km² including marine sites) where plant and animal species and their habitats are protected. Establishing the Natura 2000 network may be seen as the first pillar of action relating to the conservation of natural habitats. However, EU legislation also foresees measures to establish a second pillar through strict protection regimes for certain animal species (for example, the Arctic fox and the Iberian lynx, both of which are under serious threat of extinction).
In 1998, the EU adopted a biodiversity strategy. Four action plans covering the conservation of natural resources, agriculture, fisheries, and economic and development cooperation were subsequently agreed as part of this strategy in 2001. The European Commission released a Communication ((2006) 216) on ‘halting the loss of biodiversity by 2010 – and beyond’; this underlined the importance of biodiversity protection as a pre-requisite for sustainable development and set out an action plan which addressed the challenge of integrating biodiversity concerns into other policy areas.
In May 2011 the European Commission adopted the Communication ‘Our life insurance, our natural capital: an EU biodiversity strategy to 2020’ (COM(2011) 244); this aims to halt the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services in the EU by 2020. There are six main targets and 20 actions to help reach this goal. Biodiversity loss is seen as an enormous challenge in the EU, with around one in four species currently threatened with extinction and 88 % of fish stocks over-exploited or significantly depleted. The six targets cover:
- full implementation of EU nature legislation to protect biodiversity;
- better protection for ecosystems and more use of green infrastructure;
- more sustainable agriculture and forestry;
- better management of fish stocks;
- tighter controls on invasive alien species;
- a bigger EU contribution to averting global biodiversity loss.
The strategy is in line with two commitments made in March 2010:
- the 2020 headline target – halting the loss of biodiversity and the degradation of ecosystem services in the EU by 2020, and restoring them insofar as feasible, while stepping up the EU contribution to averting global biodiversity loss;
- the 2050 vision – which foresees that by 2050, the EU’s biodiversity and the ecosystem services it provides – its natural capital – are protected, valued and appropriately restored for biodiversity's intrinsic value, and for their essential contribution to human well-being and economic prosperity, and so that catastrophic changes caused by the loss of biodiversity are avoided.
The strategy is also in line with global commitments made in Nagoya in October 2010, in the context of the Convention on Biological Diversity, where world leaders adopted a package of measures to address global biodiversity loss over the coming decade.
Further Eurostat information
Publications
Main tables
- Environment (t_env), see:
- Biodiversity (t_env_biodiv)
Database
- Environment (env), see:
- Biodiversity (env_biodiv)
- Protected Areas for biodiversity: Habitats Directive (env_bio1)
- Protection of natural resources - Common bird index (env_bio2)
- Fish catches from stocks outside of 'safe biological limits' (env_biofish1)
Other information
- Communication 'Our life insurance, our natural capital: an EU biodiversity strategy to 2020' (COM(2011) 244)
- Communication 'Halting the loss of biodiversity by 2010 - and beyond - Sustaining ecosystem services for human well-being' COM(2006) 216 final
- Directive 79/409/EEC ('Birds Directive') of 2 April 1979 on the conservation of wild birds
- Directive 92/43/EEC ('Habitats Directive') on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora
Source data for tables and figures (MS Excel)
External links
- EBCC - European Bird Census Council
- European Commission - Environment - Biodiversity & Nature
- Convention on Biological Diversity (UNEP - United Nations Environment Programme)