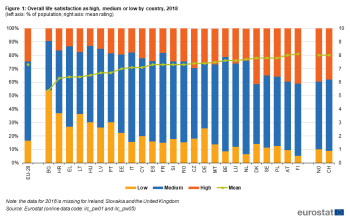
Archive:Income inequality statistics, data 2012
Income Inequality- Nearly 40 per cent of national income was earned by the fifth quintile
Statistics in focus XX/2014; Author: Emanuela DI FALCO
ISSN:2314-9647 Catalogue number:KS-SF-14-XXX-EN-N
Income inequality is a complex phenomenon, the result of interaction between several factors. It can be related to employment patterns, income sources, individual characteristics (education level, age, gender, etc.) or household features (number of earners in the household, family size, etc.). Inequality is a broader concept than poverty; while poverty mainly relates to the lowest part of the income distribution, inequality takes into account the living conditions of all people in a society.
The analysis showed that Norway and Slovenia had the lowest level of inequality (as measured by the Gini coefficient ) in Europe in 2012, and that Spain and Latvia had the highest level. Overall, ten countries had a level of inequality higher than the EU-28 average in 2012. In Europe, nearly 40% of total national equivalised income goes on average to people belonging to the highest (fifth) income quintile, and less than 10% to people in the first quintile. This distribution of income explains the income discrepancies among people. It should be noted that inequality decreased in 12 EU countries in 2008-12, mainly due to the income losses seen in the upper part of the income distribution during the financial and economic crisis.
Main statistical findings
The Gini coefficient across the EU in 2012
The Gini coefficient reveals differences of approximately 10 points across the EU in 2012.
Income inequality measured by the Gini coefficient varied by approximately 10 points across Europe in 2012, with the lowest levels of inequality seen in Norway and Slovenia and the highest in Spain and Latvia. Only four countries (France, Croatia, Poland and Cyprus) had an income inequality level around the EU-28 average (30.6). In ten countries, income discrepancies were above the EU-28 average, ranging from 32 in Italy and Lithuania to 35 or more in Spain and Latvia.
In the remaining countries, the income disparities were below the EU-28 average , ranging from 28.3 in Germany to less than 24 in Slovenia and Norway. To summarise, the analysis showed high levels of inequality across southern Europe, as seen in Figure 1, but there no dominant pattern in central- and northern-European countries.
Social benefits and pensions played an important role in reducing inequality in 2012
Figure 2 shows the Gini coefficients based on total equivalised disposable household income . These were calculated without including social benefits and pensions among the income sources, to measure the impact of social transfers in reducing inequality. As expected, income inequality would have been greater in all countries if social benefits and pensions were not included, with the highest values seen in the United Kingdom and Greece and the lowest in Malta, Iceland, Norway and Slovakia. Social transfers and pensions played a crucial role in Sweden, where excluding them reduced inequality (measured by a Gini coefficient calculated without social benefits) by around 53%, and in another nine countries where excluding them reduced inequality by 40%. Excluding social benefits and pensions did not significantly affect inequality in Bulgaria and Cyprus.
Income disparities increased in Denmark and decreased in Iceland and Norway in 2008-12
Although inequality in the EU-28 remained almost at the same level in 2008-12, a different pattern is seen for individual countries. Income discrepancies decreased in 12 EU Member States and the three EFTA countries included in the analysis, and increased in the remaining countries. Despite their high levels of inequality in 2012, Romania, Bulgaria and Lithuania managed to reduce inequality by about 5 % or more over the period analysed. In contrast, despite low inequality levels in 2012, all countries included in the red circle in Figure 3 saw an increase in inequality since 2008, up to 5 % and more in Austria, Slovakia, Hungary and Denmark. Denmark and Iceland saw the biggest changes in 2008-12: a 12% increase in inequality in Denmark and a 12 % decrease in Iceland.
Data sources and availability
<description of data sources, survey and data availability (completeness, recency) and limitations>
Context
<context of data collection and statistical results: policy background, uses of data, …>
See also
- Name of related Statistics Explained article
- Name of related online publication in Statistics Explained (online publication)
- Name of related Statistics in focus article in Statistics Explained
- Subtitle of Statistics in focus article=PDF main title - Statistics in focus x/YYYY
Further Eurostat information
Data visualisation
- Regional Statistics Illustrated - select statistical domain 'xxx' (= Agriculture, Economy, Education, Health, Information society, Labour market, Population, Science and technology, Tourism or Transport) (top right)
Publications
Publications in Statistics Explained (either online publications or Statistics in focus) should be in 'See also' above
Main tables
- Title(s) of second level folder (if any)
- Title(s) of third level folder (if any)
Database
- Title(s) of second level folder (if any)
- Title(s) of third level folder (if any)
Dedicated section
Methodology / Metadata
<link to ESMS file, methodological publications, survey manuals, etc.>
- Name of the destination ESMS metadata file (ESMS metadata file - ESMS code, e.g. bop_fats_esms)
- Title of the publication
Source data for tables, figures and maps (MS Excel)
Other information
<Regulations and other legal texts, communications from the Commission, administrative notes, Policy documents, …>
- Regulation 1737/2005 (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32005R1737:EN:NOT Regulation 1737/2005]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
- Directive 2003/86/EC (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32003L0086:EN:NOT Directive 2003/86/EC]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
- Commission Decision 2003/86/EC (generating url [http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32003D0086:EN:NOT Commission Decision 2003/86/EC]) of DD Month YYYY on ...
<For other documents such as Commission Proposals or Reports, see EUR-Lex search by natural number>
<For linking to database table, otherwise remove: {{{title}}} ({{{code}}})>
External links
Notes
[[Category:<Under construction>|Name of the statistical article]]
[[Category:<Household_income,_expenditure_and_debt>|Income inequality statistics]] [[Category:<Living_conditions>|Income inequality statistics]] [[Category:<Statistical article>|Income inequality statistics]] [[Category:<Statistics in focus>|Income inequality statistics]]